Abstract
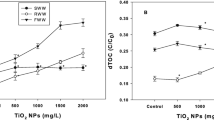
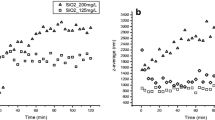
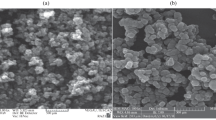
Flocculation using titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) as a coagulant is an efficient and economical application because the flocculated sludge can be recycled to produce a valuable byproduct, namely titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles. However, toxicity of TiCl4 has not yet been assessed while it is used in water treatment. The aquatic toxicity of TiCl4 flocculation process was investigated to assess the environmental safety of the coagulant. D. magna and V. fischeri bioassays were carried out to evaluate the supernatant toxicity after TiCl4 flocculation. Artificial wastewater, biologically treated sewage effluent, and seawater were used to study the toxicity of TiCl4 flocculation. Results showed that supernatant toxicity was very low when TiCl4 flocculation was conducted (no observed effect concentration = 100 mg/L and lowest observed effect concentration = 150 mg/L exposed to D. magna and V. fischeri, respectively). Similarly, TiO2 nanoparticles recovered from wastewater and seawater flocculated sludge were also found to have low toxicity. The regenerated TiO2 nanoparticles indicated low toxicity values when compared to the commercial-TiO2 nanoparticle, P-25.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM International (2002) Standard test method for assessing the microbial detoxification of chemically contaminated water and soil using a toxicity test with a luminescent marine bacterium. Document number: ASTM D5660-96. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Bozzi A, Dhananjeyan M, Guasaquillo I, Parra S, Pulgarin C, Weins C, Kiwi J (2004) Evolution of toxicity during melamine photocatalysis with TiO2 suspensions. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 162(1):179–185. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00352-6
DeWolfe J, Dempsey B, Taylor M, Potter JW (2003) Guidance manual for coagulant changeover. American Water Works Association Press, Denver
Gellert G (2000) Sensitivity and significance of luminescent bacteria in chronic toxicity testing based on growth and bioluminescence. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:87–91. doi:10.1006/eesa.1999.1849
Jennings VLK, Rayner-Brandes MH, Bird DJ (2001) Assessing chemical toxicity with the bioluminescent photo-bacterium (Vibrio fischeri): a comparison of three commercial systems. Water Res 14:3448–3456. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00067-7
Johnson DW, Haley MV, Hart GS, Muse WT, Landis WG (1986) Acute tocixity of brass particles to Daphnia magna. J Appl Toxicol 6(3):225–228. doi:10.1002/jat.2550060313
Kapias T, Griffiths RF (2005) Accidental releases of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) in the context of major hazards—spill behaviour using REACTPOOL. J Hazard Mater 119(1–3):41–52. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.12.001
Lee KP, Kelly DP, Schneide PW (1986) Inhalation toxicity study on rats exposed to titanium tetrachloride atmospheric hydrolysis products for two years. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 83(1):30–45. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(86)90320-0
Lewis RJ (1996) Sax’s dangerous properties of industrial materials, 9th edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Lokshin EP, Belikov ML (2003) Water purification with titanium compounds to remove fluoride ions. Russ J Appl Chem 76(9):1466–1471. doi:10.1023/B:RJAC.0000012668.42038.40
Lovern SB, Klaper R (2006) Daphnia magna mortality when exposed to titanium dioxide and fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(4):1132–1137. doi:10.1897/05-278R.1
Schaefer M, Scott-Fordsmand J (2006) Nanoparticles: does size matters? In: 16th annual meeting of SETAC Europe, The Hague, Netherlands, 7 to 11 May 2006, p. 222, Meeting, Lille (France), 22 May 2005/26 May 2005
Seo GT, Ohgaki S, Suzuki Y (1997) Sorption characteristics of biological powdered activated carbon in BPAC-MF (biological activated carbon-microfiltration) system for refractory organic removal. Water Sci Technol 35(7):163–170. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00127-3
Shon HK, Vigneswaran S, Ngo HH (2005) Is semi-flocculation effective to ultrafiltration? Water Res 39(1):147–153. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.09.003
Shon HK, Vigneswaran S, Kim IS, Cho J, Kim GJ, Kim J-B, Kim J-H (2007) Preparation of functional titanium oxide (TiO2) from sludge produced by titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) flocculation of wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 41(4):1372–1377. doi:10.1021/es062062g
Suryanarayana C (1995) Nanocrystalline materials. Int Mater Rev 40:41–64
Upton WV, Buswell AM (1937) Titanium salts in water purification. Ind Eng Chem (August):870–871. doi:10.1021/ie50332a006
USEPA (1993) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. Cinciniti, EPA/600/4-90/027F
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by UTS, ARC, Center for Seawater Desalination Plant (SeaHERO), Korea Research Foundation (KRF-2007-412-J02002), and NRL (NOM Ecology lab: ROA-2007-000-20055-0) grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.C., Kim, S., Shon, H.K. et al. Aquatic toxicity evaluation of TiO2 nanoparticle produced from sludge of TiCl4 flocculation of wastewater and seawater. J Nanopart Res 11, 2087–2096 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9574-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9574-x