Abstract
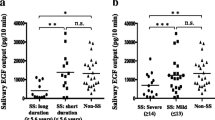
The objective of this study was to examine the clinical and immunological factors influencing the efficacy of cevimeline hydrochloride hydrate (cevimeline) for the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome (SS). Thirty primary SS patients who were medicated with cevimeline were enrolled in this study. Whole stimulated sialometry (WSS) was compared between pre- and posttreatment points (4 weeks after oral cevimeline administration) and the increment rate of WSS was calculated. Multiple regression was employed to examine the relative contributions of the clinical and immunological factors, including age, pretreatment WSS, duration of disease, sialography, minor salivary gland biopsy, anti-Ro/SS-A antibodies, anti-La/SS-B antibodies, and antibodies to muscarinic type 3 receptors to the posttreatment WSS. Patients with normal sialography findings, negative minor salivary gland biopsy, and absence of anti-La/SS-B antibodies had significantly higher increment rates of WSS compared with those with positive findings (p = 0.042, 0.002, and 0.018, respectively). Results of the multiple regression analysis showed that sialography (coefficient = −0.867, p = 0.004) and minor salivary gland biopsy (coefficient = −0.869, p = 0.003) had significant associations with the posttreatment WSS. Our preliminary results demonstrated the relationship between the effect of cevimeline on saliva secretion and the degree of salivary gland destruction evaluated by sialography and histopathological findings in the labial minor salivary glands. These diagnostic approaches could provide useful prognostic information on the efficacy of cevimeline in SS patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fox RI, Saito I (1994) Criteria for diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 20:391–407
Fox PC (2004) Salivary enhancement therapies. Caries Res 38:241–246
Iwabuchi Y, Katagiri M, Masuhara T (1994) Salivary secretion and histopathological effects after single administration of the muscarinic agonist SNI-2011 in MRL/lpr mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 328:315–325
Fife RS, Chase WF, Dore RK, Wiesenhutter CW, Lockhart PB, Tindall E, Suen JY (2002) Cevimeline for the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren syndrome: a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med 162:1293–1300
Petrone D, Condemi JJ, Fife R, Gluck O, Cohen S, Dalgin P (2002) A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of cevimeline in Sjögren’s syndrome patients with xerostomia and keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Arthritis Rheum 46:748–754
Gao J, Cha S, Jonsson R, Opalko J, Peck AB (2004) Detection of anti-type 3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor autoantibodies in the sera of Sjögren’s syndrome patients by use of a transfected cell line assay. Arthritis Rheum 50:2615–2621
Dawson LJ, Stanbury J, Venn N, Hasdimir B, Rogers SN, Smith PM (2006) Antimuscarinic antibodies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome reversibly inhibit the mechanism of fluid secretion by human submandibular salivary acinar cells. Arthritis Rheum 54:1165–1173
Fujibayashi T, Sugai S, Miyasaka N, Hayashi Y, Tsubota K (2004) Revised Japanese criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome (1999): availability and validity. Mod Rheumatol 14:425–434
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH (2002) Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis 61:554–558
Rubin P, Holt JF (1957) Secretory sialography in diseases of the major salivary glands. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 77:575–598
Greenspan JS, Daniels TE, Talal N, Sylvester RA (1974) The histopathology of Sjögren’s syndrome in labial salivary gland biopsies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 37:217–229
Naito Y, Matsumoto I, Wakamatsu E, Goto D, Sugiyama T, Matsumura R, Ito S, Tsutsumi A, Sumida T (2005) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor autoantibodies in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 64:510–511
Rosas J, Ramos-Casals M, Ena J, Garcia-Carrasco M, Verdu J, Cervera R, Font J, Caballero O, Ingelmo M, Pascual E (2002) Usefulness of basal and pilocarpine-stimulated salivary flow in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Correlation with clinical, immunological and histological features. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:670–675
Vivino FB, Al-Hashimi I, Khan Z, LeVeque FG, Salisbury PL III, Tran-Johnson TK, Muscoplat CC, Trivedi M, Goldlust B, Gallagher SC (1999) Pilocarpine tablets for the treatment of dry mouth and dry eye symptoms in patients with Sjögren syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose, multicenter trial. P92-01 Study Group. Arch Intern Med 159:174–181
Papas AS, Sherrer YS, Charney M, Golden HE, Medsger TA Jr, Walsh BT, Trivedi M, Goldlust B, Gallagher SC (2004) Successful treatment of dry mouth and dry eye symptoms in Sjögren’s syndrome patients with oral pilocarpine: a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-adjustment study. J Clin Rheumatol 10:169–177
Matsumura R, Umemiya K, Kagami M, Tomioka H, Tanabe E, Sugiyama T, Sueishi M, Nakajima A, Azuma M, Okumura K, Sumida T (1998) Glandular and extraglandular expression of the Fas–Fas ligand and apoptosis in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 16:561–568
Edgar WM (1992) Saliva: its secretion, composition and functions. Br Dent J 172:305–312
Saito T, Fukuda H, Arisue M, Matsuda A, Shindoh M, Amemiya A, Ohmori K (1991) Relationship between sialographic findings of parotid glands and histopathologic finding of labial glands in Sjögren’s syndrome. Relation to clinical and immunologic findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 72:675–680
Robinson CP, Brayer J, Yamachika S, Esch TR, Peck AB, Stewart CA, Peen E, Jonsson R, Humphreys-Beher MG (1998) Transfer of human serum IgG to nonobese diabetic Igmu null mice reveals a role for autoantibodies in the loss of secretory function of exocrine tissues in Sjögren’s syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7538–7543
Yamamoto H, Sims NE, Macauley SP, Nguyen KH, Nakagawa Y, Humphreys-Beher MG (1996) Alterations in the secretory response of non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice to muscarinic receptor stimulation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 78:245–255
Nguyen KH, Brayer J, Cha S, Diggs S, Yasunari U, Hilal G, Peck AB, Humphreys-Beher MG (2000) Evidence for antimuscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibody-mediated secretory dysfunction in nod mice. Arthritis Rheum 43:2297–2306
Washio T, Kohsaka K, Arisawa H, Masunaga H (2003) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the novel muscarinic receptor agonist SNI-2011 in rats and dogs. Arzneimittelforschung 53:26–33
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully thank Tomomi Nakamura for technical assistance and Judith Nishino for helpful discussions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, H., Nakagawa, Y., Wakamatsu, E. et al. Efficacy prediction of cevimeline in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 26, 1320–1327 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0507-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0507-8