Abstract
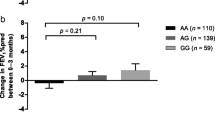
Variants of glucocorticoid induced transcript 1 (GLCCI1) result decreased response to inhaled corticosteroids, while intronic variant of low-affinity IgE receptor (FCER2) is associated with exacerbation rates in children with asthma. We examined the ethnic differences, allele and genotype frequencies of two linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs37972, rs37973) of GLCCI1 and rs28364072 intronic variant of FCER2 gene in average Roma and Hungarian population. A study population of 474 healthy Roma and 397 Hungarian subjects were characterized for GLCCI1 and FCER2 polymorphisms using real time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism method. The rs37972 and rs37973 polymorphisms in GLCCI1 were found in 100 % linkage disequilibrium both in Romas and in Hungarians. We found significant differences between the two groups regarding both minor allele frequencies (54.5 vs. 43.8 %, p ≤ 0.01) and homozygous genotype (31.6 vs. 21.3 %, p ≤ 0.01) of GLCCI1. For FCER2 rs28364072 the homozygous variant genotype was present in 2.8 % in Romas, while in Hungarians it was 5.8 % (p = 0.032). The opposite changes of these two polymorphisms strongly suggest that contrary current belief analyses of GLCCI1 variants are insufficient for personalised glucocorticoid therapies in different populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukherjee AB, Zhang Z (2011) Allergic asthma: influence of genetic and environmental factors. J Biol Chem 286(38):32883–32889. doi:10.1074/jbc.R110.197046
Pascual RM, Bleecker ER (2010) Pharmacogenetics of asthma. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10(3):226–235. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2010.05.013
Drazen JM, Silverman EK, Lee TH (2000) Heterogeneity of therapeutic responses in asthma. Br Med Bull 56(4):1054–1070
Kazani S, Wechsler ME, Israel E (2010) The role of pharmacogenomics in improving the management of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125 (2):295–302; quiz 303-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.12.014
Tantisira KG, Lasky-Su J, Harada M, Murphy A, Litonjua AA, Himes BE, Lange C, Lazarus R, Sylvia J, Klanderman B, Duan QL, Qiu W, Hirota T, Martinez FD, Mauger D, Sorkness C, Szefler S, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF Jr, Peters SP, Lima JJ, Nakamura Y, Tamari M, Weiss ST (2011) Genomewide association between GLCCI1 and response to glucocorticoid therapy in asthma. N Engl J Med 365(13):1173–1183. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911353
Cheong HI, Kang HG, Schlondorff J (2012) GLCCI1 single nucleotide polymorphisms in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 27(9):1595–1599. doi:10.1007/s00467-012-2197-6
Maitland-van der Zee AH, Raaijmakers JA (2012) Variation at GLCCI1 and FCER2: one step closer to personalized asthma treatment. Pharmacogenomics 13(3):243–245. doi:10.2217/pgs.11.177
Acharya M, Borland G, Edkins AL, Maclellan LM, Matheson J, Ozanne BW, Cushley W (2010) CD23/FcepsilonRII: molecular multi-tasking. Clin Exp Immunol 162(1):12–23. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04210.x
Okun E, Mattson MP, Arumugam TV (2010) Involvement of Fc receptors in disorders of the central nervous system. Neuromolecular Med 12(2):164–178. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8099-5
Stone KD, Prussin C, Metcalfe DD (2010) IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(2 Suppl 2):S73–S80. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.017
Rosenwasser LJ, Meng J, Chan MA, Gigliotti NM, May BE (2011) The role of CD23 in IgE dependent signaling: implications from pharmacogenetics. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 122:27–33
Vercelli D, Jabara HH, Lee BW, Woodland N, Geha RS, Leung DY (1988) Human recombinant interleukin 4 induces Fc epsilon R2/CD23 on normal human monocytes. J Exp Med 167(4):1406–1416
Tse SM, Tantisira K, Weiss ST (2010) The pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of asthma therapy. Pharmacogenomics J 11(6):383–392. doi:10.1038/tpj.2011.46
Tantisira KG, Silverman ES, Mariani TJ, Xu J, Richter BG, Klanderman BJ, Litonjua AA, Lazarus R, Rosenwasser LJ, Fuhlbrigge AL, Weiss ST (2007) FCER2: a pharmacogenetic basis for severe exacerbations in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120(6):1285–1291. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.09.005
Morar B, Gresham D, Angelicheva D, Tournev I, Gooding R, Guergueltcheva V, Schmidt C, Abicht A, Lochmuller H, Tordai A, Kalmar L, Nagy M, Karcagi V, Jeanpierre M, Herczegfalvi A, Beeson D, Venkataraman V, Warwick Carter K, Reeve J, de Pablo R, Kucinskas V, Kalaydjieva L (2004) Mutation history of the roma/gypsies. Am J Hum Genet 75(4):596–609. doi:10.1086/424759
Gresham D, Morar B, Underhill PA, Passarino G, Lin AA, Wise C, Angelicheva D, Calafell F, Oefner PJ, Shen P, Tournev I, de Pablo R, Kucinskas V, Perez-Lezaun A, Marushiakova E, Popov V, Kalaydjieva L (2001) Origins and divergence of the Roma (gypsies). Am J Hum Genet 69(6):1314–1331. doi:10.1086/324681
Kalaydjieva L, Gresham D, Calafell F (2001) Genetic studies of the Roma (Gypsies): a review. BMC Med Genet 2:5
Zeman CL, Depken DE, Senchina DS (2003) Roma health issues: a review of the literature and discussion. Ethn Health 8(3):223–249. doi:10.1080/1355785032000136434
Muscat M (2011) Who gets measles in Europe? J Infect Dis 204(Suppl 1):S353–S365. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir067
Masseria C, Mladovsky P, Hernandez-Quevedo C (2010) The socio-economic determinants of the health status of Roma in comparison with non-Roma in Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania. Eur J Public Health 20(5):549–554. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckq102
http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Variation/Population?db=core;r=19:7754785-7755785;v=rs28364072;vdb=variation;vf=100595325 http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Variation/Population?db=core;r=19:7754785-7755785;v=rs28364072;vdb=variation;vf=100595325
http://alfred.med.yale.edu/alfred/SiteTable1A_working.asp?siteuid=SI391198F http://alfred.med.yale.edu/alfred/SiteTable1A_working.asp?siteuid=SI391198F
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of the Hungarian Science Foundation OTKA K103983.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szalai, R., Matyas, P., Varszegi, D. et al. Admixture of beneficial and unfavourable variants of GLCCI1 and FCER2 in Roma samples can implicate different clinical response to corticosteroids. Mol Biol Rep 41, 7665–7669 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3659-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3659-7