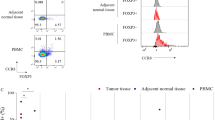
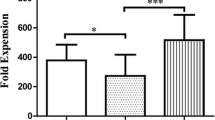
CD4 +CD25 + regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to inhibit cytotoxic lymphocytes-mediated immune responses. Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells exert high impact on adoptive immunotherapeutic approaches. Therefore, the purpose of this report was to determine the effect of Tregs on CIK cell growth and CIK-induced cytotoxicity for inhibition of tumor growth in vivo as well as in vitro. After depletion of CD4 +CD25 + cells before culture, the proliferation and cytotoxicity of CIK cells, which indicated in bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) assays, were significantly increased. Depletion of CD4 +CD25 + cells preculture also enhanced the suppression effect on the lung cancer cells inoculated in experimental animals. Blockage of glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) by antibodies partially abrogated the suppressive effect of CD4 +CD25 + cells on CIK. These results indicated that Tregs could inhibit the antitumor activity of CIK cells. The molecules TGF-β and GITR may contribute to the suppressive function of CD4 +CD25 + cells.











Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Sakaguchi S: Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 22:531–562, 2004
Antony PA, Piccirillo CA, Akpinarli A, et al.: CD8+ T cell immunity against a tumor/self-antigen is augmented by CD4+ T helper cells and hindered by naturally occurring T regulatory cells. J Immunol 174:2591–2601, 2005
Smyth MJ, Teng MW, Swann J, et al.: CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells suppress NK cell-mediated immunotherapy of cancer. J Immunol 176:1582–1587, 2006
Azuma T, Takahashi T, Kunisato A, et al.: Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress NKT cell functions. Cancer Res 63:4516–4520, 2003
Knutson KL, Dang Y, Lu H, et al.: IL-2 immunotoxin therapy modulates tumor-associated regulatory T cells and leads to lasting immune-mediated rejection of breast cancers in neu-transgenic mice. J Immunol 177:84–91, 2006
Taieb J, Chaput N, Schartz N, et al.: Chemoimmunotherapy of tumors: cyclophosphamide synergizes with exosome based vaccines. J Immunol 176:2722–2729, 2006
Leemhuis T, Wells S, Scheffold C, et al.: A phase I trial of autologous cytokine-induced killer cells for the treatment of relapsed Hodgkin disease and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 11:181–187, 2005
Zhang YS, Yuan FJ, Jia GF, et al.: CIK cells from patients with HCC possess strong cytotoxicity to multidrug-resistant cell line Bel-7402/R. World J Gastroenterol 11:3339–45, 2005
Ren X, Yu J, Liu H, et al.: Th1 bias in PBMC induced by multicycles of auto-CIKs infusion in malignant solid tumor patients. Cancer Biotherapy & Radiopharmaceuticals 2006; 21(1):22–33
Schmidt-Wolf IGH, Lefterova P, Mehta BA, et al.: Phenotypic characterization and identification effector cells involved in tumor cells recognition of cytokine-induced killer cells. Exp Haematol 21:1673–1679, 1993
Khazaie K, von Boehmer H: The impact of CD4+CD25+ Treg on tumor specific CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:124–136, 2006
Comes A, Rosso O, Orengo AM, et al.: CD25+ regulatory T cell depletion augments immunotherapy of micrometastases by an IL-21-secreting cellular vaccine. J Immunol 176:1750–1758, 2006
Chakraborty NG, Chattopadhyay S, Mehrotra S, et al.: Regulatory T-cell response and tumor vaccine-induced cytotoxic T lymphocytes in human melanoma. Hum Immunol 65:794–802, 2004
Kanamaru F, Youngnak P, Hashiguchi M, et al.: Costimulation via glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor in both conventional and CD25+ regulatory CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 172:7306–7314, 2004
Chen WJ, Wahl SM: TGF-b: the missing link in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell-mediated immunosuppression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:85–89, 2003
Marie JC, Letterio JJ, Gavin M, et al.: TGF-beta1 maintains suppressor function and Foxp3 expression in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 201(7):1061–1067, 2005
Birebent B, Lorho R, Lechartier H, et al.: Suppressive properties of human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells are dependent on CTLA-4 expression. Eur J Immunol 34:3485–3496, 2004
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Yan Fang, Department of Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine for providing help and assistance for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yu, JP., Cao, S. et al. CD4 +CD25 + Regulatory T Cells Decreased the Antitumor Activity of Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cells of Lung Cancer Patients. J Clin Immunol 27, 317–326 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9076-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9076-0