Abstract
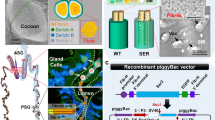
As a result of breeding for more than 4,000 years, the silkworm, Bombyx mori, has acquired the ability to synthesize bulk amounts of silk proteins in its silk glands. To utilize this capacity for mass production of useful proteins, transgenic silkworms were generated that synthesized recombinant proteins in the silk gland and secreted them into the silk cocoon. The silk gland is classified into two main regions: the posterior (PSG) and the middle silk gland (MSG). By controlling the expressed regions of the recombinant protein gene in the silk gland, we were able to control the localization of the synthesized protein in the silk thread. Expression in the PSG or MSG led to localization in the insoluble fibroin core or hydrophilic outer sericin layer, respectively. This review focuses on the expression of recombinant protein in the MSG of transgenic silkworms. The recombinant protein secreted in the sericin layer is extractable from the cocoon with only a small amount of endogenous silk protein contamination by soaking the cocoon in mild aqueous solutions. The possibility of utilizing transgenic silkworms as a valuable tool for the mass production of therapeutic and industrially relevant recombinant proteins is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Tomita M, Yoshizato K (2005) Synthesis of prolyl 4-hydroxylase alpha subunit and type IV collagen in hemocytic granular cells of silkworm, Bombyx mori: involvement of type IV collagen in self-defense reaction and metamorphosis. Matrix Biol 24:136–154
Adachi T, Tomita M, Shimizu K et al (2006) Generation of hybrid transgenic silkworms that express Bombyx mori prolyl-hydroxylase alpha-subunits and human collagens in posterior silk glands: production of cocoons that contained collagens with hydroxylated proline residues. J Biotechnol 126:205–219
Adachi T, Wang X, Murata T et al (2010) Production of a non-triple helical collagen alpha chain in transgenic silkworms and its evaluation as a gelatin substitute for cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 106:860–870
Altmann F, Schwihla H, Staudacher E et al (1995) Insect cells contain an unusual, membrane-bound β-N-acetylglucosaminidase probably involved in the processing of protein N-glycans. J Biol Chem 270:17344–17349
Bencúrová M, Hemmer W, Focke-Tejkl M (2004) Specificity of IgG and IgE antibodies against plant and insect glycoprotein glycans determined with artificial glycoforms of human transferrin. Glycobiology 14:457–466
Bole DG, Hendershot LM, Kearney JF (1986) Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol 102:1558–1566
Cary LC, Goebel M, Corsaro BG et al (1989) Transposon mutagenesis of baculoviruses: analysis of Trichoplusia ni transposon IFP2 insertions within the FP-locus of nuclear polyhedrosis viruses. Virology 172:156–169
Choudary PV, Kamita SG, Maeda S (1995) Expression of foreign genes in Bombyx mori larvae using baculovirus vectors. Methods Mol Biol 39:243–264
Dyck MK, Lacroix D, Pothier F et al (2003) Making recombinant proteins in animals-different systems, different applications. Trends Biotechnol 21:394–399
Giddings G, Allison G, Brooks D et al (2000) Transgenic plants as factories for biopharmaceuticals. Nat Biotechnol 18:1151–1155
Gomord V, Chamberlain P, Jefferis R et al (2005) Biopharmaceutical production in plants: problems, solutions and opportunities. Trends Biotechnol 23:559–565
Grzelak K (1995) Control of expression of silk protein genes. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 110:671–681
Harvey AJ, Speksnijder G, Baugh LR et al (2002) Expression of exogenous protein in the egg white of transgenic chickens. Nat Biotechnol 20:396–399
Hendershot L, Bole D, Köhler G et al (1987) Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate posttranslationally with immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein. J Cell Biol 104:761–767
Hino R, Tomita M, Yoshizato K (2006) The generation of germline transgenic silkworms for the production of biologically active recombinant fusion proteins of fibroin and human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 27:5715–5724
Houdebine LM (2000) Transgenic animal bioreactors. Transgenic Res 9:305–320
Iizuka M, Tomita M, Shimizu K et al (2008) Translational enhancement of recombinant protein synthesis in transgenic silkworms by a 5′-untranslated region of polyhedrin gene of Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Biosci Bioeng 105:595–603
Iizuka M, Ogawa S, Takeuchi A et al (2009) Production of a recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody in transgenic silkworm cocoons. FEBS J 276:5806–5820
Inoue S, Tanaka K, Arisaka F et al (2000) Silk fibroin of Bombyx mori is secreted, assembling a high molecular mass elementary unit consisting of H-chain, L-chain, and P25, with a 6:6:1 molar ratio. J Biol Chem 275:40517–40528
Kojima K, Kuwana Y, Sezutsu H et al (2007) A new method for the modification of fibroin heavy chain protein in the transgenic silkworm. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:2943–2951
Kubelka V, Altmann F, Kornfeld G et al (1994) Structures of the N-linked oligosaccharides of the membrane glycoproteins from three lepidopteran cell lines (Sf-21, IZD-Mb-0503, Bm-N). Arch Biochem Biophys 308:148–157
Kulakosky PC, Hughes PR, Wood HA (1998) N-linked glycosylation of a baculovirus-expressed recombinant glycoprotein in insect larvae and tissue culture cells. Glycobiology 8:741–745
Kurihara H, Sezutsu H, Tamura T et al (2007) Production of an active feline interferon in the cocoon of transgenic silkworms using the fibroin H-chain expression system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 20:976–980
Lillico SG, McGrew MJ, Sherman A et al (2005) Transgenic chickens as bioreactors for protein-based drugs. Drug Discov Today 10:191–196
Maeda S, Kawai T, Obinata M et al (1985) Production of human alpha-interferon in silkworm using a baculovirus vector. Nature 315:592–594
Michaille JJ, Garel A, Prudhomme JC (1990) Cloning and characterization of the highly polymorphic Ser2 gene of Bombyx mori. Gene 86:177–184
Ogawa S, Tomita M, Shimizu K et al (2007) Generation of a transgenic silkworm that secretes recombinant proteins in the sericin layer of cocoon: production of recombinant human serum albumin. J Biotechnol 128:531–544
Okamoto H, Ishikawa E, Suzuki Y (1982) Structural analysis of sericin genes. Homologies with fibroin gene in the 5′ flanking nucleotide sequences. J Biol Chem 257:15192–15199
Perdrix-Gillot S (1979) DNA synthesis and endomitoses in the giant nuclei of the silkgland of Bombyx mori. Biochimie 61:171–204
Royer C, Jalabert A, Da Rocha M et al (2005) Biosynthesis and cocoon-export of a recombinant globular protein in transgenic silkworms. Transgenic Res 14:463–472
Rubin GM, Spradling AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Shields RL, Lai J, Keck R et al (2002) Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human FccRIII and antibodydependent cellular toxicity. J Biol Chem 277:26733–26740
Shimizu K, Ogawa S, Hino R et al (2007) Structure and function of 5′-flanking regions of Bombyx mori fibroin heavy chain gene: identification of a novel transcription enhancing element with a homeodomain protein-binding motif. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:713–725
Shinkawa T, Nakamura K, Yamane N et al (2003) The absence of fucose but not the presence of galactose or bisecting N-acetylglucosamine of human IgG1 complex-type oligosaccharides shows the critical role of enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 278:3466–3473
Staudacher E, Kubelka V, März L (1992) Distinct N-glycan fucosylation potentials of three lepidopteran cell lines. Eur J Biochem 207:987–993
Takasu Y, Yamada H, Tamura T et al (2007) Identification and characterization of a novel sericin gene expressed in the anterior middle silk gland of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:1234–1240
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C et al (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Tatematsu K, Kobayashi I, Uchino K et al (2010) Construction of a binary transgenic gene expression system for recombinant protein production in the middle silk gland of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Transgenic Res 19:473–487
Tomita M, Munetsuna H, Sato T et al (2003) Transgenic silkworms produce recombinant human type III procollagen in cocoons. Nat Biotechnol 21:52–56
Tomita M, Hino R, Ogawa S et al (2007) A germline transgenic silkworm that secretes recombinant proteins in the sericin layer of cocoon. Transgenic Res 16:449–465
Urano S, Kaneko C, Nei T et al (2010) A cell-free assay to estimate the neutralizing capacity of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor autoantibodies. J Immunol Methods 360:141–148
Yanagisawa S, Zhu Z, Kobayashi I et al (2007) Improving cell-adhesive properties of recombinant Bombyx mori silk by incorporation of collagen or fibronectin derived peptides produced by transgenic silkworms. Biomacromolecules 8:3487–3492
Zhao A, Zhao T, Zhang Y et al (2010) New and highly efficient expression systems for expressing selectively foreign protein in the silk glands of transgenic silkworm. Transgenic Res 19:29–44
Zhu Z, Kikuchi Y, Kojima K et al (2010) Mechanical properties of regenerated Bombyx mori silk fibers and recombinant silk fibers produced by transgenic silkworms. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 21:395–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomita, M. Transgenic silkworms that weave recombinant proteins into silk cocoons. Biotechnol Lett 33, 645–654 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0498-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0498-z