Abstract
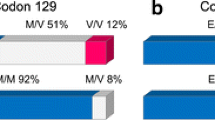
Since variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) was described for the first time in 1995 and fears of an epidemic ensued, the assumed culprit the prion protein (PrP) and its precursor the prion-gene (PRNP) have been subjects to intense studies. Several polymorphisms in PRNP modify disease probability and phenotype. Importantly, two common variants of codon 129 in PRNP code for methionine (Met) or valine (Val), respectively. All hitherto known cases of vCJD have been Met/Met homozygotes. The aim of this study was to investigate the susceptibility to vCJD in the Danish population by determining the distribution of the codon 129 polymorphism. The occurrence of three other relevant polymorphisms were investigated: An alanine (Ala) silent mutation on codon 117, an aspargine-serine (Asn-Ser) mutation on codon 171 and deletions or insertions in the moeity known as the octapeptide region of PRNP. DNA was isolated from 352 samples and alleles were detected by allele specific real-time PCR and/or restriction endonuclease treatment followed by agarose gelelectrophoresis. The distribution of the genotypes at codon 129 was found to be Met/Met 35%, Met/Val 48% and Val/Val 17%. The other polymorphisms were found to be very rare. These data are similar to British data; but differ from the Finnish, Slovakian, Turkish and Japanese distributions, where the Met allele is more abundant. The genetic results indicate that the Danish population is vulnerable to vCJD to the same degree as the British. In Finland, Slovakia, Turkey and Japan the higher frequency of the Met allele may increase the vulnerability to vCJD.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Asn:
-
Aspargine
- BSE:
-
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy
- CJD:
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Met:
-
Methionine
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PRNP:
-
Human prion-coding gene
- Prp:
-
Prion protein
- sCJD:
-
Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Ser:
-
Serine
- Val:
-
Valine
- vCJD:
-
Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
References
Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SM, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, Poser S, Pocchiari M, Hofman A, Smith PG. A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet 1996;347:921–5.
Britton TC, Sl-Sarraj S, Dhaw C, Campbell T, Collinge J. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a 16-year-old In the UK. The Lancet 1995;346:1155.
Bateman D, Hilton D, Love S, Zeidler M, Beck J, Collinge J. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a 18-year-old In the UK. The Lancet 1995;346:1155–6.
Jakob A. Ûber eine der multiplen Sklerose klinisch nahestehende Erkankung des Zentralnervensystems 1921 (spastische Pseudosklerose) mit bemerkenswerden anatomischen Befunden. Med Klin 1921;13:372–6.
Will RB. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp 2002;62:167–73.
Hur K, Kim J-I, Cjoi S-I, Choi E-K, Carp RI, Kim Y-S. The pathogenic mechanisms of prion diseases. Mech Ageing Develop 2002;123:1637–47.
Bruce ME, Will RG, Ironside JW, McConnell I, Drummond D, Suttle A, McCardie L, Chree A, Hope J, Birkett C, Cousens A, Fraser H, Bostock CJ. Transmissions to mice indicate that ‘new variant’ CJD is caused by the BSE agent. Nature 1997;389.
Collinge J, Rossor MK. A new variant of prion disease (see pages 921, 945). The Lancet 1996;347:916–7.
Collinge J, Beck J, Campbell T, Estibeiro K, Will RG. Prion gene analysis in new variant cases of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1996;348:56.
Windl O, Dempster M, Estibeiro JP, Lathe Richard de Silva R, Esmonde T, Will R, Springbett A, Campbell Tracy A, Sidle KCL, Palmer MS, Collinge J. Genetic basis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the United Kingdom: a systematic analysis of predisposing mutations and allelic variation in hte PRNP gene. Hum Genet 1996;98:259–64.
Doh-Ura K, Kitamoto T, Sakaki Y, Tataishi J. CJD discrepancy. Nature 1991;853:801–2.
Collinge J, Palmer MS, Dryden AJ: Genetic predisposition to iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1991;337:1441–2.
Erginel-Unaltuna N, Peoc’h K, Komurcu E, Acuner TT, Issever H, Laplanche J-L. Distribution of the M129V polymorphism of the prion protein gene in a Turkish population suggests a high risk for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur J Hum Genet 2001;9:965–8.
Palmer MS, van Leeven RH, Mahal SP, Campbell TA, Humphreys CB, Collinge J. Sequence variation in intron of prion protein gene, crucial for complete diagnostic strategies. Hum Mutat 1995;7:280–1.
Mead S, Mahal SP, Beck J, Campbell T, Farrall M, Fisher E, Collinge J. Sporadic—but Not Variant—Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Is Associated with Polymorphisms Upstream of PRNP Exon 1. Am J Hum Genet 2001;69:1225–35.
Samaia HB, Jesus Mari J, Vallada HP, Moura RP, Simpson AJG, Brentani RR. A prion-linked psychiatric disorder. Nature 1997;390:241.
YU S-L, Jin L, Sy M-S, Mei F-H, Kang S-L, Sun G-H, Tien P, Wang F-S, Xiao G-F. Polymorphisms of the PRNP gene in Chinese populations and the identification of a novel insertion mutation. Eur J Hum Genet 2004;12:867–70.
Goldschmidt E. Variations in the ABO blood group distribution in Denmark. Acta Genet Stat Med 1961;11:86–96.
Nurmi MH, Bishop M, Strain L, Brett F, McGuigan C, Hutchison M, Farrell M, Tilvis R, Erkkilä S, Simell O, Knight R, Haltia M. The normal population distribution of PRNP codon 129 polymorphism. Acta Neurol Scand 2003;108:374–8.
Bratosiewicz J, Kordek R, Kulczycki J, Botts G, Liberski PP. Molecular analysis of PRNP gene in Polish population and in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Folia Neuropathol 1999;37:277–80.
Plaitkis A et al. Increased incidence of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease on the island of Crete associated with a high rate of PRNP 129-methionine homogozygosity in the local population. Ann Neurol 2001;50:227–33.
Saetta AA, Michalopoulos NV, Malamis G, Papanastasiou I, Mazmanian N, Karlou M, Kouzoupis A, Korkolopoulou P, Patsouris E. Analysis of PRNP gene docon 129 polymorphism in the Greek population. Eur J Epidemiol 2006;21:211–5.
Mitrová E, Mayer V, Jovankovièová V, Slivarichová D, Wsólová L. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease risk and PRNP codon 129 polymorphism: necessity to revalue current data. Eur J Neurol 2005;12:998–1001.
Deslys JP, Marce D, Dormond D. Similar genetic susceptibility in iatrogenic and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J general virol 1994;75:23–7.
Laplance JL, Delasnerie-Laupretre N, Brandel JP, Chatelain J, Beaudry P, Alperovitch A, Launay JM. Molecular genetics of prion disease in France. French Research Group on Epidemiology of Human Spongiform Encephalopathies. Neurology 1994;44:2347–51.
Georgsson G, Tryggvason T, Jonasdottir AD, Gudmundsson S, Thorgeirsdottir S. Polymorphism of PRNP codons in the normal Icelandic population. Acta Neurol Scand 2006;113:419–25.
Zimmermann K, Turecek PL, Schwarz HP. Genotyping of the prion protein at codon 129. Acta Neuropathol 1999;97:355–8.
Calavas D, Ducrot C, Baron TG. Past, present and future of bovine spongiform encephalopathy in France. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2004;284:51–63.
Palmer MS, Dryden AJ, Hughes JT, Collinge J. Homozygous prion protein genotype predisposes to sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature 1991;352:40.
Glatzel M, Ott PM, Linder T, Gebbers JO, Gmür A, Wüst WHG, Moch H, Podvinec M, Stamm B, Aguzzi A. Human prion diseases: epidemiology and integrated risk assessment. The Lancet Neurol 2003;2:757–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dyrbye, H., Broholm, H., Dziegiel, M.H. et al. The M129V polymorphism of codon 129 in the prion gene (PRNP) in the Danish population. Eur J Epidemiol 23, 23–27 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9197-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9197-z