Abstract
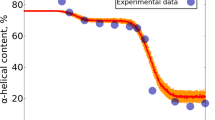
Phase transition of a protein globule is considered in the frameworks of (i) the generalized mean-field theory for the order parameter, characterizing the extent of the deviation of a protein three-dimensional structure from its native state and (ii) the network model that treats a protein globule as a small-world network with a significant percent of long-range links between amino acid residues. Temperature dependencies of the introduced order parameter are defined and phase-transition temperatures are found on the basis of the function defining the distribution of links’ numbers for protein residues. An important role of long-range links, promoting considerable rise of thermal protein stability, is demonstrated by the example of a correlation between protein melting temperature and a fraction of disulfide bonds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabási, A.L., Oltvai, Z.N.: Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 101–113 (2004)
Newman, M.E.J.: The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 5, 167–256 (2003)
Atilgan, C., Okan, O.B., Atilgan, A.R.: Network-based models as tools hinting at non-evident protein functionality. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 41, 205–225 (2012)
Miyazawa, S., Jernigan, R.L.: Residue–residue potentials with a favorable contact pair term and an unfavorable high packing density term, for simulation and threading. J. Mol. Biol. 256, 623–644 (1996)
Bagler, G., Sinha, S.: Assortative mixing in protein contact networks and protein folding kinetics. Bioinformatics 23, 1760–1767 (2007)
Atilgan, A.R., Akan, P., Baysal, C.: Small-world communication of residues and significance for protein dynamics. Biophys. J. 86, 85–91 (2004)
Vendruscolo, M., Dokholyan, N.V., Paci, E., Karplus, M.: Small-world view of the amino acids that play a key role in protein folding. Phys. Rev. 65, 061910 (2002)
Gaci, O., Balev, S.: Motif prediction in amino acid interaction networks, vol. l. In: Proc. World Congress on Eng. and Comp. Sci, San Francisco, USA (2009)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature (London) 393, 440–442 (1998)
Milgram, S.: The small-world problem. Psychol. Today 1, 61–67 (1967)
Jiao, X., Chang, S.: Scoring function based on weighted residue network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 8773–8786 (2011)
Plaxco, K.W., Simons, K.T., Baker, D.: Contact order, transition state placement and the refolding rates of single domain proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 277, 985–994 (1998)
Ivankov, D.N., Garbuzynskiy, S.O., Alm, E., Plaxco, K.W., Baker, D., Finkelstein, A.V.: Contact order revisited: influence of protein size on the folding rate. Protein Sci. 12, 2057–062 (2003)
Finkelstein, A.V., Ivankov, D.N., Garbuzynskiy, S.O., Galzitskaya, O.V.: Understanding the folding rates and folding nuclei of globular proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 8, 521–536 (2007)
Herrero, C.P.: Ising model in small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 65, 66110 (2002)
Grosberg, A.Y., Khokhlov, A.R.: Statistical Physics of Macromolecules. Springer (1994)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Statistical Physics. Butterworth-Heinemann (1980)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics. Wiley (2004)
Chandrasekhar, S.: Liquid Crystals. Cambridge Univ. Press (1994)
Birstein, T.M., Ptitsy, O.B.: Conformation of Macromolecules. Nauka, Moscow (in Russian) (1964)
Mallick, P., Boutz, D.R., Eisenberg, D., Yeates, T.O.: Genomic evidence that the intracellular proteins of archaeal microbes contain disulfide bonds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 96799684 (2002)
Jorda, J., Yeates, T.O.: Widespread disulfide bonding in proteins from thermophilic Archaea. Hindawi Publ. Corp, Archaea, vol. 2011, 9 p. Article ID 409156. doi:10.1155/2011/409156
Meilikhov, E.Z., Farzetdinova, R.M.: Generalized mean-field theory for Ising spins in small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 71, 046111 (2005)
Berman, H., Henrick, K., Nakamura, H.: Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 980 (2003)
Huang, J., Kawashima, S.I., Kanehisa, M.: New amino acid indices based on residue network topology. Gen. Inf. 18, 152–161 (2007)
Romero, P., Obradovic, Z., Kissinger, C., Villafrance, J.E., Dunker, A.K.: Identifying disordered regions in proteins from amino acid sequence. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 91–95 (1997)
Scopes, R.K.: Protein Purification: Principles and Practice, 3rd edn., pp. 98–100. Springer (1994)
Privalov, P.L., Dragan, A.I.: Microcalorimetry of biological macromolecules. Biophys. Chem. 126, 16–24 (2007)
Volkenshtein, M.V.: Biophysics. Mir, Moscow (1983)
Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry, 2nd edn. Klabunde, K.J., Richards, R.M. (eds.). Wiley (2009)
Zhou, Y., Vitkup, D., Karplus, M.: Native proteins are surface-molten solids: application of the Lindemann criterion for the solid versus liquid state. J. Mol. Biol. 285, 1371–1375 (1999)
Privalov, P.L.: Stability of proteins. Proteins which do not present a single cooperative system. Adv. Protein Chem. 35, 1–104 (1982)
Lopes, J.V., Pogorelov, Y.G., Lopes dos Santos, J.B.M., Toral, R.: Exact solution of Ising model on a small-world network. Phys. Rev. E 70, 026112 (2004)
Peierls, R.: On Ising model of ferro magnetis. Proc. Camb. Philol. Soc. 32, 477–481 (1936)
Grifths, R.B.: Peierls proof of spontaneous magnetization in a two-dimensional Ising ferromagnet. Phys. Rev. 136, A437–A439 (1964)
Meilikhov, E.Z., Farzetdinova, R.M.: Curie temperature for small-world Ising systems of different dimensions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 300, 254–256 (2006)
Birgelson, J.D., Wolynes, P.G.: Spin glasses and the statistical mechanics of protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 84, 7524–7528 (1987)
Birgelson, J.D., Wolynes, P.G.: Intermediates and barrier crossing in random energy model with application to protein folding. J. Phys. Chem. 93, 6902–6915 (1989)
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported by Grants ## 12-02-00550, 11-02-00363a of the Russian Foundation of Basic Researches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meilikhov, E.Z., Farzetdinova, R.M. Network model of a protein globule. J Biol Phys 39, 673–685 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-013-9326-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-013-9326-8