Abstract
Objectives
HERMEX is a population-based study, which tries to evaluate the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in the population of Extremadura, Spain. This report provides the data concerning albuminuria in the elderly people recruited in the survey.
Design and methods
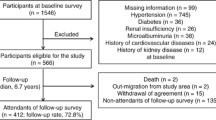
3,402 subjects were randomly selected from the database of the Health Care System of Extremadura. The final sample included 2,813 subjects (mean age 51.2 years, 53.5 % female). Urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) in the first morning urine sample was analyzed. Albuminuria was diagnosed when UAER (albumin-to-creatinine ratio) was ≥22 mg/g in men or ≥31 mg/g in women.
Results
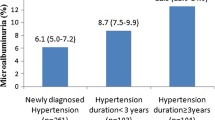
The prevalence of abnormal UAER in the elderly population was 10.9 % (microalbuminuria: 8.9 %; overt proteinuria: 1.8 %). The younger subjects showed a lower prevalence of microalbuminuria (3.4 %, p < 0.001). Elderly patients showed a higher prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors than the younger ones. The elderly had higher systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure than the younger ones. Furthermore, the elderly subjects had lower plasma levels of HDL cholesterol, but higher triglycerides, glucose, creatinine, and glycosylated hemoglobin; no differences were found for total and LDL cholesterol. When the prevalence of causes of microalbuminuria was compared between age groups, we found a sharp increase in diabetic and, especially, hypertensive patients in the elderly group. The multivariate analysis showed an independent association of microalbuminuria with systolic blood pressure and plasma creatinine.
Conclusions
A high prevalence of abnormal UAER in elderly people was detected in a randomly selected sample of Spanish general population. In most elderly patients, microalbuminuria was associated with high blood pressure and, less frequently, with diabetes mellitus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dinneen SF, Gerstein HC (1997) The association of micro albuminuria and mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a systematic overview of the literature. Arch Intern Med 157:1413–1418
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR (2003) UKPDS group: development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int 63:225–232
Mogensen CE (2003) Micro albuminuria and hypertension with focus on type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Intern Med 254:45–66
Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B et al (2001) Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA 286:421–426
Jensen JS, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, Schroll M, Borch- Johnsen K (2000) Arterial hypertension, micro albuminuria, and risk of ischemic heart disease. Hypertension 35:898–903
Bigazzi R, Bianchi S, Baldari D, Campese VM (1998) Micro albuminuria predicts cardiovascular events and renal insufficiency in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens 16:1325–1333
Hillege HL, Fidler V, Diercks GFH, van Gilst WH, de Zeeuw D, van Veldhuisen DJ et al (2002) For the prevention of renal and vascular end stage disease (PREVEND) study group. Urinary albumin excretion predicts cardiovascular and non cardiovascular mortality in general population. Circulation 106:1777–1782
Robles NR, Mena C, Velasco J, Angulo E, Garrote T, Garcia Gallego F (2008) En representación de los investigadores del estudio MICREX Riesgo cardiovascular asociado a micro albuminuria en pacientes diabéticos y en pacientes con hipertensión arterial. Med Clin (Barc) 130:206–209
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee (2003) The Seventh report of joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G et al (2007) Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European society of hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 25:1105–1187
Levey AS, Cattran D, Friedman A, Miller WG, Sedor J, Tuttle K et al (2009) Proteinuria as a surrogate outcome in CKD: report of a scientific workshop sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation and the US Food and Drug Administration. Am J Kidney Dis 54:205–226
Jones CA, Francis ME, Eberhardt MS, Chavers B, Coresh J, Engelgau M et al (2002) Micro albuminuria in the US population: third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 39:445–459
Robles NR, Felix FJ, Fernandez-Berges D, Perez-Castán JF, Zaro MJ, Lozano L, et al. Prevalence of abnormal urinary albumin excretion in a population based study in Spain: results from the Hermex study. Eur J Clin Invest. (in press)
Simera I, Moher D, Hoey J, Schulz KF, Altman DG (2010) A catalogue of reporting guidelines for health research. Eur J Clin Invest 40:35–53
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC Jr, Stone NJ, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association (2004) Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation 110:227–239
Banegas JR, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Ruilope LM, Graciani A, Luque M et al (2002) Hypertension magnitude and management in the elderly population of Spain. J Hypertens 20:2157–2164
Gutzwiller F, Keil U, Tuomilehto J (1990) Societal and community effects on blood pressure. In: Laragh JH, Brenner BM (eds) Hypertension: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Raven Press Publishers, New York, pp 147–158
Roberts J, Maurer K (1977) Blood pressure levels of persons 6–74 Years. United States, 1971–1974. Vital and health statistics, Series 11, No. 203. Washington, DC: US Dept of Health, Education, and Welfare, 1–103
Bigazzi R, Bianchi S (1995) Micro albuminuria as a marker of cardiovascular and renal disease in essential hypertension. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10(Suppl 6):10–14
Giaconi S, Levanti C, Fommei E, Innocenti F, Seghieri G, Palla L et al (1989) Micro albuminuria and casual and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in normotensive and in patients with borderline and mild essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2:259–261
Cerasola G, Cottone S, Mule G, Nardi E, Mangano MT, Andronico G et al (1996) Micro albuminuria, renal dysfunction and cardiovascular complication in essential hypertension. J Hypertens 14:915–920
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Calvo C (2007) Optimal timing for antihypertensive dosing: focus on valsartan. Ther Clin Risk Manag 3:119–131
Ritz E, Viberti GC, Ruilope LM, Rabelink AJ, Izzo JL Jr, Katayama S et al (2010) Determinants of urinary albumin excretion within the normal range in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Randomised Olmesartan and Diabetes Micro albuminuria Prevention (ROADMAP) study. Diabetologia 53:49–57
Lurbe E, Redon J, Kesani A, Pascual JM, Tacons J, Alvarez V et al (2002) Increase in nocturnal blood pressure and progression to micro albuminuria in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 347:797–805
Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Pietraszek L, Riis Hansen P, Parving HH (2005) Improved prognosis in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy: a prospective follow-up study. Kidney Int 68:1250–1257
Afsar B, Sezer S, Elsurer R, Ozdemir FN (2007) Is HOMA index a predictor of nocturnal non dipping in hypertensives with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus? Blood Press Monit 12:133–139
Canonico V, Caprio LD, Vigorito C, Forgione L, Tedeschi C, Guanni P et al (1990) Differences in blood pressure profile between young and elderly hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 4:405–440
James MA, Fotherby MD, Potter JF (1994) Clinical correlates of left ventricular mass in elderly hypertensives. J Hum Hypertens 8:409–415
Nakatsuka H, Imai Y, Abe K, Nagai K, Ikeda M, Satoh H et al (1991) Population study of ambulatory blood pressure in a rural community in Northern Japan. Tohoku I Exp Med 163:119–127
Fotherby MD, Potter JF (1995) Twenty-four-hour ambulatory blood pressure in old and very old subjects. J Hypertens 13:1742–1746
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH (1998) Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 21:1414–1431
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM (2006) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295:1549–1555
Zimmet P, Alberti KGM, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787
Boyle JP, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, Hoerger TJ, Geiss LS, Chen H et al (2001) Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the US. Diabetes Care 24:1936–1940
Pollock CA, Poronnik P (2007) Albumin transport and processing by the proximal tubule: physiology and pathophysiology. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:359–364
Coresh J, Byrd-Holt D, Astor BC, Briggs JP, Eggers PW, Lacher DA et al (1999) Chronic kidney disease awareness prevalence, and trends among US adults, to 2000. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005(16):180–188
Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS (2003) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: third national health and nutrition examination survey. Am J Kidney Dis 41:1–12
Bakker AJ (1999) Detection of macro albuminuria—Receiver operating curve analysis favors albumin-to-creatinine ratio over albumin concentration. Diabetes Care 22:307–313
Houlihan CA, Tsalamandris C, Akdeniz A, Jerums G (2002) Albumin to creatinine ratio: a screening test with limitations. Am J Kidney Dis 39:1183–1189
Incerti J, Zelmanovitz T, Camargo JL, Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ (2005) Evaluation of tests for micro albuminuria screening in patients with diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2402–2407
Brantsma AH, Bakker SJ, Hillege HL, de Zeeuw D, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT (2005) Urinary albumin excretion and its relation with C-reactive protein and the metabolic syndrome in the prediction of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28:2525–2530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robles, N.R., Felix, F.J., Fernandez-Berges, D. et al. Prevalence of abnormal urinary albumin excretion in elderly people: a Spanish survey. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 553–560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0380-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0380-8