Summary
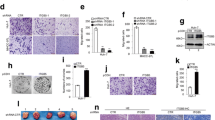
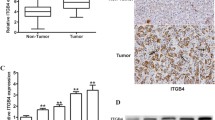
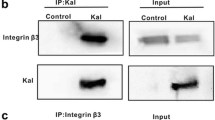
The epigenetic modulation by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors including trichostatin A (TSA) has been known to block cell proliferation, induce apoptosis and inhibit cell migration in human cancer cells that represents the potential therapeutic agents for cancers and fibrosis. However, more than 55% of Hep3B cells remained alive after our initial study of 100 nM TSA treatment. To further study the epigenetic modulation and the biological function of newly activated genes by HDAC inhibitor involved in HCC progression and metastasis, we profiled 23 integrin genes including 15α and 8β in TSA-treated Hep3B cells. Six integrins including three down-regulated α6, α10, β8 and three significant up-regulated α4, β2, β6 integrins were revealed after semi-quantitative RT-PCR. To confirm the epigenetic modulation and explore their biological functions, we selected the three significantly up-regulated integrins for confirmation of protein up-regulation, hyperacetylated-histones by ChIP assays, and functional inhibition by specific neutralizing antibodies of integrins. Our results indicated that epigenetic modulation in TSA-treated Hep3B cells up-regulated new integrins including α4, β2 and β6 and reduced migration activities by specific neutralizing antibodies to 61.3%, 42.4% and 34.5%, respectively. Our novel findings provided a better understanding of the epigenetic modulation of integrins and suggested that targeting the epigenetic up-regulated integrins to abrogate the migration activity might be a promising strategy to prevent HCC progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsuuchi Y., Testa J.R. 2002. Cytogenetics and molecular genetics of lung cancer. Am J Med Genet 115:183–188
Feinberg A.P. (2004). The epigenetics of cancer etiology. Semin Cancer Biol 14:427–432
Momparler R.L. (2003). Cancer epigenetics. Oncogene 22:6479–6483
Berger S.L. (2002). Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:142–148
Luo R.X., Dean D.C. (1999). Chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1288–1294
Toh Y., Yamamoto M., Endo K., Ikeda Y., Baba H., Kohnoe S., Yonemasu H., Hachitanda Y., Okamura T., Sugimachi K. (2003). Histone H4 acetylation and histone deacetylase 1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 10:333–338
Yasui W., Oue N., Ono S., Mitani Y., Ito R., Nakayama H. (2003). Histone acetylation and gastrointestinal carcinogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 983:220–231
Marks P.A., Richon V.M., Rifkind R.A. (2000). Histone deacetylase inhibitors: inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1210–1216
Johnstone R.W. (2002). Histone-deacetylase inhibitors: novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:287–299
Hood J.D., Cheresh D.A. (2002). Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2:91–100
Jin H., Varner J. (2004). Integrins: roles in cancer development and as treatment targets. Br J Cancer 90:561–565
Pupa S.M., Menard S., Forti S., Tagliabue E. (2002). New insights into the role of extracellular matrix during tumor onset and progression. J Cell Physiol 192:259–267
Jaskiewicz K., Chasen M.R. (1995). Differential expression of transforming growth factor alpha, adhesions molecules and integrins in primary, metastatic liver tumors and in liver cirrhosis. Anticancer Res 15:559–562
Torimura T., Ueno T., Kin M., Inuzuka S., Sugawara H., Tamaki S., Tsuji R., Sujaku K., Sata M., Tanikawa K. (1997). Coordinated expression of integrin alpha6beta1 and laminin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol 28:1131–1138
Giannelli G., Bergamini C., Fransvea E., Marinosci F., Quaranta V., Antonaci S. (2001). Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells require both alpha3beta1 integrin and matrix metalloproteinases activity for migration and invasion. Lab Invest 81:613–627
Nejjari M., Hafdi Z., Dumortier J., Bringuier A.F., Feldmann G., Scoazec J.Y. (1999). alpha6beta1 integrin expression in hepatocarcinoma cells: regulation and role in cell adhesion and migration. Int J Cancer 83:518–525
Yang C., Zeisberg M., Lively J.C., Nyberg P., Afdhal N., Kalluri R. (2003). Integrin alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 are the key regulators of hepatocarcinoma cell invasion across the fibrotic matrix microenvironment. Cancer Res 63:8312–8317
Nejjari M., Hafdi Z., Gouysse G., Fiorentino M., Beatrix O., Dumortier J., Pourreyron C., Barozzi C., D’errico A., Grigioni W.F., Scoazec J.Y. (2002). Expression, regulation, and function of alpha V integrins in hepatocellular carcinoma: an in vivo and in vitro study. Hepatology 36:418–426
Strait K.A., Dabbas B., Hammond E.H., Warnick C.T., Iistrup S.J., Ford C.D. (2002). Cell cycle blockade and differentiation of ovarian cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A are associated with changes in p21, Rb, and Id proteins. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1181–1190
Donadelli M., Costanzo C., Faggioli L., Scupoli M.T., Moore P.S., Bassi C., Scarpa A., Palmieri M. (2003). Trichostatin A, an inhibitor of histone deacetylases, strongly suppresses growth of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog 38:59–69
Suzuki T., Yokozaki H., Kuniyasu H., Hayashi K., Naka K., Ono S., Ishikawa T., Tahara E., Yasui W. (2000). Effect of trichostatin A on cell growth and expression of cell cycle- and apoptosis-related molecules in human gastric and oral carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 88:992–997
Yamashita Y., Shimada M., Harimoto N., Rikimaru T., Shirabe K., Tanaka S., Sugimachi K. (2003). Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A induces cell-cycle arrest/apoptosis and hepatocyte differentiation in human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer 103:572–576
Liu L.T., Chang H.C., Chiang L.C., Hung W.C. (2003). Histone deacetylase inhibitor up-regulates RECK to inhibit MMP-2 activation and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 63:3069–3072
Rombouts K., Niki T., Wielant A., Hellemans K., Geerts A. (2001). Trichostatin A, lead compound for development of antifibrogenic drugs. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 64:239–246
Choi, H. S., Lee, J. H., Park, J. G., and Lee, Y. I. 2002. Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, activates the IGFBP-3 promoter by upregulating Sp1 activity in hepatoma cells: alteration of the Sp1/Sp3/HDAC1 multiprotein complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:1005–1012
Gray S.G., Kytola S., Lui W.O., Larsson C., Ekstrom T.J. (2000). Modulating IGFBP-3 expression by trichostatin A: potential therapeutic role in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med 5:33–41
Kitazono M., Goldsmith M.E., Aikou T., Bates S., Fojo T. (2001). Enhanced adenovirus transgene expression in malignant cells treated with the histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228. Cancer Res 61:6328–6330
Kitazono M., Rao V.K., Robey R., Aikou T., Bates S., Fojo T., Goldsmith M.E. (2002). Histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228 enhances adenovirus infection of hematopoietic cells. Blood 99:2248–2251
Goldsmith M.E., Kitazono M., Fok P., Aikou T., Bates S., Fojo T. (2003). The histone deacetylase inhibitor FK228 preferentially enhances adenovirus transgene expression in malignant cells. Clin Cancer Res 9:5394–5401
Hong J., Ishihara K., Yamaki K., Hiraizumi K., Ohno T., Ahn J.W., Zee O., Ohuchi K. (2003). Apicidin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces differentiation of HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett 189:197–206
Ishihara K., Hong J., Zee O., Ohuchi K. (2004). Possible mechanism of action of the histone deacetylase inhibitors for the induction of differentiation of HL-60 clone 15 cells into eosinophils. Br J Pharmacol 142:1020–1030
Kumar C.C. (1998). Signaling by integrin receptors. Oncogene 17:1365–1373
Ghosh S. (2003). Alpha 4 integrin blockade in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann Rheum Dis 62 Suppl 2:ii70–72
Tidswell M., Pachynski R., Wu S.W., Qiu S.Q., Dunham E., Cochran N., Briskin M.J., Kilshaw P.J., Lazarovits A.I., Andrew D.P., Butcher E.C., Yednock T.A., Erle D.J. (1997). Structure-function analysis of the integrin beta 7 subunit: identification of domains involved in adhesion to MAdCAM-1. J Immunol 159:1497–1505
Torimura T., Ueno T., Kin M., Harada R., Nakamura T., Kawaguchi T., Harada M., Kumashiro R., Watanabe H., Avraham R., Sata M. (2001). Autocrine motility factor enhances hepatoma cell invasion across the basement membrane through activation of beta1 integrins. Hepatology 34:62–71
Dib K. (2000). BETA 2 integrin signaling in leukocytes. Front Biosci 5:D438–451
Sun J.J., Zhou X.D., Liu Y.K., Tang Z.Y., Sun R.X., Zhao Y., Uemura T. (2000). Inhibitory effects of synthetic beta peptide on invasion and metastasis of liver cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:595–600
Xue H., Atakilit A., Zhu W., Li X., Ramos D.M., Pytela R. (2001). Role of the alpha(v)beta6 integrin in human oral squamous cell carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 288:610–618
Morgan M.R., Thomas G.J., Russell A., Hart I.R., Marshall J.F. (2004). The integrin cytoplasmic-tail motif EKQKVDLSTDC is sufficient to promote tumor cell invasion mediated by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 or MMP-9. J Biol Chem 279:26533–26539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, KT., Yeh, SH., Chen, DS. et al. Epigenetic activation of α4, β2 and β6 integrins involved in cell migration in trichostatin A-treated Hep3B cells. J Biomed Sci 12, 803–813 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-005-9005-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-005-9005-2