Summary
In a phase I study, ixabepilone, a novel non-taxane microtubule-stabilizing agent, demonstrated activity against both paclitaxel-sensitive and paclitaxel-refractory solid tumors. We conducted a phase II trial of this agent in patients with advanced germ cell tumors (GCT) who were resistant to conventional therapies.
Patients with cisplatin-refractory GCT were enrolled in this single-institution, phase II trial. Ixabepilone was administered at a dose of 40 mg/m2 intravenously over 3 hours every 21 days. Dose modifications were planned according to a nomogram for adverse events. Responses were assessed every 6 weeks using tumor markers and radiographic imaging according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). Patients who progressed (≥20% increase in tumor size or rising serum tumor markers) were taken off protocol.
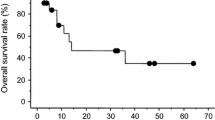
Twenty-nine cycles of treatment were administered to 12 patients. The most common Grade 3/4 toxicities were leukopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia. One patient (8%) achieved a confirmed objective partial response but this patient had not received prior treatment with a taxane. Based on slow accrual and a lack of antitumor activity in patients previously treated with a taxane, the trial was closed after enrolling 12 patients.
For patients who had previously received taxane therapy, ixabepilone was not efficacious in the treatment of cisplatin-refractory GCT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondagunta GV, Motzer RJ (2006) Chemotherapy for advanced germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol 24:5493–5502
Beyer J, Kramar A, Mandanas R et al (1996) High-dose chemotherapy as salvage treatment in germ cell tumors: a multivariate analysis of prognostic variables. J Clin Oncol 14:2638–2645
Bollag DM, McQueney PA, Zhu J et al (1995) Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a taxol-like mechanism of action. Cancer Res 55:2325–2333
Lee FY, Borzilleri R, Fairchild CR et al (2001) BMS-247550: a novel epothilone analog with a mode of action similar to paclitaxel but possessing superior antitumor efficacy. Clin Cancer Res 7:1429–1437
Chou TC, Zhang XG, Harris CR et al (1998) Desoxyepothilone B is curative against human tumor xenografts that are refractory to paclitaxel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15798–15802
Mani S, McDaid H, Hamilton A et al (2004) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of BMS-247550, a novel derivative of epothilone B, in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10:1289–1298
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Contr Clin Trials 10:1–10
Acknowledgments
This clinical trial was supported by NIH Grants CM-57732 and CA-05826 and by the Craig D. Tifford Foundation. The authors thank Carol Pearce, Writer/Editor, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Department of Medicine Editorial Unit, for her critical review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feldman, D.R., Kondagunta, G.V., Ginsberg, M.S. et al. Phase II Trial of ixabepilone in patients with cisplatin-refractory germ cell tumors. Invest New Drugs 25, 487–490 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9059-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9059-2