Abstract
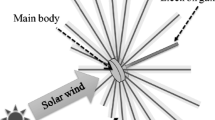
This paper presents an analysis of an asteroid deflection method based on multiple solar concentrators. A model of the deflection through the sublimation of the surface material of an asteroid is presented, with simulation results showing the achievable impact parameter with, and without, accounting for the effects of mirror contamination due to the ejected debris plume. A second model with simulation results is presented analyzing an enhancement of the Yarkovsky effect, which provides a significant deflection even when the surface temperature is not high enough to sublimate. Finally the dynamical model of solar concentrators in the proximity of an irregular celestial body are discussed, together with a Lyapunov-based controller to maintain the spacecraft concentrators at a required distance from the asteroid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barucci M., Yoshikawa M., Michel P., Kawagushi J., Yano H., Brucato J., Franchi I., Dotto E., Fulchignoni M., Ulamec S.: MARCO POLO: Near earth object sample return mission. Exp. Astron. 23(3), 785–808 (2009)
Battin, R.H.: An Introduction to the Mathematics and Methods of Astrodynamics, Revised edn. AIAA Education Series, New York (1999)
Brož, M.: Yarkovsky Effect and the Dynamics of the Solar System, PhD thesis, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Astronomical Institute, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic (2006)
Carusi A., Valsecchi G.B., D’abramo G., Bottini A.: Deflecting NEOs in route of collision with the earth. Icarus 159(2), 417–422 (2002). doi:10.1006/icar.2002.6906
Chesley, S.R.: Potential impact detection for near-Earth asteroids: The case of 99942 Apophis (2004 MN4). In: Asteroids, Comets, Meteors Proceedings, vol. 229, pp. 215–228. IAU Symposium (2005)
Colombo C., Vasile M., Radice G.: Optimal low-thrust trajectories to asteroids through an algorithm based on differential dynamic programming. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 105(1–3), 75–112 (2009)
Colombo C., Vasile M., Radice G.: Semi-analytical solution for the optimal low-thrust deflection of near-earth objects. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(3), 796–809 (2009). doi:10.2514/1.40363
Conway B.: Near-optimal deflection of earth-approaching asteroids. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 24(5), 1035–1037 (2001)
Delbò M., Cellino A., Tedesco E.: Albedo and size determination of potentially hazardous asteroids: (99942) Apophis. Icarus 188, 266–269 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.12.024
Giorgini J., Benner L., Ostroa S., Nolan M., Busch M.: Predicting the earth encounters of (99942) apophis. Icarus 193, 1–19 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.09.012
Glassmeier K.H., Boehnhardt H., Koschny D., Kührt E., Richter I.: The rosetta mission: Flying towards the origin of the solar system. Space Sci. Rev. 128(1–4), 1–21 (2007)
Gong S.P., Li J.F., BaoYin H.X.: Formation flying solar-sail gravity tractors in displaced orbit for towing near-earth asteroids. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 105(1–3), 159–177 (2009)
Hall C.D., Ross I.M.: Dynamics and control problems in the deflection of Near-Earth Objects. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 67(640), 1–18 (1997)
Hampton D., Baer J., Huisjen M., Varner C., Delamere A., Wellnitz D., A’Hearn M., Klaasen K.: An overview of the instrument suite for the deep impact mission. Space Sci. Rev. 117(1–2), 43–93 (2005)
Hu W., Scheeres D.J.: Spacecraft motion about slowly rotating asteroids. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 25(4), 765–775 (2002)
IAU Minor Planet Center: Observer services: Neos. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/iau/mpc.html (2010)
Izzo, D.: On the deflection of potentially hazardous objects. In: AIAA/AAS Space Flight Mechanics Conference. Copper Mountain, Colorado (2005)
Kahle R., Kührt E., Hahn G., Knollenberg J.: Physical limits of solar collectors in deflecting earth-threatening asteroids. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 10, 253–263 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.ast.2005.12.004
Legge, H., Boettcher, R.: Modelling control thrust plume flow and impingement. In: International Symposium on Rarefied Gas Dynamics, pp. 983–992 (1982)
Lunan D.: Need we protect earth from space objects and if so, how?. Space Policy 8(1), 90–91 (1992)
Maddock C., Vasile M.: Design of optimal spacecraft-asteorid formations through a hybrid global optimization approach. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 1(2), 239–268 (2008). doi:10.1108/17563780810874735
McAdams, J.V., Dunham, D.W., Mosher, L.E., Ray, J.C., Antreasian, P.G., Helfrich, C.E., Miller, J.K.: Maneuver history for the NEAR mission—launch through Eros orbit insertion. In: Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, AIAA-2000-4141 (2000)
Melosh H.J., Nemchinov I.V.: Solar asteroid diversion. Nature 366, 21–22 (1993)
Melosh H.J., Nemchinov I.V., Zetzer Y.I.: Non-nuclear strategies for deflecting comets and asteroids. In: Gehrels, T. (eds) Hazard Due to Comets and Asteroids, pp. 1111–1132. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (1994)
Nakamura, A.M., Michel, P.: Asteroids and their collisional disruption. In: Lecture Notes in Physics, Small Bodies in Planetary Systems, pp. 1–27. Springer, Berlin (2009)
NASA Near Earth Object program: 99942 Apophis (2004 MN4) impact risk. Online database, http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/risk/a99942.html (2010)
Near-Earth Object Science Definition Team: Study to determine the feasibility of extending the search for Near-Earth Objects to smaller limiting diameters. Tech. rep., National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) (2003)
Park S.Y., Mazanek D.D.: Deflection of earth-crossing asteroids/comets using rendezvous spacecraft and laser ablation. J. Astronaut. Sci. 53(1), 21–37 (2005)
Perozzi E., Casalino L., Colasurdo G., Rossi A., Valsecchi G.: Resonant fly-by missions to near earth asteroids. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 83(1–4), 49–62 (2002)
Rayman M., Varghese P., Lehman D., Livesay L.: Results from the deep space 1 technology validation mission. Acta Astronaut. 47(2), 475–487 (2000)
Remo J.L.: Classifying and modeling NEO material properties and interactions. In: Gehrels, T., Matthews, M.S., Schumann, A. (eds) Hazards Due to Comets and Asteroids, Space Science Series, pp. 551–596. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (1994)
Rossi A., Marzari F., Farinella P.: Orbital evolution around irregular bodies. Earth Planets Space 51, 1173–1180 (1999)
Russell C.T., Capaccioni F., Coradini A., de Sanctis M.C., Feldman W.C., Jaumann R., Keller H.U., McCord T.B., McFadden L.A., Mottola S., Pieters C.M., Prettyman T.H., Raymond C.A., Sykes M.V., Smith D.E., Zuber M.T.: Dawn mission to Vesta and Ceres. Earth Moon Planets 101(1–2), 65–91 (2007)
Sanchez J.P., Vasile M., Radice G.: Consequences of asteroid fragmentation during impact hazard mitigation. J Guid. Control Dyn. 33(1), 126–146 (2010). doi:10.2514/1.43868
Sanchez Cuartielles J.P., Colombo C., Vasile M., Radice G.: Multi-criteria comparison among several mitigation strategies for dangerous near earth objects. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(1), 121–142 (2009). doi:10.2514/1.36774
Scheeres, D.J., Schweickart, R.L.: The mechanics of moving asteroids. In: Planetary Defense Conference: Protecting Earth from Asteroids. AIAA, Orange County, California (2004)
Schweickart, R.L.: A call to (considered) action: International space development conference. Occasional Paper 0501, B612 Foundation (2005)
Stephan T.: Assessing the elemental composition of comet 81P/Wild 2 by analyzing dust collected by stardust. Space. Sci. Rev. 138(1–4), 247–258 (2008)
Vasile M., Colombo C.: Optimal impact strategies for asteroid deflection. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 31(4), 858–872 (2008). doi:10.2514/1.33432
Vasile, M., Maddock, C., Radice, G., McInnes, C.: Call for ideas: NEO Encounter 2029, NEO deflection through a multi-mirror system. Tech. Rep. Ariadna ID: 08/4301, Contract Number: 21665/08/NL/CB, ESA/ESTEC Advanced Concepts Team (2009)
Vokrouhlicky D., Chesley S., Milani A.: On the observability of radiation forces acting on near-earth asteroids. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 81(1–2), 149–165 (2001)
Wang J., Davis A., Clayton R., Hashimoto A.: Evaporation of single crystal forsterite: Evaporation kinetics, magnesium isotope fractionation, and implications of mass-dependent isotopic fractionation of a diffusion-controlled reservoir. Geochimica et Cosmochim. Acta 63(6), 953–966 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00286-5
Yoo S.M., Song Y.J., Park S.Y., Choi K.H.: Spacecraft formation flying for earth-crossing object deflections using a power limited laser ablating. Adv. Space Res. 43, 1873–1889 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2009.03.025
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is partially supported by the ESA/ESTEC Ariadna study 08/4301, contract number: 21665/08/NL/CB (Vasile et al. 2009).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasile, M., Maddock, C.A. On the deflection of asteroids with mirrors. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 107, 265–284 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9277-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9277-3