Abstract
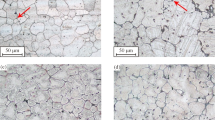
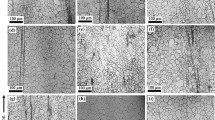
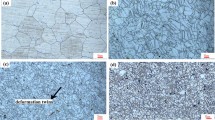
In this study, the effects of calcium (Ca) and yttrium (Y) on the microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion behaviour and biocompatibility of magnesium (Mg) alloys, i.e. Mg–xCa (x = 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0 and 20.0%, wt%, hereafter) and Mg–1Ca–1Y, were investigated. Optical microscopy, X-ray diffractometry (XRD), compressive and Vickers hardness testing were used for the characterisation and evaluation of the microstructure and mechanical properties. The in vitro cytotoxicity of the alloys was assessed using osteoblast-like SaOS2 cells. The corrosion behaviour of these alloys was evaluated by soaking the alloys in simulated body fluid (SBF) and modified minimum essential medium (MMEM) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Results indicated that the increase of the Ca content enhances the compressive strength, elastic modulus and hardness of the Mg–Ca alloys, but deteriorates the ductility, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of the Mg–Ca alloys. The Y addition leads to an increase in the ductility; but a decrease in the compressive strength, hardness, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of the Mg–1Ca–1Y alloy when compared to the Mg–1Ca alloy. Solutions of SBF and MMEM with the immersion of Mg–xCa and Mg–1Ca–1Y alloys show strong alkalisation. Our research results indicate that Mg–xCa alloys with Ca additions less than 1.0 wt% exhibited good biocompatibility, low corrosion rate as well as appropriate elastic modulus and strength; whilst the Y is not a proper element for Mg alloys for biomedical application due to its negative effects to the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G (2006) Biomaterials 27:1728
Witte F (2010) Acta Biomater 6:1680
Witte F, Hort N, Vogt C et al (2008) Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 12:63
Witte F, Ulrich H, Palm C, Willbold E (2007) J Biomed Mater Res 81(A):757
Witte F, Ulrich H, Rudert M, Willbold E (2007) J Biomed Mater Res 81(A):748
Hartwig A (2001) Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 475:113
Okuma T (2001) Nutrition 17:679
Saris N-EL, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, Khawaja JA, Lewenstam A (2000) Clin Chim Acta 294:1
Vormann J (2003) Mol Asp Med 24:27
Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H et al (2005) Biomaterials 26:3557
Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A et al (2002) J Biomed Mater Res A 62:175
Wen C, Guan S, Peng L, Ren C, Wang X, Hu Z (2009) Appl Surf Sci 255:6433
Wen CE, Mabuchi M, Yamada Y, Shimojima K, Chino Y, Asahina T (2001) Scr Mater 45:1147
Wen C, Yamada Y, Shimojima K, Chino Y, Hosokawa H, Mabuchi M (2003) Mater Sci Forum 419–422:1001
Currey JD (2006) Bones structure and mechanics. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Wang H, Shi ZM, Yang K (2008) Adv Mater Res 32:207
Wang XJ, Li YC, Hodgson PD, Wen CE (2007) Mater Forum 31:56
Li YC, Xiong JX, Wong CS, Hodgson PD, Wen CE (2009) Tissue Eng Part A 15:3151
Gibson LG, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Denkena B, Lucas A (2007) CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 56:113
Hassel T, Bach FW, Golovko A, Krause C (2006) In: Proceedings of the International Symposium Magnesium Technology Global Age, Montreal, QC, Canada, p 359
Liang H, Wan YZ, He F et al (2007) Appl Surf Sci 253:3326
Qiao L, Gao J, Wang Y, Wang S (2007) Mater Sci Forum 546–549:459
López HY, Cortés DA, Escobedo S, Mantovani D (2006) Key Eng Mater 309–311:453
Pietak A, Mahoney P, Dias George J, Staiger Mark P (2008) J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:407
Hänzi AC, Gerber I, Schinhammer M, Löffler JF, Uggowitzer PJ (2010) Acta Biomater 6:1824
Koch C, Scattergood R, Youssef K, Chan E, Zhu Y (2010) J Mater Sci 45:4725. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4252-7
Figueiredo R, Langdon T (2010) J Mater Sci 45:4827. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4589-y
Figueiredo R, Langdon T (2009) J Mater Sci 44:4758. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3725-z
Steinemann SG (1980) In: Winter GD, Leray JL, De Goot K (eds) Evaluation of biomaterials, advances in biomaterials. Wiley, Chichester
Okazaki Y, Rao S, Tateishi T, Ito Y (1998) Mater Sci Eng A 243:250
Denkena B, Witte F, Podolsky C, Lucas A (2005) In: Proceedings of the 5th euspen International Conference, Montpellier, France, p 233–236
Dabah E, Ben-Hamu G, Lisitsyn V, Eliezer D, Shin K (2010) J Mater Sci 45:3007. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4302-1
Aghion E, Levy G (2010) J Mater Sci 45:3096. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4317-7
Yao HB, Li Y, Wee ATS (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:4197
Miller PL, Shaw BA, Wendt RG, Moshier WC (1995) Corrosion 51:922
He W, Zhang E, Yang K (2010) Mater Sci Eng C 30:167
Nayab SN, Jones FH, Olsen I (2007) Biomaterials 28:38
ASTM-International (2004) G 31–72 ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Wang XJ, Li YC, Lin JG, Hodgson PD, Wen CE (2008) J Mater Res 23:1682
International organization for Standardization (1999) ISO 10993-5, ANSI/AAMI, Arlington, VA
Kruse PF, Patterson MK (1973) Tissue culture, methods and application. Academic Press, New York
Kim JH, Kang NE, Yim CD, Kim BK (2009) Mater Sci Eng A 525:18
Li SS, Tang B, Zeng DB (2007) J Alloy Compd 437:317
Li P, Tang B, Kandalova EG (2005) Mater Lett 59:671
Wang Q, Chen W, Zeng X et al (2001) J Mater Sci 36:3035. doi:10.1023/A:1017927109291
Watanabe H, Yamaguchi M, Takigawa Y, Higahshi K (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 454–455:384
Hakamada M, Shimizu K, Yamashita T, Watazu A, Saito N, Iwasaki H (2010) J Mater Sci 45:719. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3990-x
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this research through the Australia–India Strategic Research Fund (AISRF) BF030031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Hodgson, P.D. & Wen, C. The effects of calcium and yttrium additions on the microstructure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of biodegradable magnesium alloys. J Mater Sci 46, 365–371 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4843-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4843-3