Abstract
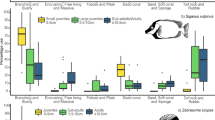
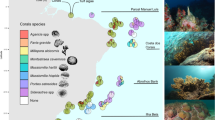
The present study describes ontogenetic shifts in habitat use for 15 species of coral reef fish at Rangiroa Atoll, French Polynesia. The distribution of fish in different habitats at three ontogenetic stages (new settler, juvenile, and adult) was investigated in coral-dominated and algal-dominated sites at two reefs (fringing reef and inner reef of motu). Three main ontogenetic patterns in habitat use were identified: (1) species that did not change habitats between new settler and juvenile life stages (60% of species) or between juvenile and adult stages (55% of species—no ontogenetic shift); (2) species that changed habitats at different ontogenetic stages (for the transition “new settler to juvenile stage”: 15% of species; for the transition “juvenile to adult stage”: 20% of species); and (3) species that increased the number of habitats they used over ontogeny (for the transition “new settler to juvenile stage”: 25% of species; for the transition “juvenile to adult stage”: 25% of species). Moreover, the majority of studied species (53%) showed a spatial variability in their ontogenetic pattern of habitat use according to alternate reef states (coral reef vs algal reef), suggesting that reef state can influence the dynamics of habitat associations in coral reef fish.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjeroud M, Chancerelle Y, Schrimm M, Perez T, Lecchini D, Galzin R, Salvat B (2005) Detecting the effects of natural disturbances on coral assemblages in French Polynesia: a decade survey at multiple scales. Aqua Liv Res 18:111–123
Booth DJ (1991) The effects of sampling frequency on estimates of recruitment of the domino damselfish Dascyllus albisella (Gill). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 14:149–159
Dahlgren CP, Eggleston DB (2000) Ecological processes underlying ontogenetic habitat shifts in a coral reef fish. Ecology 81:2227–2240
Doherty PJ (2002) Variable replenishment and the dynamics of reef fish populations. In: Sale PF (ed) Coral reef fishes: dynamics and diversity in a complex ecosystem. Academic, San Diego, pp 327–358
Dray S, Chessel D, Thioulouse J (2003) Co-inertia analysis and the linking of ecological data tables. Ecology 84:307–339
Feary DA, Almany GR, McCormick MI, Jones GP (2007) Habitat choice, recruitment and the response of coral reef fishes to coral degradation. Oecologia 153:727–737
Gillanders BM, Able KW, Brown JA, Eggleston DB, Sheridan PF (2003) Evidence of connectivity between juvenile and adult habitats for mobile marine fauna: an important component of nurseries. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 247:281–295
Harmelin-Vivien ML, Harmelin JG, Chauvet C, Duval C, Galzin R, Lejeune P, Barnabé G, Blanc F, Chevalier R, Duclerc J, Lasserre G (1985) Evaluation visuelle des peuplements et populations de poissons: Méthodes et problèmes. Terre et Vie, Revue d’Ecologie 40:467–539
Hjelm J, Svanback R, Bystrom P, Persson L, Wahlstrom E (2001) Diet-dependent morphology and ontogenetic reaction norms in Eurasian perch. Oikos 95:311–323
Jones GP, McCormick MI, Srinivasan M, Eagle JV (2004) Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc Nat Acad Sci 21:8251–8253
Kaufman L, Ebersole J, Beets J, McIvor CC (1992) A key phase in the recruitment dynamics of coral reef fishes: post-settlement transition. Env Biol Fish 34:109–118
Lecchini D, Dufour V, Carleton J, Strand S, Galzin R (2004) Study of the fish larval flux at Moorea Island: is the spatial scale significant? J Fish Biol 65:1142–1146
Lecchini D (2005) Spatial and behavioural patterns of reef habitat settlement by fish larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 301:247–252
Lecchini D, Galzin R (2005) Spatial repartition and ontogenetic shifts in habitat use by coral reef fishes (Moorea, French Polynesia). Mar Biol 147:47–58
Lecchini D, Planes S, Galzin R (2007) The influence of habitat characteristics and conspecifics on attraction and survival of coral reef fish juveniles. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 341:85–90
Lecchini D, Tsuchiya M (2008) Temporal consistency of ontogenetic shifts in habitat use by coral reef fishes in the northernmost coral ecosystem in the world (Kudaka Island, Japan). J Fish Biol 72:2645–2654
Leis JM, McCormick MI (2002) The biology, behavior, and ecology of the pelagic, larval stage of coral reef fishes. In: Sale PF (ed) Coral reef fishes: dynamics and diversity in a complex ecosystem. Academic, San Diego, pp 171–199
McCormick MI, Makey LJ (1997) Post-settlement transition in coral reef fishes: overlooked complexity in niche shifts. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 153:247–257
McCormick MI, Makey LJ, Dufour V (2002) Comparative study of metamorphosis in tropical reef fishes. Mar Biol 141:841–853
McCormick MI (2009) Behaviourally mediated phenotypic selection in a disturbed coral reef environment. PLoS One 4:e7096
McCormick MI, Moore JAY, Munday PL (2010) Influence of habitat degradation on fish replenishment. Coral Reefs 29:537–546
McDermott CJ, Shima JS (2006) Ontogenetic shifts in microhabitat preference of the temperate reef fish Forsterygion lapillum: implications for population limitation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 320:259–266
Mellin C, Kulbicki M, Ponton D (2007) Seasonal and ontogenetic patterns of habitat use in coral reef fish juveniles. Estuar Coast Shel Sci 52:1–11
Mumby PJ, Chisholm JRM, Edwards AJ, Clark CD, Andrefouet S, Jaubert J (2001) Unprecedented bleaching-induced mortality in Porites spp. at Rangiroa Atoll, French Polynesia. Mar Biol 139:183–189
Nakamura Y, Shibuno T, Lecchini D, Kawamura T, Watanabe Y (2009) Spatial variability in habitat associations of pre- and post-settlement stages of coral reef fishes at Ishigaki Island, Japan. Mar Biol 156:2413–2419
Pandolfi JM, Connolly SR, Marshall DJ (2011) Projecting coral reef futures under global warming and ocean acidification. Science 333:418–422
Pinder AC, Gozlan RE, Beyer K, Bass JAB (2005) Ontogenetic induced shifts in the ecology of sunbleak Leucaspius delineatus during early development. J Fish Biol 67:205–217
Pratchett MS, Berumen ML, Marnane MJ, Eagle JV, Pratchett DJ (2008) Habitat associations of juvenile versus adult butterflyfishes. Coral Reefs 27:541–551
Snover ML (2008) Ontogenetic habitat shifts in marine organisms: Influencing factors and the impact of climate variability. Bull Mar Sci 83:53–67
Thresher RE (1984) Reproduction in reef fishes. TFH Publications, Neptune City, NJ, p 399
Werner EE, Gilliam JF (1984) The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 15:393–425
Wilson SK, Graham NAJ, Pratchett MS, Jones GP, Polunin NVC (2006) Multiple disturbances and the global degradation of coral reefs: are reef fishes at risk or resilient? Glob Chang Biol 11:2220–2234
Wilson SK, Depczynski M, Fisher R, Holmes TH, O’Leary RA, Tinkler P (2010) Habitat associations of juvenile fish at Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia: the importance of coral and algae. PLoS One 5:1–7
Acknowledgements
Tropical Fish Tahiti, Service de la Perliculture and Service de la Pêche of French Polynesia for kindly agreeing to house this study in their facilities. This research was supported by grants from ANR (ANR-06-JCJC-0012-01), MOM (06 PF 15) and CRISP program (Coral Reef Initiative in the South Pacific—C2A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lecchini, D., Carassou, L., Frédérich, B. et al. Effects of alternate reef states on coral reef fish habitat associations. Environ Biol Fish 94, 421–429 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9958-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9958-0