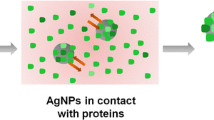
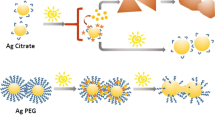
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are frequently coated with a variety of polymers, which may affect various interdependent mechanisms of toxicity or antimicrobial action, including agglomeration and dissolution rates. Here, we systematically measure how citrate, dextran, 5 and 20 kDa poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) coatings affect AgNP agglomeration, dissolution, and toxicity. In addition, to disentangle the coatings’ effects on agglomeration from their other effects, we produce multiple stable agglomerate sizes of several of the coated ~23 nm AgNPs ranging from singly-dispersed to mean agglomerate sizes of several hundred nanometers. These dispersions allow us to independently study the effects of agglomeration and polymer coating on dissolution rate and hemolytic toxicity. We find that both hemolytic toxicity and dissolution rate are highest for the 5 kDa PEG coating, and toxicity and dissolution rate decrease significantly with increasing agglomerate size independent of coating. This correlation between toxicity and dissolution rate suggests that both polymer coating and agglomeration may affect hemolytic toxicity largely through their effects on dissolution. Because both the AgNP dissolution rate and hemolysis decrease only moderately compared to the large increases in agglomerate size, AgNPs’ hemolytic toxicity may be caused by their large surface area and consequently high dissolution rate, rather than from other size-specific effects. At the silver concentrations used in this work, silver dissolved from AgNPs is expected to be primarily in the form of AgCl NPs, which are therefore more likely than Ag+ ions to be the primary drivers of hemolytic toxicity. In addition, all AgNPs we tested are much more toxic to horse red blood cells than sheep red blood cells, highlighting the complexity of toxic responses and the need to test toxicity in multiple biological systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao YWC, Jin RC, Mirkin CA (2002) Nanoparticles with Raman spectroscopic fingerprints for DNA and RNA detection. Science 297(5586):1536–1540
Cheng YW, Yin LY, Lin SH, Wiesner M, Bernhardt E, Liu J (2011) Toxicity reduction of polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles by sunlight. J Phys Chem C 115(11):4425–4432. doi:10.1021/jp109789j
Dobrovoiskaia MA, Clogston JD, Neun BW, Hall JB, Patri AK, McNeil SE (2008) Method for analysis of nanoparticle hemolytic properties in vitro. Nano Lett 8(8):2180–2187. doi:10.1021/nl0805615
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277(5329):1078–1081
Farkas J, Christian P, Gallego-Urrea JA, Roos N, Hassellov M, Tollefsen KE, Thomas KV (2011) Uptake and effects of manufactured silver nanoparticles in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gill cells. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):117–125. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.09.010
Guide (1993) Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement, 1st edn. ISO, Switzerland
Jiang JK, Oberdorster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanopart Res 11(1):77–89. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9446-4
Liu JY, Sonshine DA, Shervani S, Hurt RH (2010) Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano 4(11):6903–6913. doi:10.1021/nn102272n
MacCuspie R (2011) Colloidal stability of silver nanoparticles in biologically relevant conditions. J Nanopart Res 13(7):2893–2908. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0178-x
Murdock RC, Braydich-Stolle L, Schrand AM, Schlager JJ, Hussain SM (2008) Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to In vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicol Sci 101(2):239–253. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm240
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8959–8964. doi:10.1021/es801785m
Qureshi AT, Monroe WT, Lopez MJ, Janes ME, Dasa V, Park S, Amirsadeghi A, Hayes DJ (2011) Biocompatible/bioabsorbable silver nanocomposite coatings. J Appl Polym Sci 120(5):3042–3053. doi:10.1002/app.33481
Roca M, Haes AJ (2008) Probing cells with noble metal nanoparticle aggregates. Nanomedicine 3(4):555–565. doi:10.2217/17435889.3.4.555
Ruden S, Hilpert K, Berditsch M, Wadhwani P, Ulrich AS (2009) Synergistic interaction between silver nanoparticles and membrane-permeabilizing antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(8):3538–3540. doi:10.1128/aac.01106-08
Sharma VK (2009) Aggregation and toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in aquatic environment-A Review. J Environ Sci Health A 44(14):1485–1495. doi:10.1080/10934520903263231
Sopjani M, Foller M, Haendeler J, Gotz F, Lang F (2009) Silver ion-induced suicidal erythrocyte death. J Appl Toxicol 29(6):531–536. doi:10.1002/jat.1438
Sotiriou GA, Pratsinis SE (2010) Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ Sci Technol 44(14):5649–5654. doi:10.1021/es101072s
Stebounova L, Guio E, Grassian V (2011) Silver nanoparticles in simulated biological media: a study of aggregation, sedimentation, and dissolution. J Nanopart Res 13(1):233–244. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0022-3
Weitz DA, Oliveria M (1984) Fractal structures formed by kinetic aggregation of aqueous gold colloids. Phys Rev Lett 52(16):1433–1436
Yeo MK, Yoon JW (2009) Comparison of the effects of nano-silver antibacterial coatings and silver ions on zebrafish embryogenesis. Mole Cell Toxicol 5(1):23–31
Zhang W, Yao Y, Sullivan N, Chen Y (2011) Modeling the primary size effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles on their ion release kinetics. Environ Sci Technol 45(10):4422–4428. doi:10.1021/es104205a
Zook JM, Long SE, Cleveland D, Geronimo CLA, Maccuspie RI (2011a) Measuring silver nanoparticle dissolution in complex biological and environmental matrices using UV-Visible absorbance. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(6):1993–2002
Zook JM, Maccuspie RI, Locascio LE, Halter MD, Elliott JT (2011b) Stable nanoparticle aggregates/agglomerates of different sizes and the effect of their size on hemolytic cytotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 5(4):517–530. doi:10.3109/17435390.2010.536615
Zook JM, Rastogi V, Maccuspie RI, Keene AM, Fagan J (2011c) Measuring agglomerate size distribution and dependence of localized surface plasmon resonance absorbance on gold nanoparticle agglomerate size using analytical ultracentrifugation. ACS Nano 5(10):8070–8079. doi:10.1021/nn202645b
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Robert MacCuspie and Carly Lay Geronimo for preparing the AgNPs with different polymer coatings. JMZ was funded by an NRC postdoctoral research fellowship, and MDH was funded by an NSF Summer Undergraduate Research Fellowship at NIST. Certain commercial equipment, instruments, or materials are identified in this report to specify adequately the experimental procedure. Such identification does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, nor does it imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zook, J.M., Halter, M.D., Cleveland, D. et al. Disentangling the effects of polymer coatings on silver nanoparticle agglomeration, dissolution, and toxicity to determine mechanisms of nanotoxicity. J Nanopart Res 14, 1165 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1165-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1165-1