Abstract
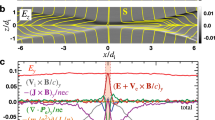
Magnetic reconnection is a fundamental plasma physics process in which ideal-MHD’s frozen-in constraints are broken and the magnetic field topology is dramatically re-arranged, which often leads to a violent release of the free magnetic energy. Most of the magnetic reconnection research done to date has been motivated by the applications to systems such as the solar corona, Earth’s magnetosphere, and magnetic confinement devices for thermonuclear fusion. These environments have relatively low energy densities and the plasma is adequately described as a mixture of equal numbers of electrons and ions and where the dissipated magnetic energy always stays with the plasma. In contrast, in this paper I would like to introduce a different, new direction of research—reconnection in high energy density radiative plasmas, in which photons play as important a role as electrons and ions; in particular, in which radiation pressure and radiative cooling become dominant factors in the pressure and energy balance. This research is motivated in part by rapid theoretical and experimental advances in High Energy Density Physics, and in part by several important problems in modern high-energy astrophysics. I first discuss some astrophysical examples of high-energy-density reconnection and then identify the key physical processes that distinguish them from traditional reconnection. Among the most important of these processes are: special-relativistic effects; radiative effects (radiative cooling, radiation pressure, and radiative resistivity); and, at the most extreme end—QED effects, including pair creation. The most notable among the astrophysical applications are situations involving magnetar-strength fields (1014–1015 G, exceeding the quantum critical field B ∗≃4×1013 G). The most important examples are giant flares in soft gamma repeaters (SGRs) and magnetic models of the central engines and relativistic jets of Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs). The magnetic energy density in these environments is so high that, when it is suddenly released, the plasma is heated to ultra-relativistic temperatures. As a result, electron-positron pairs are created in copious quantities, dressing the reconnection layer in an optically thick pair coat, thereby trapping the photons. The plasma pressure inside the layer is then dominated by the combined radiation and pair pressure. At the same time, the timescale for radiation diffusion across the layer may, under some conditions, still be shorter than the global (along the layer) Alfvén transit time, and hence radiative cooling starts to dominate the thermodynamics of the problem. The reconnection problem then becomes essentially a radiative transfer problem. In addition, the high pair density makes the reconnection layer highly collisional, independent of the upstream plasma density, and hence radiative resistive MHD applies. The presence of all these processes calls for a substantial revision of our traditional physical picture of reconnection when applied to these environments and thus opens a new frontier in reconnection research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Aly, J. Kuijpers, Flaring interactions between accretion disk and neutron star magnetosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 227, 473–482 (1990)
J. Arons, Pulsars: Progress, Problems and Prospects (2007)
N. Bessho, A. Bhattacharjee, Collisionless reconnection in an electron-positron plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(24), 245001 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.245001
N. Bessho, A. Bhattacharjee, Fast collisionless reconnection in electron-positron plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 14(5), 056503 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2714020
A. Bhattacharjee, Y. Huang, H. Yang, B. Rogers, Fast reconnection in high-Lundquist-number plasmas due to the plasmoid instability. Phys. Plasmas 16(11), 112102 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3264103
J. Birn, J.F. Drake, M.A. Shay, B.N. Rogers, R.E. Denton, M. Hesse, M. Kuznetsova, Z.W. Ma, A. Bhattacharjee, A. Otto, P.L. Pritchett, Geospace Environmental Modeling (GEM) magnetic reconnection challenge. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 3715–3720 (2001). doi:10.1029/1999JA900449
D. Biskamp, E. Schwarz, J.F. Drake, Two-fluid theory of collisionless magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 4, 1002–1009 (1997). doi:10.1063/1.872211
E.G. Blackman, G.B. Field, Kinematics of relativistic magnetic reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 494–497 (1994). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.494
A. Brandenburg, E.G. Zweibel, Effects of pressure and resistivity on the ambipolar diffusion singularity: too little, too late. Astrophys. J. 448, 734 (1995). doi:10.1086/176001
A. Burrows, L. Dessart, E. Livne, C.D. Ott, J. Murphy, Simulations of magnetically driven supernova and hypernova explosions in the context of rapid rotation. Astrophys. J. 664, 416–434 (2007). doi:10.1086/519161
P.A. Cassak, J.F. Drake, M.A. Shay, A model for spontaneous onset of fast magnetic reconnection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 644, 145–148 (2006). doi:10.1086/505690
P.A. Cassak, J.F. Drake, M.A. Shay, Catastrophic onset of fast magnetic reconnection with a guide field. Phys. Plasmas 14(5), 054502 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2734948
P.A. Cassak, D.J. Mullan, M.A. Shay, From solar and stellar flares to coronal heating: theory and observations of how magnetic reconnection regulates coronal conditions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 676, 69–72 (2008). doi:10.1086/587055
P.A. Cassak, M.A. Shay, J.F. Drake, Catastrophe model for fast magnetic reconnection onset. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(23), 235002 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.235002
P.A. Cassak, M.A. Shay, J.F. Drake, Scaling of Sweet-Parker reconnection with secondary islands. Phys. Plasmas 16(12), 120702 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3274462
A.R. Choudhuri, Astrophysics for Physicists (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010), p. 329
I. Contopoulos, The role of reconnection in the pulsar magnetosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 466, 301–307 (2007). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065973
F.V. Coroniti, Magnetically striped relativistic magnetohydrodynamic winds - The Crab Nebula revisited. Astrophys. J. 349, 538–545 (1990). doi:10.1086/168340
C.R. D’Angelo, H.C. Spruit, Episodic accretion on to strongly magnetic stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 406, 1208–1219 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16749.x
W. Daughton, V. Roytershteyn, B.J. Albright, H. Karimabadi, L. Yin, K.J. Bowers, Transition from collisional to kinetic regimes in large-scale reconnection layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(6), 065004 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.065004
T. Di Matteo, A. Celotti, A.C. Fabian, Magnetic flares in accretion disc coronae and the spectral states of black hole candidates: the case of GX339-4. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 304, 809–820 (1999). doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02375.x
V.L. Dorman, R.M. Kulsrud, One-dimensional merging of magnetic fields with cooling. Astrophys. J. 449, 777 (1995). doi:10.1086/176097
R.P. Drake, High-Energy-Density Physics: Fundamentals, Inertial Fusion, and Experimental Astrophysics (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
G. Drenkhahn, H.C. Spruit, Efficient acceleration and radiation in Poynting flux powered GRB outflows. Astron. Astrophys. 391, 1141–1153 (2002). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020839
B.D. Farris, T.K. Li, Y.T. Liu, S.L. Shapiro, Relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamics in dynamical spacetimes: Numerical methods and tests. Phys. Rev. D 78(2), 024023 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.78.024023
E.D. Feigelson, T. Montmerle, High-energy processes in young stellar objects. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 37, 363–408 (1999). doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.37.1.363
A.A. Galeev, R. Rosner, G.S. Vaiana, Structured coronae of accretion disks. Astrophys. J. 229, 318–326 (1979). doi:10.1086/156957
D. Giannios, H.C. Spruit, Spectra of Poynting-flux powered GRB outflows. Astron. Astrophys. 430, 1–7 (2005). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20047033
D. Giannios, H.C. Spruit, The role of kink instability in Poynting-flux dominated jets. Astron. Astrophys. 450, 887–898 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054107
D. Giannios, H.C. Spruit, Spectral and timing properties of a dissipative γ-ray burst photosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 469, 1–9 (2007). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066739
D. Giannios, D.A. Uzdensky, M.C. Begelman, Fast TeV variability in blazars: jets in a jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 29–33 (2009). doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00635.x
D. Giannios, D.A. Uzdensky, M.C. Begelman, Fast TeV variability from misaligned minijets in the jet of M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 1649–1656 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16045.x
J. Goodman, D. Uzdensky, Reconnection in marginally collisionless accretion disk coronae. Astrophys. J. 688, 555–558 (2008). doi:10.1086/592345
A.P. Goodson, R.M. Winglee, K. Boehm, Time-dependent accretion by magnetic young stellar objects as a launching mechanism for stellar jets. Astrophys. J. 489, 199 (1997). doi:10.1086/304774
F. Haardt, L. Maraschi, A two-phase model for the X-ray emission from Seyfert galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 380, 51–54 (1991). doi:10.1086/186171
A.K. Harding, D. Lai, Physics of strongly magnetized neutron stars. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 2631–2708 (2006). doi:10.1088/0034-4885/69/9/R03
M.R. Hayashi, K. Shibata, R. Matsumoto, X-ray flares and mass outflows driven by magnetic interaction between a protostar and its surrounding disk. Astrophys. J. Lett. 468, 37 (1996). doi:10.1086/310222
F. Heitsch, E.G. Zweibel, Fast reconnection in a two-stage process. Astrophys. J. 583, 229–244 (2003). doi:10.1086/345082
H. Herold, Compton and Thomson scattering in strong magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 19, 2868–2875 (1979). doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.19.2868
M. Hesse, S. Zenitani, Dissipation in relativistic pair-plasma reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 14(11), 112102 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2801482
Y. Huang, A. Bhattacharjee, Scaling laws of resistive magnetohydrodynamic reconnection in the high-Lundquist-number, plasmoid-unstable regime. Phys. Plasmas 17(6), 062104 (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3420208
C.H. Jaroschek, M. Hoshino, Radiation-dominated relativistic current sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(7), 075002 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.075002
C.H. Jaroschek, H. Lesch, R.A. Treumann, Relativistic kinetic reconnection as the possible source mechanism for high variability and flat spectra in extragalactic radio sources. Astrophys. J. Lett. 605, 9–12 (2004a). doi:10.1086/420767
C.H. Jaroschek, R.A. Treumann, H. Lesch, M. Scholer, Fast reconnection in relativistic pair plasmas: Analysis of particle acceleration in self-consistent full particle simulations. Phys. Plasmas 11, 1151–1163 (2004b). doi:10.1063/1.1644814
J.G. Kirk, O. Skjæraasen, Dissipation in poynting-flux-dominated flows: the σ-problem of the Crab pulsar wind. Astrophys. J. 591, 366–379 (2003). doi:10.1086/375215
R.G. Kleva, J.F. Drake, F.L. Waelbroeck, Fast reconnection in high temperature plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 2, 23–34 (1995). doi:10.1063/1.871095
S.S. Komissarov, Multidimensional numerical scheme for resistive relativistic magnetohydrodynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 382, 995–1004 (2007). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12448.x
S.S. Komissarov, M.V. Barkov, Magnetar-energized supernova explosions and gamma-ray burst jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 382, 1029–1040 (2007). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12485.x
D.A. Larrabee, R.V.E. Lovelace, M.M. Romanova, Lepton acceleration by relativistic collisionless magnetic reconnection. Astrophys. J. 586, 72–78 (2003). doi:10.1086/367640
A. Lazarian, E.T. Vishniac, Reconnection in a weakly stochastic field. Astrophys. J. 517, 700–718 (1999). doi:10.1086/307233
H.K. Lee, R.A.M.J. Wijers, G.E. Brown, The Blandford-Znajek process as a central engine for a gamma-ray burst. Phys. Rep. 325, 83–114 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(99)00084-8
H. Lesch, W. Reich, The origin of monoenergetic electrons in the Arc of the Galactic Center - Particle acceleration by magnetic reconnection. Astron. Astrophys. 264, 493–499 (1992)
C.K. Li, F.H. Séguin, J.A. Frenje, J.R. Rygg, R.D. Petrasso, R.P.J. Town, O.L. Landen, J.P. Knauer, V.A. Smalyuk, Observation of megagauss-field topology changes due to magnetic reconnection in laser-produced plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(5), 055001 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.055001
B.F. Liu, S. Mineshige, K. Ohsuga, Spectra from a magnetic reconnection-heated corona in active galactic nuclei. Astrophys. J. 587, 571–579 (2003). doi:10.1086/368282
W. Liu, H. Li, L. Yin, W. Daughton, B.J. Albright, K.J. Bowers, E.P. Liang, Particle Energization in 3D Magnetic Reconnection of Relativistic Pair Plasmas (2010)
N.F. Loureiro, A.A. Schekochihin, S.C. Cowley, Instability of current sheets and formation of plasmoid chains. Phys. Plasmas 14(10), 100703 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2783986
D. Lynden-Bell, Magnetic collimation by accretion discs of quasars and stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 279, 389–401 (1996)
Y.E. Lyubarskii, A model for the energetic emission from pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. 311, 172–178 (1996)
Y. Lyubarsky, J.G. Kirk, Reconnection in a striped pulsar wind. Astrophys. J. 547, 437–448 (2001). doi:10.1086/318354
Y.E. Lyubarsky, The termination shock in a striped pulsar wind. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 345, 153–160 (2003). doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06927.x
Y.E. Lyubarsky, On the relativistic magnetic reconnection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 358, 113–119 (2005). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08767.x
M. Lyutikov, Explosive reconnection in magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, 540–554 (2003a). doi:10.1046/j.1365-2966.2003.07110.x
M. Lyutikov, Role of reconnection in AGN jets. New Astron. Rev. 47, 513–515 (2003b). doi:10.1016/S1387-6473(03)00083-6
M. Lyutikov, Magnetar giant flares and afterglows as relativistic magnetized explosions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 367, 1594–1602 (2006a). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10069.x
M. Lyutikov, The electromagnetic model of gamma-ray bursts. New J. Phys. 8, 119 (2006b). doi:10.1088/1367-2630/8/7/119
M. Lyutikov, A high-sigma model of pulsar wind nebulae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 405, 1809–1815 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16553.x
M. Lyutikov, E.G. Blackman, Gamma-ray bursts from unstable Poynting-dominated outflows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 321, 177–186 (2001). doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04190.x
M. Lyutikov, R. Blandford, Dynamics of Relativistic Magnetic Explosions in Gamma Ray Bursters. APS Meeting Abstracts (2002)
M. Lyutikov, R. Blandford, Gamma Ray Bursts as Electromagnetic Outflows (2003)
M. Lyutikov, D. Uzdensky, Dynamics of relativistic reconnection. Astrophys. J. 589, 893–901 (2003). doi:10.1086/374808
Z.W. Ma, A. Bhattacharjee, Fast impulsive reconnection and current sheet intensification due to electron pressure gradients in semi-collisional plasmas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 1673–1676 (1996). doi:10.1029/96GL01600
A.I. MacFadyen, S.E. Woosley, Collapsars: gamma-ray bursts and explosions in “failed supernovae”. Astrophys. J. 524, 262–289 (1999). doi:10.1086/307790
Y. Masada, S. Nagataki, K. Shibata, T. Terasawa, Solar-type magnetic reconnection model for magnetar giant flares. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 62, 1093 (2010)
E.P. Mazets, T.L. Cline, R.L. Aptekar’, P.S. Butterworth, D.D. Frederiks, S.V. Golenetskii, V.N. Il’Inskii, V.D. Pal’Shin, Activity of the soft gamma repeater SGR 1900 + 14 in 1998 from Konus-Wind observations: 2. The giant August 27 outburst. Astron. Lett. 25, 635–648 (1999)
J.C. McKinney, D.A. Uzdensky, A reconnection switch to trigger gamma-ray burst jet dissipation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. (2010, submitted). arXiv:1011.1904 [astro-ph]
M.V. Medvedev, Thermodynamics of photons in relativistic e + e − γ plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 59, 4766 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.59.R4766
P. Meszaros, M.J. Rees, Optical and long-wavelength afterglow from gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 476, 232 (1997). doi:10.1086/303625
F.C. Michel, Magnetic structure of pulsar winds. Astrophys. J. 431, 397–401 (1994). doi:10.1086/174493
F.S. Mozer, S.D. Bale, T.D. Phan, Evidence of diffusion regions at a subsolar magnetopause crossing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(1), 015002 (2002). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.015002
K. Nalewajko, M. Begelman, D. Giannios, D. Uzdensky, M. Sikora, Radiative properties of reconnection-powered minijets in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. (2010, accepted). arXiv:1007.3994 [astro-ph]
P.M. Nilson, L. Willingale, M.C. Kaluza, C. Kamperidis, S. Minardi, M.S. Wei, P. Fernandes, M. Notley, S. Bandyopadhyay, M. Sherlock, R.J. Kingham, M. Tatarakis, Z. Najmudin, W. Rozmus, R.G. Evans, M.G. Haines, A.E. Dangor, K. Krushelnick, Magnetic reconnection and plasma dynamics in two-beam laser-solid interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(25), 255001 (2006). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.255001
M. Øieroset, T.D. Phan, M. Fujimoto, R.P. Lin, R.P. Lepping, In situ detection of collisionless reconnection in the Earth’s magnetotail. Nature 412, 414–417 (2001). doi:10.1038/35086520
B. Paczynski, Are gamma-ray bursts in star-forming regions? Astrophys. J. Lett. 494, 45 (1998). doi:10.1086/311148
T. Padmanabhan, Theoretical Astrophysics, vol. 1 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000), pp. 239–240
D.M. Palmer, S. Barthelmy, N. Gehrels, R.M. Kippen, T. Cayton, C. Kouveliotou, D. Eichler, R.A.M.J. Wijers, P.M. Woods, J. Granot, Y.E. Lyubarsky, E. Ramirez-Ruiz, L. Barbier, M. Chester, J. Cummings, E.E. Fenimore, M.H. Finger, B.M. Gaensler, D. Hullinger, H. Krimm, C.B. Markwardt, J.A. Nousek, A. Parsons, S. Patel, T. Sakamoto, G. Sato, M. Suzuki, J. Tueller, A giant γ-ray flare from the magnetar SGR 1806 - 20. Nature 434, 1107–1109 (2005). doi:10.1038/nature03525
E.N. Parker, Sweet’s mechanism for merging magnetic fields in conducting fluids. J. Geophys. Res. 62, 509–520 (1957)
E.N. Parker, The solar-flare phenomenon and the theory of reconnection and annihilation of magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 8, 177 (1963). doi:10.1086/190087
J. Pétri, Y. Lyubarsky, Magnetic reconnection at the termination shock in a striped pulsar wind. Astron. Astrophys. 473, 683–700 (2007). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066981
H.E. Petschek, Magnetic field annihilation, in The Physics of Solar Flares, ed. by W.N. Hess (1964), p. 425
T.D. Phan, J.T. Gosling, M.S. Davis, R.M. Skoug, M. Øieroset, R.P. Lin, R.P. Lepping, D.J. McComas, C.W. Smith, H. Reme, A. Balogh, A magnetic reconnection X-line extending more than 390 Earth radii in the solar wind. Nature 439, 175–178 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature04393
D. Proga, A.I. MacFadyen, P.J. Armitage, M.C. Begelman, Axisymmetric magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the collapsar model for gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 599, 5–8 (2003). doi:10.1086/381158
M.J. Rees, P. Mészáros, Dissipative photosphere models of gamma-ray bursts and X-ray flashes. Astrophys. J. 628, 847–852 (2005). doi:10.1086/430818
B.N. Rogers, R.E. Denton, J.F. Drake, M.A. Shay, Role of dispersive waves in collisionless magnetic reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(19), 195004 (2001). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.195004
M.M. Romanova, R.V.E. Lovelace, Magnetic field, reconnection, and particle acceleration in extragalactic jets. Astron. Astrophys. 262, 26–36 (1992)
M.M. Romanova, G.V. Ustyugova, A.V. Koldoba, V.M. Chechetkin, R.V.E. Lovelace, Dynamics of magnetic loops in the coronae of accretion disks. Astrophys. J. 500, 703 (1998). doi:10.1086/305760
R. Samtaney, N.F. Loureiro, D.A. Uzdensky, A.A. Schekochihin, S.C. Cowley, Formation of plasmoid chains in magnetic reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(10), 105004 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.105004
R. Schopper, H. Lesch, G.T. Birk, Magnetic reconnection and particle acceleration in active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 335, 26–32 (1998)
L.S. Shepherd, P.A. Cassak, Comparison of Secondary Islands in collisional reconnection to hall reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(1), 015004 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.015004
K. Shibata, S. Tanuma, Plasmoid-induced-reconnection and fractal reconnection. Earth Planets Space 53, 473–482 (2001)
A. Spitkovsky, Pulsar magnetosphere: the incredible machine, in 40 Years of Pulsars: Millisecond Pulsars, Magnetars and More, ed. by C. Bassa, Z. Wang, A. Cumming, V.M. Kaspi. American Institute of Physics Conference Series, vol. 983 (2008), pp. 20–28 doi:10.1063/1.2900143
H.C. Spruit, F. Daigne, G. Drenkhahn, Large scale magnetic fields and their dissipation in GRB fireballs. Astron. Astrophys. 369, 694–705 (2001). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010131
R.S. Steinolfson, G. van Hoven, Radiative tearing - magnetic reconnection on a fast thermal-instability time scale. Astrophys. J. 276, 391–398 (1984). doi:10.1086/161623
P.A. Sweet, The neutral point theory of solar flares, in Electromagnetic Phenomena in Cosmical Physics, ed. by B. Lehnert. IAU Symposium, vol. 6 (1958), p. 123
C. Thompson, A model of gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 270, 480 (1994)
C. Thompson, R.C. Duncan, The soft gamma repeaters as very strongly magnetized neutron stars - I. Radiative mechanism for outbursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 275, 255–300 (1995)
C. Thompson, R.C. Duncan, The giant flare of 1998 August 27 from SGR 1900+14. II. Radiative mechanism and physical constraints on the source. Astrophys. J. 561, 980–1005 (2001). doi:10.1086/323256
C. Thompson, M. Lyutikov, S.R. Kulkarni, Electrodynamics of magnetars: implications for the persistent X-ray emission and spin-down of the soft gamma repeaters and anomalous X-ray pulsars. Astrophys. J. 574, 332–355 (2002). doi:10.1086/340586
C.A. Tout, J.E. Pringle, Can a disc dynamo generate large-scale magnetic fields? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 281, 219–225 (1996)
M. Umizaki, S. Shibata, Method of the particle-in-cell simulation for the Y-point in the pulsar magnetosphere. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 62, 131 (2010)
D.A. Uzdensky, Partial field opening and current sheet formation in the disk magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 572, 432–444 (2002). doi:10.1086/340308
D.A. Uzdensky, Magnetic interaction between stars and accretion disks. Astrophys. Space Sci. 292, 573–585 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:ASTR.0000045064.93078.87
D.A. Uzdensky, Magnetic Reconnection in Astrophysical Systems (2006)
D.A. Uzdensky, The fast collisionless reconnection condition and the self-organization of solar coronal heating. Astrophys. J. 671, 2139–2153 (2007). doi:10.1086/522915
D.A. Uzdensky, Magnetic reconnection of super-strong magnetic fields in magnetar magnetospheres. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 53, 4-3200843 (2008)
D.A. Uzdensky, J. Goodman, Statistical description of a magnetized corona above a turbulent accretion disk. Astrophys. J. 682, 608–629 (2008). doi:10.1086/588812
D.A. Uzdensky, A.I. MacFadyen, Stellar explosions by magnetic towers. Astrophys. J. 647, 1192–1212 (2006). doi:10.1086/505621
D.A. Uzdensky, A.I. MacFadyen, Magnetar-driven magnetic tower as a model for gamma-ray bursts and asymmetric supernovae. Astrophys. J. 669, 546–560 (2007a). doi:10.1086/521322
D.A. Uzdensky, A.I. MacFadyen, Magnetically dominated jets inside collapsing stars as a model for gamma-ray bursts and supernova explosions. Phys. Plasmas 14(5), 056506 (2007b). doi:10.1063/1.2721969
D.A. Uzdensky, J.C. McKinney, Magnetic reconnection with radiative cooling. I. Optically-thin regime. Phys. Plasmas (2010, submitted). arXiv:1007.0774 [astro-ph]
D.A. Uzdensky, A. Königl, C. Litwin, Magnetically linked star-disk systems. I. Force-free magnetospheres and effects of disk resistivity. Astrophys. J. 565, 1191–1204 (2002a). doi:10.1086/324720
D.A. Uzdensky, A. Königl, C. Litwin, Magnetically linked star-disk systems. II. Effects of plasma inertia and reconnection in the magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 565, 1205–1215 (2002b). doi:10.1086/324724
D.A. Uzdensky, N.F. Loureiro, A.A. Schekochihin, Fast magnetic reconnection in the plasmoid-dominated regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(23), 235002 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.235002
A.A. van Ballegooijen, Energy release in stellar magnetospheres. Space Sci. Rev. 68, 299–307 (1994). doi:10.1007/BF00749156
M.H.P.M. van Putten, A. Levinson, Theory and astrophysical consequences of a magnetized torus around a rapidly rotating black hole. Astrophys. J. 584, 937–953 (2003). doi:10.1086/345900
M.H.P.M. van Putten, E.C. Ostriker, Hyper- and suspended-accretion states of rotating black holes and the durations of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 552, 31–34 (2001). doi:10.1086/320253
N. Vlahakis, A. Königl, Magnetohydrodynamics of gamma-ray burst outflows. Astrophys. J. Lett. 563, 129–132 (2001). doi:10.1086/338652
B. Warner, P.A. Woudt, Dwarf nova oscillations and quasi-periodic oscillations in cataclysmic variables - II. A low-inertia magnetic accretor model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 335, 84–98 (2002). doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05596.x
N. Watanabe, T. Yokoyama, Two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic simulations of relativistic magnetic reconnection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 647, 123–126 (2006). doi:10.1086/507520
P.M. Woods, C. Thompson, in Soft Gamma Repeaters and Anomalous X-ray Pulsars: Magnetar Candidates, ed. by W.H.G. Lewin, M. van der Klis (2006), pp. 547–586
S.E. Woosley, Gamma-ray bursts from stellar mass accretion disks around black holes. Astrophys. J. 405, 273–277 (1993). doi:10.1086/172359
M. Yamada, R. Kulsrud, H. Ji, Magnetic reconnection. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 603–664 (2010). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.82.603
M. Yamada, Y. Ren, H. Ji, J. Breslau, S. Gerhardt, R. Kulsrud, A. Kuritsyn, Experimental study of two-fluid effects on magnetic reconnection in a laboratory plasma with variable collisionality. Phys. Plasmas 13, 2119 (2006). doi:10.1063/1.2203950
S. Zenitani, M. Hoshino, The generation of nonthermal particles in the relativistic magnetic reconnection of pair plasmas. Astrophys. J. Lett. 562, 63–66 (2001). doi:10.1086/337972
S. Zenitani, M. Hoshino, Three-dimensional evolution of a relativistic current sheet: triggering of magnetic reconnection by the guide field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(9), 095001 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.095001
S. Zenitani, M. Hoshino, Particle acceleration and magnetic dissipation in relativistic current sheet of pair plasmas. Astrophys. J. 670, 702–726 (2007). doi:10.1086/522226
S. Zenitani, M. Hoshino, The role of the guide field in relativistic pair plasma reconnection. Astrophys. J. 677, 530–544 (2008). doi:10.1086/528708
S. Zenitani, M. Hesse, A. Klimas, Two-fluid magnetohydrodynamic simulations of relativistic magnetic reconnection. Astrophys. J. 696, 1385–1401 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/696/2/1385
E.G. Zweibel, Magnetic reconnection in partially ionized gases. Astrophys. J. 340, 550–557 (1989). doi:10.1086/167416
E.G. Zweibel, M. Yamada, Magnetic reconnection in astrophysical and laboratory plasmas. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 47, 291–332 (2009). doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-082708-101726
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzdensky, D.A. Magnetic Reconnection in Extreme Astrophysical Environments. Space Sci Rev 160, 45–71 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9744-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9744-5