Abstract
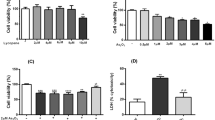
Besides acting as potent free radical scavengers, tocopherols and tocotrienols have been known to have non-antioxidant properties such as the involvement of α-tocopherol (αT) in PKC pathway and the anti-cancer properties of γ-tocotrienol (γT3). This study aims to elucidate whether protective effects shown by αT and γT3 in H2O2-induced neuron cultures have anti-apoptotic or pro-apoptotic tendency toward the initiation of neuronal apoptosis. H2O2 is used to induce apoptosis in primary cerebellar neuron cultures which is attenuated by pretreatment of αT or γT3 at concentrations ≤10 μM. Similar to our previous work, γT3 was found to be neurotoxic at concentrations ≥100 μM, whereas αT showed no neurotoxicity. Cellular uptake of γT3 was higher than that of αT. Treating cells simultaneously with either γT3 or αT and with then H2O2 led to higher expression of Bax and Bcl-2 than in neurons exposed to H2O2 alone. Analysis of Bcl-2/Bax ratio as ‘survival index’ showed that both pretreatment of γT3 and αT followed by H2O2 increase the ‘survival index’ of Bcl-2/Bax ratio compared to H2O2-treated cells, while treatment of γT3 alone decrease the ratio compared to unchanged Bcl2/Bax ratio of similar treatment with αT alone. Similar treatment of γT3 decreased p53 expression and activates p38 MAPK phosphorylation, whereas αT did not alter its expression compared to H2O2-treated cells. Treating neurons with only γT3 or αT increased the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, p53, and p38 MAPK compared to control with γT3 exerting stronger expression for proteins involved than αT. In conclusion, low doses of γT3 and αT confer neuroprotection to H2O2-treated neurons via their antioxidant mechanism but γT3 has stronger pro-apoptosis tendency than αT by activating molecules involved in the neuronal apoptotic pathway in the absence of H2O2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal MK, Agarwal ML, Athar M, Gupta S (2004) Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil activates p53, modulates Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and induces apoptosis independent of cell cycle association. Cell Cycle 3:1–7
Alvarado C, Alvarez P, Puerto M, Gausserès N, Jiménez L, De la Fuente M (2006) Dietary supplementation with antioxidants improves functions and decreases oxidative stress of leukocytes from prematurely aging mice. Nutrition 22:767–777. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2006.05.007
Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod JJ, Mazzei G, Maundrell K, Gambale F, Sadoul R, Martinou JC (1997) Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science 277:370–372. doi:10.1126/science.277.5324.370
Azzi A, Stocker A (2000) Vitamin E: non-antioxidant roles. Prog Lipid Res 39:231–255. doi:10.1016/S0163-7827(00)00006-0
Banudevi S, Krishnamoorthy G, Venkataraman P, Vignesh C, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2006) Role of alpha-tocopherol on antioxidant status in liver, lung and kidney of PCB exposed male albino rats. Food Chem Toxicol 44:2040–2046. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.017
Busciglio J, Yankner BA (1995) Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down’s syndrome neurons in vitro. Nature 378:776–779. doi:10.1038/378776a0
Butterfield DA, Sultana R (2007) Redox Proteomics identification of oxidatively modified brain proteins in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: insights into the progression of this dementing disorder. J Alzheimers Dis 12:61–72
Chen J, Errico ST, Freed WJ (2005) Reactive oxygen species and p38 phosphorylation regulate the protective effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the apoptotic response to NMDA. Neurosci Lett 389:99–103. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.07.028
Chong ZZ, Li FQ, Maeise K (2005) Oxidative stress in the brain: novel cellular targets that govern survival during neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol 75:207–246. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.02.004
Crouzin N, Ferreira MC, Cohen-Solal C, Aimar RF, Vignes M, Guiramand J (2007) α-Tocopherol-mediated long-lasting protection against oxidative damage involves an attenuation of calcium entry through TRP-like channels in cultured hippocampal neurons. Free Radic Biol Med 42:1326–1337. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.01.032
Culmsee C, Mattson MP (2005) p53 in neuronal apoptosis. Biochem Biophy Res Comm 331:761–777
Drögen W, Schipper HM (2007) Oxidative stress and aberrant signaling in aging and cognitive decline. Aging Cell 6:361–370. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00294.x
Emerit J, Edeas M, Bricaire F (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 58:39–46. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2003.11.004
Engelhart MJ, Geerlings MI, Ruitenberg A, van Swieten JC, Hofman A, Wittenman JCM, Breteler MMB (2002) Dietary intake of antioxidant and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA 287:3223–3229. doi:10.1001/jama.287.24.3223
Ferreira MC, Crouzin N, Barbanel G, Cohen-Solal C, Récasens M, Vignes M, Guiramand J (2005) A transient treatment of hippocampal neurons with α-tocopherol induces a long-lasting protection against oxidative damage via a genomic action. Free Radic Biol Med 39:1009–1020. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.05.021
Ferrer I, Gomez-Isla T, Puig B, Freixes M, Ribé E, Dalfó E, Avila J (2005) Current advances on different kinases involved in tau phosphorylation, and implications in Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathies. Curr Alzheimer Res 21:3–18. doi:10.2174/1567205052772713
Galbussera A, Tremolizzo L, Brighina L, Testa D, Lovati R, Ferrarese C, Cavaletti G, Filippini G (2006) Vitamin E intake and the quality of life in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: a follow-up case series study. Neurol Sci 27:190–193. doi:10.1007/s10072-006-0668-x
Gomez-Lazaro M, Galindo MF, Melero-Fernandez de Mera RM, Fernandez-Gómez FJ, Concannon CG, Segura MF, Comella JX, Prehn JHM, Jordan J (2007) Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activate Bax to induce mitochondrial cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to malonate. Mol Pharmacol 71:736–743. doi:10.1124/mol.106.030718
Golbe LI, Farrell TM, Davis PH (1998) Case-control study of early life dietary factors in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 45:1350–1353
Graf M, Ecker D, Horowski R, Kramer B, Riederer P, Gerlach M, Hager C, Ludolph AC, Becker G, Osterhage J, Jost WH, Schrank B, Stein C, Kostopulos P, Lubik S, Wekwerth K, Dengler R, Troeger M, Wuerz A, Hoge A, Schrader C, Schimke N, Krampfl K, Petri S, Zierz S, Eger K, Neudecker S, Traufeller K, Sievert M, Neundorfer B, Hecht M (2005) High-dose vitamin E therapy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as add-on therapy to riluzole: a result of placebo controlled double blind study. J Neural Transm 112(5):649–660. doi:10.1007/s00702-004-0220-1
Khanna S, Roy S, Parinandi NL, Maurer M, Sen CK (2006) Characterization of the potent neuroprotective properties of the natural vitamin E a-tocotrienol. J Neurochem 98:1474–1486. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04000.x
Kikuta K, Masamune A, Satoh M, Suzuki N, Satoh K, Shimosegawa T (2006) Hydrogen peroxide activates activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinases in pancreatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem 291:11–20. doi:10.1007/s11010-006-9189-4
Kolosova NG, Shcheglova TV, Sergeeva SV, Loskutova LV (2006) Long-term antioxidant supplementation attenuates oxidative stress markers and cognitive deficits in senescent-accelerated OXYS rats. Neurobiol Aging 27:1289–1297. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.07.022
Krantic S, Mechawar N, Reix S, Quirion R (2005) Molecular basis of programmed cell death involved in neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci 28:670–676
Kumar KS, Raghavan M, Hieber K, Ege C, Mog S, Parra N, Hildabrand A, Singh V, Srinivasan V, Toles R, Karikari P, Petrovics G, Seed T, Srivastava S, Papas A (2006) Prefencial radiation sensitization of prostate cancer in nude mice by nutraceutical antioxidant γ-tocotrienol. Life Sci 78:2099–2104. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.12.005
Mariani E, Polidori MC, Cherubini A, Mecocci P (2005) Oxidative stress in brain aging, neurodegenerative and vascular disease: An overview. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 827:65–75. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.04.023
Mazlan M, Then SM, Gapor MT, Wan Zurinah WN (2006) Comparative effects of α-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol against hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis on primary-cultured astrocytes. J Neurol Sci 243:5–12. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2005.10.006
Moreira PI, Siedlak SL, Aliev G, Zhu X, Cash AD, Smith MA, Perry G (2005) Oxidative stress mechanism and potential therapeutics in Alzheimer disease. J Neural Transm 112:921–932. doi:10.1007/s00702-004-0242-8
Morris MC, Beckeet LA, Scherr PA, Herbert LE, Bennett DA, Field TS, Evans DA (1998) Vitamin E and vitamin C supplement use and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 12:121–126. doi:10.1097/00002093-199809000-00001
Morrison RS, Kinoshita Y, Johnson MD, Guo W, Garden GA (2003) p53-dependent cell death signaling in neurons. Neurochem Res 28:15–27. doi:10.1023/A:1021687810103
Numakawa Y, Numakawa T, Matsumoto T, Yagasaki Y, Kumamaru E, Kunugi H, Taguchi T, Niki E (2006) Vitamin E protected cultured cortical neurons from oxidative stressed-induced cell death through the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. J Neurochem 97:1191–1202. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03827.x
Onyango IG (2007) Mitochondrial and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem Res 33:589–597. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9482-y
Osakada F, Hashino A, Kume T, Katsuki H, Kaneko S, Akaike A (2003) Neuroprotective effects of α-tocopherol on oxidative stress in rat straital cultures. Eur J Pharmacol 465:15–22. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(03)01495-X
Osakada F, Hashino A, Kume T, Katsuki H, Kaneko S, Akaike A (2004) α-Tocotrienol provides the most potent neuroprotection among vitamin E analogs on cultured striatal neurons. Neuropharmacol 47:904–915. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.06.029
Peter ME, Krammer PH (2003) The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ 10:26–35. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401186
Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M, Bennett D, Doody R, Ferris S (2005) Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med 352:2379–2388. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050151
Roy S, Lado BH, Khanna S, Sen CK (2002) Vitamin E sensitive genes in the developing rat fetal brain: a high-density oligonucleotide microarray analysis. FEBS Lett 530:17–23. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03309-4
Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas RG, Klauber MR, Schafer K, Grundman M, Woodbury P, Growdon J, Cotman CW, Pfeiffer E, Schneider LS, Thal LJ (1997) A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. N Engl J Med 336(17):1216–1222. doi:10.1056/NEJM199704243361704
Sastry PS, Rao KK (2000) Apoptosis and the Nervous System. J Neurochem 74:1–20. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0740001.x
Sen CK, Khanna S, Roy S, Packer L (2000) Molecular basis of vitamin E: tocotrienol potently inhibits glutamate-induced pp60c-src kinase activation and death of HT4 neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 275:13049–13055. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.17.13049
Shabnam MS, Srinivasam R, Wali A, Majumdar S, Joshi K, Behera D (2004) Expression of p53 protein and the apoptotic regulatory molecules Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Bax in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 45:181–188. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.01.021
Srinivas G, Kusumakumary P, Nair MK, Panicker KR, Pillai MR (2000) Mutant p53 protein, Bcl/Bax ratios and apoptosis in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:62–67. doi:10.1007/s004320050010
Srivastava JK, Gupta S (2006) Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis selectively in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:447–453. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.147
Sylvester PW (2007) Vitamin E and apoptosis. Vitam Horm 76:329–356. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(07)76012-0
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462. doi:10.1126/science.7878464
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT, Thompson CB (1997) Bcl-xL regulates the membrane potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell 91:627–637. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80450-X
Vervaart P, Knight KR (1996) Oxidative stress and the cell. Clin Biochem Rev 17:3–16
Wali VB, Sylvester PW (2007) Synergistic antiproliferative effects of gamma-tocotrienol and statin treatment on mammary tumor cells. Lipids 42:1113–1123. doi:10.1007/s11745-007-3102-0
Wang JY, Shum AY, Ho YJ (2003) Oxidative neurotoxicity in rat cerebral cortex neurons: synergistic effects of H2O2 and NO on apoptosis involving activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and caspase-3. J Neurosci Res 72:508–519. doi:10.1002/jnr.10597
Wang X, Quinn PJ (2000) The location and function of vitamin E in membranes. Mol Membr Biol 17:143–156. doi:10.1080/09687680010000311
Yoshida Y, Niki E, Noguchi N (2003) Comparative study on the action of tocopherols and tocotrienols as antioxidants: chemical and physical effects. Chem Phys Lipids 123:63–75. doi:10.1016/S0009-3084(02)00164-0
Yoshida Y, Saito Y, Jones LS, Shigeri Y (2007) Chemical preactivities and physical effects in comparison between tocopherols and tocotrienols: physiological significance and prospects as antioxidants. J Biosci Bioeng 104:439–445. doi:10.1263/jbb.104.439
Zhang B, Tanaka J, Yang L, Yang L, Sakanaka M, Hata R, Maeda N, Mitsuda N (2004) Protective effect of vitamin E against focal brain ischemia and neuronal death through induction of target genes of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Neuroscience 126:433–440. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.03.057
Zingg JM (2007) Modulation of signal transduction by vitamin E. Mol Aspects Med 28:481–506. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2006.12.009
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X (1999) An Apaf-1 cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem 274:11549–11556. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.17.11549
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation of Malaysia under Intensified Research Prioritized Area (IRPA) grant 06-02-02-0022/PR0008/09-07. We thank Dr. Coral Sanfeliu from the Institute of Biomedical Research of Barcelona (IIBB) in Spain for her invaluable assistance in setting of the neuronal culture system in our laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Then, S.M., Mazlan, M., Mat Top, G. et al. Is Vitamin E Toxic to Neuron Cells?. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29, 485–496 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9340-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9340-8