Abstract
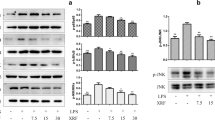
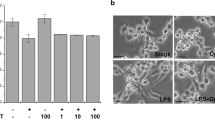
ACTG-toxin H (AH) originates from Alternaria sp. In this study, we explored the molecular mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory properties of AH. Treatment with AH inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced interleukin-6, IL-1β, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and cyclooxygenase-2 expression and nitric oxide production. Furthermore, AH inhibited LPS-induced P38 MAPK and Akt activation in RAW264.7 cells. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) showed that AH inhibited LPS-induced nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) DNA-binding activity. Using transfection assay and measurement of an NFκB-sensitive promoter region, we found that transfection of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) increased LPS-induced NFκB transcription activity in 293T cells. AH significantly blocked LPS-induced NFκB activation in TLR4-transfected cells. Taken together, our data indicated that anti-inflammatory properties of AH resulted from the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines and enzyme production via the TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiao LR, Yuan L, Gao JM, Zhao PJ, Kang QJ, Shen YM (2007) Tricycloalternarene derivatives produced by an endophyte Alternaria alternata isolated from Maytenus hookeri. J Basic Microbiol 47:340–343
Murakami A, Ohigashi H (2007) Targeting NOX INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. Int J Cancer 121:2357–2363
Payne CM, Bernstein C, Bernstein H, Gerner EW, Garewal H (1999) Reactive nitrogen species in colon carcinogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal 1:449–467
Park JY, Pillinger MH, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB (2006) Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: the role of PGE2 synthases. Clin Immunol 119:229–240
Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T (2004) Inhibition of IL-6 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:386–391
Kawai T, Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ 13:816–825
Carmody RJ, Chen YH (2007) Nuclear factor-κB: activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 4:31–41
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 11:443–451
Compton T, Kurt-Jones EA, Boehme KW, Belko J, Latz E, Goldenbock DT, Finberg RW (2003) Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and toll-like receptor 2. J Virol 77:4588–4596
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2004) Toll-like receptors: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Microbes Infect 6:1382–1387
Brown KL, Cosseau CL, Gardy JL, Hancock REW (2007) Complexities of targeting innate immunity to treat infection. Trends Immunol 28:6–206
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151
Kaminska B (2005) MAPK signaling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta 1754:253–262
Shao DZ, Lin M (2008) Platonin inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappa B by preventing activation of Akt and IKK-beta in human PBMC. Inflamm Res 57:601–606
Yang XY, Du L, Tang XL, Jung SY, Zheng B, Soh BY (2009) Brevicompanine E reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines and enzymes in microglia by inhibiting activation of activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-κB. J Neuroimmunol 216:32–38
Hoffmann A, Natoli G, Ghosh G (2006) Transcriptional regulation via the NFκB signaling module. Oncogene 25:6706–6716
Billack B (2006) Macrophage activation: role of toll-like receptors, nitric oxide, and nuclear factor kappa B. Am J Pharm Educ 70:102
Hobbs AJ, Higgs A, Moncada S (1999) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase as a potential therapeutic target. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:191–220
Anderson GD, Hauser SD, McGarity KL, Bremer ME, Isakson PC, Gregory SA (1996) Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 reverses inflammation and expression of COX-2 and interleukin 6 in rat adjuvant arthritis. J Clin Invest 97:2672–2679
Willoughby DA, Moore AR, Colville-Nash PR (2000) COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 and the future treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Lancet 355:646–648
Turini ME, DuBois RN (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2: a therapeutic target. Annu Rev Med 53:35–57
Palin K, Verrier D, Tridon V, Hurst J, Perry VH, Dantzer R, Lestage J (2004) Influence of the course of brain inflammation on the endogenous IL-1beta/IL-1Ra balance in the model of brain delayed-type hypersensitivity response to bacillus Calmette–Guérin in Lewis rats. J Neuroimmunol 149:22–30
Liang B, Song Z, Wu B, Gardner D, Shealy D, Song XY, Wooley PH (2009) Evaluation of anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody therapy using murine type II collagen-induced arthritis. J Inflamm 6:10
Novotny NM, Markel TA, Crisostomo PR, Meldrum DR (2008) Differential IL-6 and VEGF secretion in adult and neonatal mesenchymal stem cells: role of NFκB. Cytokine 43:215–219
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ (1994) A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 265:808–811
Nick JA, Avdi NJ, Gerwins P, Johnson GL, Worthen GS (1996) Activation of a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in human neutrophils by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 156:4867–4875
Rafi MM, Yadav PN, Rossi AO (2007) Glucosamine inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in mouse macrophage cells (RAW264.7) by inhibition of p38-MAP kinase and transcription factor NF-kappa B. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:587–593
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401:82–85
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Public Welfare & Safety Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (20120006545); the Chinese National Natural Science Fund (30973627); and a grant from Shandong Province of China (No. ZR2009CZ016).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The authors Xinying Yang, Guojian Zhang, and Xuelian Tang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, G., Tang, X. et al. Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway is involved in ACTG-toxin H-mediated anti-inflammatory effect. Mol Cell Biochem 374, 29–36 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1502-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1502-9