Abstract
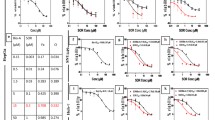
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of bufalin on the anti-proliferative activity of sorafenib in the human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines PLC/PRF/5 and Hep G-2 and to determine the relevant molecular mechanism. Concurrent treatment with sorafenib and bufalin at a fixed ratio (25:1) for 48 h resulted in synergistic growth inhibition in HCC cell lines as determined by CCK-8 cell viability assays. Exposure of both PLC/PRF/5 and Hep G-2 cells to this combination of sorafenib (6.25 μM) and bufalin (50 nM) resulted in noticeable increases in apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by the disruption of mitochondria, compared to treatment with either agent alone. Although both sorafenib (6.25 μM) and bufalin (250 nM) alone inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK, the reduction in pERK was more pronounced in the cells treated with a combination of bufalin (50 nM) and sorafenib (250 nM). Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of bufalin on pERK was blocked by the PI3kinase inhibitor LY294002, suggesting that the reduction in pERK induced by bufalin might be mediated by AKT in these two HCC cell lines. Taken together, the results of our study suggest that bufalin enhances the anti-cancer effects of sorafenib on PLC/PRF/5 and Hep G-2 by contributing to the downregulation of ERK.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM et al (2001) Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol 35:421–430
Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42:1208–1236
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362:1907–1917
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Zhao JD, Liu J, Ren ZG et al (2010) Maintenance of Sorafenib following combined therapy of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy/intensity-modulated radiation therapy and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase I/II study. Radiat Oncol 5:12–18
Shiratori O (1967) Growth inhibitory effect of cardiac glycosides and aglycones on neoplastic cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. Gann 58:521–528
Takai N, Ueda T, Nishida M et al (2008) Bufalin induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 21:637–643
Mijatovic T, Roland I, Van Quaquebeke E et al (2007) The alpha1 subunit of the sodium pump could represent a novel target to combat non-small cell lung cancers. J Pathol 212:170–179
Yeh JY, Huang WJ, Kan SF et al (2003) Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate 54:112–124
Newman RA, Kondo Y, Yokoyama T et al (2007) Autophagic cell death of human pancreatic tumor cells mediated by oleandrin, a lipid-soluble cardiac glycoside. Integr Cancer Ther 6:354–364
Yang Z, Luo H, Wang H et al (2008) Preparative isolation of bufalin and cinobufagin from Chinese traditional medicine ChanSu. J Chromatogr Sci 46:81–85
Chou TC (2010) Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 70:440–446
Ramos IB, Campos CB, Sorgine MH et al (2011) Calreticulin expression levels and endoplasmic reticulum during late oogenesis and early embryogenesis of Rhodnius prolixus Stahl. Mol Biol Rep 38(3):1757–1767. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0290-0
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN (2008) Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 48:2047–2063
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL et al (2006) Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:249–279
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P et al (2008) Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3129–3140
Zhang Z, Zhou X, Shen H et al (2009) Phosphorylated ERK is a potential predictor of sensitivity to sorafenib when treating hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence from an in vitro study. BMC Med 7:41
Dai R, Chen R, Li H (2009) Cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell cycle progression and cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 34:1749–1757
Rommel C, Clarke BA, Zimmermann S et al (1999) Differentiation stage-specific inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by Akt. Science 286:1738–1741
Sun L, Chen T, Wang X et al (2009) Bufalin induces reactive oxygen species dependent bax translocation and apoptosis in ASTC-a-1 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med doi:10.1093/ecam/nep082 (in press)
Li D, Qu X, Hou K et al (2009) PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 20:59–64
Dolado I, Nebreda AR (2008) AKT and oxidative stress team up to kill cancer cells. Cancer Cell 14:427–429
Nogueira V, Park Y, Chen CC et al (2008) Akt determines replicative senescence and oxidative or oncogenic premature senescence and sensitizes cells to oxidative apoptosis. Cancer Cell 14:458–470
Chen FS, Cui YZ, Luo RC et al (2008) Coadministration of sorafenib and cisplatin inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28:1684–1687
Wu J, Luo RC, Zhang H et al (2008) Inhibitory effect of sorafenib combined with arsenic trioxide on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28:639–641
Li N, Zhang Y, Wu T et al (2009) Schedule-dependent effects of sorafenib in combination with paclitaxel on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402. Ai Zheng 28:838–843
Wang Z, Zhou J, Fan J et al (2008) Effect of rapamycin alone and in combination with sorafenib in an orthotopic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14:5124–5130
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by NCI U19 grant (CA12150301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Li, HX., Xu, LT. et al. Bufalin enhances the anti-proliferative effect of sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of ERK. Mol Biol Rep 39, 1683–1689 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0908-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0908-x