Abstract
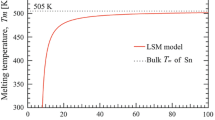
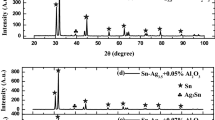
The Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu (wt%) lead-free solder alloy is considered to be one of the most promising alternatives to replace the traditionally used Sn–Pb solders. This alloy composition possesses, however, some weaknesses, mainly as a result of its higher melting temperature compared to the eutectic Sn–Pb solders. Nanoparticles of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy nanoparticles were prepared by chemical reduction with NaBH4 as a reducing agent at room temperature. The melting temperature of the synthesized Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu alloy nanoparticles was determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The results showed that the calorimetric onset melting temperature of the Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu alloy nanoparticles could be as low as 200 °C, which was about 17 °C lower than that of the bulk alloy (217 °C). The field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the as-prepared nanoparticles indicated that the major particle size of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu nanoparticles is smaller than 50 nm. The structure and morphology of the nanoparticles were analyzed with high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The Ag3Sn and Sn phase were observed in the HRTEM images, which was in good agreement with the XRD results. These low melting temperature Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu alloy nanoparticles show a potential to manufacture high quality lead-free solders for electronic products.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abtew, G. Selvaduray, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 27, 95 (2000)
C.M.L. Wu, D.Q. Yu, C.M.T. Law et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. R 44, 1 (2004)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 49, 1 (2005)
I. Ohnuma, M. Miyashita, K. Anzai et al., J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1137 (2000)
R. Kinyanjui, L.P. Lehman, L. Zavalij et al., J. Mater. Res. 20, 2914 (2005)
S. Park, R. Dhakal, L. Lehman et al., Acta Mater. 55, 3253 (2007)
S. Mallik, N.N. Ekere, R. Durairaj et al., Mater. Design 30, 4502 (2009)
Q.S. Mei, K. Lu, Prog. Mater. Sci. 52, 1175 (2007)
M. Takagi, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 9, 359 (1954)
T. Bachels, H.-J. Gutherodt, R. Schaer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1250 (2000)
M. Quaas, I. Shyjumon, R. Hippler, et al., Z. Kristallogr. Suppl 26, 267 (2007)
L. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Bian et al., Phys. Lett. A 310, 197 (2003)
J. Sun, S.L. Simon, Thermochim. Acta 463, 32 (2007)
M. Dippel, A. Maier, V. Gimple et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 095505 (2001)
K.F. Peters, J.B. Cohen, Y.-W. Chung, Phys. Rev. B 57, 13430 (1998)
P. Buffat, J.P. Borel, Phys. Rev. A 13, 2287 (1976)
Y. Wang, S. Teitel, C. Dellago, Chem. Phys. Lett. 394, 257 (2004)
E. Haro-Poniatowski, M. Jimenez De Castro, J. M. Fernandez Navarro, et al., Nanotechnology 18 (2007)
E.A. Olson, M.Y. Efremov, M. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys. 97, 034304 (2005)
C.R.M. Wronski, Br. J. Appl. Phys. 18, 1731 (1967)
G.L. Allen, R.A. Bayles, W.W. Gile et al., Thin Solid Films 144, 297 (1986)
F.P. Kevin, C. Yip-Wah, B.C. Jerome, Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 2391 (1997)
S.L. Lai, G. Ramanath, L.H. Allen et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 1229 (1995)
S.L. Lai, J.Y. Guo, V. Petrova et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 99 (1996)
H.W. Sheng, K. Lu, E. Ma, Acta Mater. 46, 5195 (1998)
H. Jiang, K.-S. Moon, H. Dong et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 429, 492 (2006)
G. Manai, F. Delogu, Physica B 392, 288 (2007)
E. Haro-Poniatowski, R. Serna, C.N. Afonso et al., Thin Solid Films 453–454, 467 (2004)
W.A. Jesser, G.J. Shiflet, G.L. Allen et al., Mater. Res. Innov. 2, 211 (1999)
C. Schamp, W. Jesser, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1825 (2006)
W.A. Jesser, R.Z. Shneck, W.W. Gile, Phys. Rev. B 69, 144121 (2004)
H. Jiang, K.S. Moon, F. Hua et al., Chem. Mater. 19, 4482 (2007)
H. Jiang, K.-S. Moon and C.P. Wong, in Electronic Components and Technology Conference, ECTC 08 (Florida, USA, 2008) p. 1400
L.Y. Hsiao, J.G. Duh, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, J105 (2005)
Y. Gao, C. Zou, B. Yang et al., J. Alloys Compd. 484, 777 (2009)
P.R. Couchman, W.A. Jesser, Nature 269, 481 (1977)
Q. Jiang, S. Zhang, M. Zhao, Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 225 (2003)
W.H. Qi, M.P. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 88, 280 (2004)
C. Zou, Y. Gao, B. Yang et al., T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 20, 248 (2010)
R. Fisker, J.M. Carstensen, M.F. Hansen et al., J. Nanopart. Res. 2, 267 (2000)
E. Muthuswamy, S. Ramadevi, H.N. Vasan et al., J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 561 (2007)
J. Muñoz, J. Cervantes, R. Esparza et al., J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 945 (2007)
A. Corrias, G. Ennas, G. Licheri et al., Chem. Mater. 2, 363 (1990)
D. Zeng, M.J. Hampden-Smith, Chem. Mater. 5, 681 (1993)
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant no. 08520740500) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 50971086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, C., Gao, Y., Yang, B. et al. Nanoparticles of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu alloy synthesized at room temperature with large melting temperature depression. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 2–7 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0376-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0376-z