Abstract
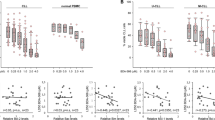
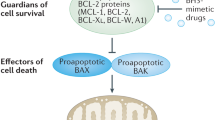
Apoptosis is a complex pathway regulated by the concerted action of multiple pro- and anti-apoptotic molecules. The intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway of apoptosis is governed up-stream of mitochondria, by the family of Bcl-2 proteins, and down-stream of mitochondria, by low-probability events, such as apoptosome formation, and by feedback circuits involving caspases and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), such as XIAP. All these regulatory mechanisms ensure that cells only commit to death once a threshold of damage has been reached and the anti-apoptotic reserve of the cell is overcome. As cancer cells are invariably exposed to strong intracellular and extracellular stress stimuli, they are particularly reliant on the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins. Hence, many cancer cells undergo apoptosis when exposed to agents that inhibit anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 molecules, such as BH3 mimetics, while normal cells remain relatively insensitive to single agent treatments with the same class of molecules. Targeting different proteins within the apoptotic network with combinatorial treatment approaches often achieves even greater specificity. This led us to investigate the sensitivity of leukemia and lymphoma cells to a pro-apoptotic action of a BH3 mimetic combined with a small molecule inhibitor of XIAP. Using the computational probabilistic model of the apoptotic pathway, verified by experimental results from human leukemia and lymphoma cell lines, we show that inhibition of XIAP has a non-linear effect on sensitization towards apoptosis induced by the BH3 mimetic HA14-1. This study justifies further ex vivo and animal studies on the potential of the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma with a combination of BH3 mimetics and XIAP inhibitors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chonghaile TN, Letai A (2008) Mimicking the BH3 domain to kill cancer cells. Oncogene 27(Suppl 1):S149–S157
Labi V, Grespi F, Baumgartner F, Villunger A (2008) Targeting the Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis pathway by BH3 mimetics: a breakthrough in anticancer therapy? Cell Death Differ 15:977–987
Skommer J, Wlodkowic D, Deptala A (2007) Larger than life: mitochondria and the Bcl-2 family. Leuk Res 31:277–286
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42
Kohl TM, Hellinger C, Ahmed F, Buske C, Hiddemann W, Bohlander SK, Spiekermann K (2007) BH3 mimetic ABT-737 neutralizes resistance to FLT3 inhibitor treatment mediated by FLT3-independent expression of BCL2 in primary AML blasts. Leukemia 21:1763–1772
High LM, Szymanska B, Wilczynska-Kalak U, Barber N, O’Brien R, Khaw SL, Vikstrom IB, Roberts AW, Lock RB (2010) The Bcl-2 homology domain 3 mimetic ABT-737 targets the apoptotic machinery in acute lymphoblastic leukemia resulting in synergistic in vitro and in vivo interactions with established drugs. Mol Pharmacol 77:483–494
Lehár J, Krueger AS, Avery W, Heilbut AM, Johansen LM, Price ER et al (2009) Synergistic drug combinations tend to improve therapeutically relevant selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 27:659–666
Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Xu L, Hu Z, Tomita Y, Li P, Roller PP et al (2004) Discovery of embelin as a cell-permeable, small-molecular weight inhibitor of XIAP through structure-based computational screening of a traditional herbal medicine three-dimensional structure database. J Med Chem 47:2430–2440
Skommer J, Brittain T, Raychaudhuri S (2010) Bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis by increasing the time-to-death and intrinsic cell-to-cell variations in the mitochondrial pathway of cell death. Apoptosis 15:1223–1233
Raychaudhuri S, Willgohs E, Nguyen TN, Khan EM, Goldkorn T (2008) Monte Carlo simulation of cell death signaling predicts large cell-to-cell stochastic fluctuations through the type 2 pathway of apoptosis. Biophys J 95(8):3559–3562
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR (2000) The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell Biol 2:156–162
Albeck JG, Burke JM, Spencer SL, Lauffenburger DA, Sorger PK (2008) Modeling a snap-action, variable-delay switch controlling extrinsic cell death. PLoS Biol 6:2831–2852
Rehm M, Huber HJ, Dussmann H, Prehn JH (2006) Systems analysis of effector caspase activation and its control by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. EMBO J 25:4338–4349
Legewie S, Blüthgen N, Herzel H (2006) Mathematical modeling identifies inhibitors of apoptosis as mediators of positive feedback and bistability. PLoS Comput Biol 2:e120
Tamm I, Kornblau SM, Segall H, Krajewski S, Welsh K, Kitada S, Scudiero DA, Tudor G, Qui YH, Monks A, Andreeff M, Reed JC (2000) Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin Cancer Res 6(5):1796–1803
Carter BZ, Milella M, Tsao T, McQueen T, Schober WD, Hu W, Dean NM, Steelman L, McCubrey JA, Andreeff M (2003) Regulation and targeting of antiapoptotic XIAP in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 17(11):2081–2089
Dressler V, Müller G, Sühnel J (1999) CombiTool—a new computer program for analyzing combination experiments with biologically active agents. Comput Biomed Res 32:145–160
Jun YW, Sheikholeslami S, Hostetter DR, Tajon C, Craik CS, Alivisatos AP (2009) Continuous imaging of Plasmon rules in live cells reveals early-stage caspase-3 activation at the single-molecule level. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:17735–17740
Raychaudhuri S (2010) Minimal model of a signaling network elucidates cell-to-cell stochastic variability in apoptosis. PLoS One 5:e11930
Swierniak A, Kimmel M, Smieja J (2009) Mathematical modeling as a tool for planning anticancer therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 625(1–3):108–121
Marin-Sanguino A, Gupta SK, Voit EO, Vera J (2011) Biochemical pathway modeling tools for drug target detection in cancer and other complex diseases. Methods Enzymol 487:319–369
Liso A, Castiglione F, Cappuccio A, Stracci F, Schlenk RF, Amadori S, Thiede C, Schnittger S, Valk PJ, Döhner K, Martelli MF, Schaich M, Krauter J, Ganser A, Martelli MP, Bolli N, Löwenberg B, Haferlach T, Ehninger G, Mandelli F, Döhner H, Michor F, Falini B (2008) A one-mutation mathematical model can explain the age incidence of acute myeloid leukemia with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1). Haematologica 93(8):1219–1226
Attolini CS, Cheng YK, Beroukhim R, Getz G, Abdel-Wahab O, Levine RL, Mellinghoff IK, Michor F (2010) A mathematical framework to determine the temporal sequence of somatic genetic events in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(41):17604–17609
Foo J, Drummond MW, Clarkson B, Holyoake T, Michor F (2009) Eradication of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: a novel mathematical model predicts no therapeutic benefit of adding G-CSF to imatinib. PLoS Comput Biol 5(9):e1000503
Kronik N, Kogan Y, Elishmereni M, Halevi-Tobias K, Vuk-Pavlović S, Agur Z (2010) Predicting outcomes of prostate cancer immunotherapy by personalized mathematical models. PLoS One 5(12):e15482
Wang JL, Liu D, Zhang ZJ, Shan S, Han X, Srinivasula SM, Croce CM, Alnemri ES, Huang Z (2000) Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(13):7124–7129
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. R. Dunbar (SBS, University of Auckland) for providing U937 and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, Prof B. Baguley (UoA) for providing Raji CEM and HL-60 cells, Dr J. Taylor (SBS, UoA) for THP-1α cells, and Dr D. Wlodkowic (Department of Chemistry, UoA) for providing PhiPhiLux-G1D1 reagent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
S. C. Das and A. Nair contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skommer, J., Das, S.C., Nair, A. et al. Nonlinear regulation of commitment to apoptosis by simultaneous inhibition of Bcl-2 and XIAP in leukemia and lymphoma cells. Apoptosis 16, 619–626 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0593-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0593-1