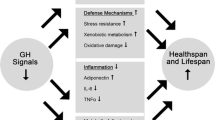
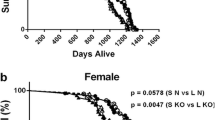
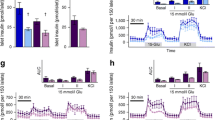
Abstract
Poor blood glucose homeostatic regulation is common, consequential, and costly for older and elderly populations, resulting in pleiotrophically adverse clinical outcomes. Somatotrophic signaling deficiency and dietary restriction have each been shown to delay the rate of senescence, resulting in salubrious phenotypes such as increased survivorship. Using two growth hormone (GH) signaling-related, slow-aging mouse mutants we tested, via longitudinal analyses, whether genetic perturbations that increase survivorship also improve blood glucose homeostatic regulation in senescing mammals. Furthermore, we institute a dietary restriction paradigm that also decelerates aging, an intermittent fasting (IF) feeding schedule, as either a short-term or a sustained intervention beginning at either middle or old age, and assess its effects on blood glucose control. We find that either of the two genetic alterations in GH signaling ameliorates fasting hyperglycemia; additionally, both longevity-inducing somatotrophic mutations improve insulin sensitivity into old age. Strikingly, we observe major and broad improvements in blood glucose homeostatic control by IF: IF improves ad libitum-fed hyperglycemia, glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity, and reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis, in aging mutant and normal mice. These results on correction of aging-resultant blood glucose dysregulation have potentially important clinical and public health implications for our ever-graying global population, and are consistent with the Longevity Dividend concept.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba M, Salvatori R (2004) A mouse with targeted ablation of the growth hormone-releasing hormone gene: a new model of isolated growth hormone deficiency. Endocrinology 145(9):4134–4143
Alengrin F, Grossi G, Canivet B, Dolais-Kitabgi J (1987) Inhibitory effects of metformin on insulin and glucagon action in rat hepatocytes involve post-receptor alterations. Diabete Metab 13(6):591–597
Anson RM, Guo Z, de Cabo R, Iyun T, Rios M, Hagepanos A, Ingram DK, Lane MA, Mattson MP (2003) Intermittent fasting dissociates beneficial effects of dietary restriction on glucose metabolism and neuronal resistance to injury from calorie intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(10):6216–6220
Anson RM, Jones B, de Cabo R (2005) The diet restriction paradigm: a brief review of the effects of every-other-day feeding. Age 27:7–25
Arum O, Bonkowski MS, Rocha JS, Bartke A (2009) The growth hormone receptor gene-disrupted mouse fails to respond to an intermittent fasting diet. Aging Cell 8(6):756–760
Arum O, Rasche ZA, Rickman DJ, Bartke A. (2013) Prevention of neuromusculoskeletal frailty in slow-aging ames dwarf mice: longitudinal investigation of interaction of longevity genes and caloric restriction. PLoS One 8(10):e72255. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072255
Arum O, Rickman DJ, Kopchick JJ, Bartke A (2014) The slow-aging growth hormone receptor/binding protein gene-disrupted (GHR-KO) mouse is protected from aging-resultant neuromusculoskeletal frailty. Age (Dordr) 36(1):117–27. doi:10.1007/s11357-013-9551-x
Bartke A (1965) The response of two types of dwarf mice to growth hormone, thyrotropin, and thyroxine. Gen Comp Endocrinol 5:418–426
Bartke A (2006) Long-lived Klotho mice: new insights into the roles of IGF-1 and insulin in aging. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17(2):33–35
Bartke A (2008) Insulin and aging. Cell Cycle 7(21):3338–3343
Bartke A (2011) Single-gene mutations and healthy ageing in mammals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 366(1561):28–34
Bartke A (2012) Healthy aging: is smaller better? — a mini-review. Gerontology 58:337–343
Bartke A, Brown-Borg H (2004) Life extension in the dwarf mouse. Curr Top Dev Biol 63:189–225
Bartke A, Wright JC, Mattison JA, Ingram DK, Miller RA, Roth GS (2001) Extending the lifespan of long-lived mice. Nature 414(6862):412
Barzilai N, Huffman DM, Muzumdar RH, Bartke A (2012) The critical role of metabolic pathways in aging. Diabetes 61(6):1315–1322
Berryman DE, List EO, Coschigano KT, Behar K, Kim JK, Kopchick JJ (2004) Comparing adiposity profiles in three mouse models with altered GH signaling. Growth Hormon IGF Res 14(4):309–318
Berryman DE, Christiansen JS, Johannsson G, Thorner MO, Kopchick JJ (2008) Role of the GH/IGF-1 axis in lifespan and healthspan: lessons from animal models. Growth Hormon IGF Res 18(6):455–471
Berryman DE, List EO, Palmer AJ, Chung MY, Wright-Piekarski J, Lubbers E, O'Connor P, Okada S, Kopchick JJ (2010) Two-year body composition analyses of long-lived GHR null mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 65(1):31–40
Bonkowski MS, Rocha JS, Masternak MM, Al Regaiey KA, Bartke A (2006) Targeted disruption of growth hormone receptor interferes with the beneficial actions of calorie restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(20):7901–7905
Boparai RK, Arum O, Khardori R, Bartke A (2010) Glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in growth hormone-transgenic mice: a cross-sectional analysis. Biol Chem 391(10):1149–1155
Borg KE, Brown-Borg HM, Bartke A (1995) Assessment of the primary adrenal cortical and pancreatic hormone basal levels in relation to plasma glucose and age in the unstressed Ames dwarf mouse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 210(2):126–133
Bourdel-Marchasson I, Berrut G (2005) Caring the elderly diabetic patient with respect to concepts of successful aging and frailty. Diabetes Metab 31(2):5S13–5S19
Brown-Borg HM, Borg KE, Meliska CJ, Bartke A (1996) Dwarf mice and the ageing process. Nature 384(6604):33
Carlson AJ, Hoelzel F (1946) Apparent prolongation of the life span of rats by intermittent fasting. J Nutr 31:363–375
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services (2011) National Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2011. (http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services (2012) Diabetes Report Card 2012. (http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/DiabetesReportCard.pdf)
Chang AM, Halter JB (2003) Aging and insulin secretion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284(1):E7–E12
Chen LK, Chen YM, Lin MH, Peng LN, Hwang SJ (2010) Care of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus: a focus on frailty. Ageing Res Rev 9(Suppl 1):S18–S22
Collier B, Dossett LA, May AK, Diaz JJ (2008) Glucose control and the inflammatory response. Nutr Clin Pract 23(1):3–15
Conover CA, Bale LK (2007) Loss of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A extends lifespan in mice. Aging Cell 6(5):727–729
Conover CA, Mason MA, Levine JA, Novak CM (2008) Metabolic consequences of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A deficiency in mice: exploring possible relationship to the longevity phenotype. J Endocrinol 198(3):599–605
Coschigano KT et al. (1999) 81st Annual Meeting of the Endocrine Society, San Diego, CA
Coschigano KT, Clemmons D, Bellush LL, Kopchick JJ (2000) Assessment of growth parameters and life span of GHR/BP gene-disrupted mice. Endocrinology 141(7):2608–2613
Coschigano KT, Holland AN, Riders ME, List EO, Flyvbjerg A, Kopchick JJ (2003) Deletion, but not antagonism, of the mouse growth hormone receptor results in severely decreased body weights, insulin, and insulin-like growth factor I levels and increased life span. Endocrinology 144(9):3799–3810
Couet C, Delarue J, Constans T, Lamisse F (1992) Age-related insulin resistance: a review. Horm Res 38(1–2):46–50
Cozzi R, Attanasio R (2012) Octreotide long-acting repeatable for acromegaly. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 5(2):125–143
Crandall JP, Shamoon H, Cohen HW, Reid M, Gajavelli S, Trandafirescu G, Tabatabaie V, Barzilai N (2009) Post-challenge hyperglycemia in older adults is associated with increased cardiovascular risk profile. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(5):1595–1601
Dominguez LJ, Paolisso G, Barbagallo M (2010) Glucose control in the older patient: from intensive to effective and safe. Aging Clin Exp Res 22(4):274–280
Dominici FP, Hauck S, Argentino DP, Bartke A, Turyn D (2002) Increased insulin sensitivity and upregulation of insulin receptor, insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 in liver of Ames dwarf mice. J Endocrinol 173(1):81–94
Farrokhi F, Smiley D, Umpierrez GE (2011) Glycemic control in non-diabetic critically ill patients. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25(5):813–824
Finch CE (2009) The neurobiology of middle-age has arrived. Neurobiol Aging 30(4):515–520, discussion 530–33
Flurkey K, Papaconstantinou J, Miller RA, Harrison DE (2001) Lifespan extension and delayed immune and collagen aging in mutant mice with defects in growth hormone production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(12):6736–6741
Fontana L, Meyer TE, Klein S, Holloszy JO (2004) Long-term calorie restriction is highly effective in reducing the risk for atherosclerosis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(17):6659–6663
Fontana L, Klein S, Holloszy JO (2010) Effects of long-term calorie restriction and endurance exercise on glucose tolerance insulin action, and adipokine production. Age (Dordr) 32(1):97–108
Gage PJ, Roller ML, Saunders TL, Scarlett LM, Camper SA (1996) Anterior pituitary cells defective in the cell-autonomous factor, df, undergo cell lineage specification but not expansion. Development 122(1):151–160
Glantz SA (2002) Primer of biostatistics. How to summarize data (Chapter 2), 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY
Gong Z, Muzumdar RH (2012) Pancreatic function type 2 diabetes, and metabolism in aging. Int J Endocrinol 2012:320482
Goto S (2006) Health span extension by later-life caloric or dietary restriction: a view based on rodent studies. Biogerontology 7(3):135–138
Greene DA (1986) Acute and chronic complications of diabetes mellitus in older patients. Am J Med 80(5A):39–53
Guo Y, Lu Y, Houle D, Robertson K, Tang Z, Kopchick JJ, Liu YL, Liu JL (2005) Pancreatic islet-specific expression of an insulin-like growth factor-I transgene compensates islet cell growth in growth hormone receptor gene-deficient mice. Endocrinology 146(6):2602–2609
Halter JB (2012) Diabetes mellitus in an aging population: the challenge ahead. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67(12):1297–1299
Heilbronn LK, Smith SR, Martin CK, Anton SD, Ravussin E (2005) Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 81(1):69–73
Heilbronn LK, de Jonge L, Frisard MI, DeLany JP, Larson-Meyer DE, Rood J, Nguyen T, Martin CK, Volaufova J, Most MM, Greenway FL, Smith SR, Deutsch WA, Williamson DA, Ravussin E, Pennington CALERIE Team (2006) Effect of 6-month calorie restriction on biomarkers of longevity, metabolic adaptation, and oxidative stress in overweight individuals: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295(13):1539–1548, Erratum in: JAMA. 2006 Jun 7;295(21):2482
Hundal RS, Krssak M, Dufour S, Laurent D, Lebon V, Chandramouli V, Inzucchi SE, Schumann WC, Petersen KF, Landau BR, Shulman GI (2000) Mechanism by which metformin reduces glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 49(12):2063–2069
Ikeno Y, Bronson RT, Hubbard GB, Lee S, Bartke A (2003) Delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in Ames dwarf mice: correlation to extended longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 58(4):291–296
Ikeno Y, Hubbard GB, Lee S, Cortez LA, Lew CM, Webb CR, Berryman DE, List EO, Kopchick JJ, Bartke A (2009) Reduced incidence and delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in growth hormone receptor/binding protein knockout mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(5):522–529
Johnson MA (2013) Strategies to improve diet in older adults. Proc Nutr Soc 72(1):166–172
Kenyon CJ (2010) The genetics of ageing. Nature 464(7288):504–512, Erratum in: Nature. 2010 Sep 30;467(7315):622
Kinney BA, Coschigano KT, Kopchick JJ, Steger RW, Bartke A (2001a) Evidence that age-induced decline in memory retention is delayed in growth hormone resistant GH-R-KO (Laron) mice. Physiol Behav 72(5):653–660
Kinney BA, Meliska CJ, Steger RW, Bartke A (2001b) Evidence that Ames dwarf mice age differently from their normal siblings in behavioral and learning and memory parameters. Horm Behav 39(4):277–284
Kinney-Forshee BA, Kinney NE, Steger RW, Bartke A (2004) Could a deficiency in growth hormone signaling be beneficial to the aging brain? Physiol Behav 80(5):589–594
Kinsella K, Wan H (2009) U.S. Census Bureau, International Population Reports, P95/09-1, An aging world: 2008. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC. (http://www.census.gov/prod/2009pubs/p95-09-1.pdf)
Klempel MC, Bhutani S, Fitzgibbon M, Freels S, Varady KA (2010) Dietary and physical activity adaptations to alternate day modified fasting: implications for optimal weight loss. Nutr J 9:35
Klover PJ, Mooney RA (2004) Hepatocytes: critical for glucose homeostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(5):753–758
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Nandi A, Gurnani P, McGuinness OP, Chikuda H, Yamaguchi M, Kawaguchi H, Shimomura I, Takayama Y, Herz J, Kahn CR, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309(5742):1829–1833
Lazar HL (2012) How important is glycemic control during coronary artery bypass? Adv Surg 46:219–235
Liu JL, Coschigano KT, Robertson K, Lipsett M, Guo Y, Kopchick JJ, Kumar U, Liu YL (2004) Disruption of growth hormone receptor gene causes diminished pancreatic islet size and increased insulin sensitivity in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(3):E405–E413
Lu J, Lezi E, Wang W, Frontera J, Zhu H, Wang WT, Lee P, Choi IY, Brooks WM, Burns JM, Aires D, Swerdlow RH (2011) Alternate day fasting impacts the brain insulin-signaling pathway of young adult male C57BL/6 mice. J Neurochem 117(1):154–163
Mair W, Goymer P, Pletcher SD, Partridge L (2003) Demography of dietary restriction and death in Drosophila. Science 301(5640):1731–1733
Martin B, Mattson MP, Maudsley S (2006) Caloric restriction and intermittent fasting: two potential diets for successful brain aging. Ageing Res Rev 5(3):332–353
Mattson MP, Duan W, Guo Z (2003) Meal size and frequency affect neuronal plasticity and vulnerability to disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Neurochem 84(3):417–431
McCay CM, Crowell MF, Maynard LA (1935) The effect of retarded growth upon the length of life span and upon the ultimate body size. Nutrition 5(3):155–171, discussion 172
Miller RA (2009) “Dividends” from research on aging—can biogerontologists, at long last, find something useful to do? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(2):157–160
Miller RA, Burke D, Nadon N (1999) Announcement: four-way cross mouse stocks: a new, genetically heterogeneous resource for aging research. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54(8):B358–B360
Moghissi ES (2010) Reexamining the evidence for inpatient glucose control: new recommendations for glycemic targets. Am J Health Syst Pharm 67(16 Suppl 8):S3–S8
Moreschi C (1909) Ztschr. f. Immunitätsforsch. u. exper. Therap 2:651
Olshansky SJ, Perry D, Miller RA, Butler RN (2007) Pursuing the longevity dividend: scientific goals for an aging world. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1114:11–13
Panici JA, Wang F, Bonkowski MS, Spong A, Bartke A, Pawlikowska L, Kwok PY, Masternak MM (2009) Is altered expression of hepatic insulin-related genes in growth hormone receptor knockout mice due to GH resistance or a difference in biological life spans? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(11):1126–1133
Pucher J, Stewart J (2004) Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep 4(1):46–50
Rochon J, Bales CW, Ravussin E, Redman LM, Holloszy JO, Racette SB, Roberts SB, Das SK, Romashkan S, Galan KM, Hadley EC, Kraus WE, CALERIE Study Group (2011) Design and conduct of the CALERIE study: comprehensive assessment of the long-term effects of reducing intake of energy. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66(1):97–108
Roe FJC, Lee PN, Conybeare G, Kelly D, Matter B, Prentice D, Tobin G (1995) The BIOSURE Study: influence of composition of diet and food consumption on longevity, degenerative diseases and neoplasia in Wistar rats studied for up to 30 months postweaning. Food Chem Toxicol 33(Suppl 1):1S–100S
Roth LW, Polotsky AJ (2012) Can we live longer by eating less? A review of caloric restriction and longevity. Maturitas 71(4):315–319
Rous P (1914) The influence of diet on transplanted and spontaneous mouse tumors. J Exp Med 20(5):433–451
Salonen PH, Koskela HO, Niskanen L (2012) Prevalence and determinants of hyperglycaemia in pneumonia patients. Scand J Infect Dis 45(2):88–94
Schaible R, Gowen JW (1961) A new dwarf mouse. Genetics 46:896
Slabaugh M, Lieberman M, Rutledge J, Gorski J (1981) Growth hormone and prolactin synthesis in normal and homozygous Snell and Ames dwarf mice. Endocrinology 109:1040–1046
Smith NL, Savage PJ, Heckbert SR, Barzilay JI, Bittner VA, Kuller LH, Psaty BM (2002) Glucose, blood pressure, and lipid control in older people with and without diabetes mellitus: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 50(3):416–423
Sornson MW, Wu W, Dasen JS, Flynn SE, Norman DJ, O'Connell SM, Gukovsky I, Carrière C, Ryan AK, Miller AP, Zuo L, Gleiberman AS, Andersen B, Beamer WG, Rosenfeld MG (1996) Pituitary lineage determination by the Prophet of Pit-1 homeodomain factor defective in Ames dwarfism. Nature 384(6607):327–333
Topinková E (2008) Aging, disability and frailty. Ann Nutr Metab 52(Suppl 1):6–11
Trepanowski JF, Bloomer RJ (2010) The impact of religious fasting on human health. Nutr J 9:57
Trepanowski JF, Canale RE, Marshall KE, Kabir MM, Bloomer RJ (2011) Impact of caloric and dietary restriction regimens on markers of health and longevity in humans and animals: a summary of available findings. Nutr J 10:107
Valeri C, Pozzilli P, Leslie D (2004) Glucose control in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 20(Suppl 2):S1–S8
van der Lely AJ, Biller BM, Brue T, Buchfelder M, Ghigo E, Gomez R, Hey-Hadavi J, Lundgren F, Rajicic N, Strasburger CJ, Webb SM, Koltowska-Häggström M (2012) Long-term safety of pegvisomant in patients with acromegaly: comprehensive review of 1288 subjects in ACROSTUDY. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(5):1589–1597
Varady KA (2011) Intermittent versus daily calorie restriction: which diet regimen is more effective for weight loss? Obes Rev 12(7):e593–e601
Varady KA, Hellerstein MK (2007) Alternate-day fasting and chronic disease prevention: a review of human and animal trials. Am J Clin Nutr 86(1):7–13
Varady KA, Bhutani S, Church EC, Klempel MC (2009) Short-term modified alternate-day fasting: a novel dietary strategy for weight loss and cardioprotection in obese adults. Am J Clin Nutr 90(5):1138–1143
Viljoen A, Sinclair AJ (2011) Diabetes and insulin resistance in older people. Med Clin N Am 95(3):615–629, xi–xii
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F (2012) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond) 122(6):253–270
Wang C, Weindruch R, Fernández JR, Coffey CS, Patel P, Allison DB (2004) Caloric restriction and body weight independently affect longevity in Wistar rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(3):357–362
Warner H, Sierra F (2009) The longevity dividend: why invest in basic aging research? Can J Aging 28(4):391–394, French 395–8
Wijsman CA, Rozing MP, Streefland TC, le Cessie S, Mooijaart SP, Slagboom PE, Westendorp RG, Pijl H, van Heemst D, Leiden Longevity Study Group (2011) Familial longevity is marked by enhanced insulin sensitivity. Aging Cell 10(1):114–121
Zhou Y, Xu BC, Maheshwari HG, He L, Reed M, Lozykowski M, Okada S, Cataldo L, Coschigamo K, Wagner TE, Baumann G, Kopchick JJ (1997) A mammalian model for Laron syndrome produced by targeted disruption of the mouse growth hormone receptor/binding protein gene (the Laron mouse). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(24):13215–13220
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institute on Aging Grants AG19899, U19 AG023122, and 3R01AG019899-07S1, as well as a Senior Scholar Award in Aging from The Ellison Medical Foundation and The Glenn Foundation for Medical Research; this work was vitally supported by a grant from the Center for Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders at The Southern Illinois University, and the authors especially thank Drs. Thomas A. Ala and Robert G. Struble.
Conflict of interest
The authors aver that they have no conflicts of interest related to this publication.
Authors’ contributions
O.A. and A.B.. acquired funding for this study; O.A. conceived and designed this study; O.A. and R.K.B. methodologically executed this study; O.A. statistically analyzed the data; O.A., J.K.S., R.K.K., and A.B.. prepared the manuscript for this study; and J.J.K. provided founder populations of some of the mice used for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 2073 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Arum, O., Saleh, J.K., Boparai, R.K. et al. Preservation of blood glucose homeostasis in slow-senescing somatotrophism-deficient mice subjected to intermittent fasting begun at middle or old age. AGE 36, 9651 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9651-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9651-2