Abstract
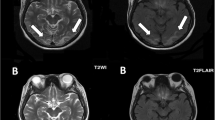
We report a young female patient with Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) nephritis complicated by reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS). The patient suddenly showed generalized seizures and cortical blindness with severe hypertension due to renal insufficiency approximately 1 year after cessation of corticosteroid treatment for HSP nephritis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated bilateral abnormal signals mainly in the cerebellum and white matter of the occipital lobe. Clinical symptoms quickly improved in conjunction with disappearance of abnormal signals on brain MRI after starting control of hypertension and continuous hemodiafiltration with steroid pulse therapy and plasmapheresis. RPLS may be caused by vasculitis and also by hemodynamic change due to severe hypertension in HSP, particularly in patients with nephropathy. In such cases intensive treatment should be performed as soon as possible to avoid neurological sequelae.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brogan PA, Dillon MJ (2000) Vasculitis from the pediatric perspective. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2:411–416
Belman AL, Leicher CR, Moshe SL, Mezey AP (1985) Neurologic manifestations of Schönlein–Henoch purpura: report of three cases and review of the literature. Pediatrics 75:687–692
Ha TS, Cha SH (1996) Cerebral vasculitis in Henoch–Schönlein purpura: a case report with sequential magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Nephrol 10:634–636
Woolfenden AR, Hukin J, Poskitt KJ, Connolly MB (1998) Encephalopathy complicating Henoch–Schönlein purpura: reversible MRI changes. Pediatr Neurol 19:74–77
Perez C, Maravi E, Olier J, Guarch R (2000) MR imaging of encephalopathy in adult Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Am J Roentgenol 175:922–923
Bakkaloglu SA, Ekim M, Tumer N, Deda G, Erden I, Erdem T (2000) Cerebral vasculitis in Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:246–248
Chen CL, Chiou YH, Wu CY, Lai PH, Chung HM (2000) Cerebral vasculitis in Henoch–Schönlein purpura: a case report with sequential magnetic resonance imaging changes and treated with plasmapheresis alone. Pediatr Nephrol 15:276–278
Eun SH, Kim SJ, Cho DS, Chung GH, Lee DY, Hwang PH (2003) Cerebral vasculitis in Henoch–Schönlein purpura: MRI and MRA findings, treated with plasmapheresis alone. Pediatr Int 45:484–487
Ozcakar BZ, Ekim M, Fitoz S, Teber S, Hizel S, Acar B et al (2004) Hypertension induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a report of two cases. Eur J Pediatr 163:728–730
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A et al (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334:494–500
Counahan R, Winterborn MH, White RHR, Heaton JM, Meadow SR, Bluett NH et al (1977) Prognosis of Henoch–Schönlein nephritis in children. Br Med J 2:11–14
Ahn KJ, You WJ, Jeong SL, Lee JW, Kim BS, Lee JH et al (2004) Atypical manifestations of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: findings on diffusion imaging and ADC mapping. Neuroradiology (Epub ahead of print)
Kumai Y, Toyoda K, Fujii K, Ibayashi S (2002) Hypertensive encephalopathy extending into the whole brainstem and deep structures. Hypertens Res 25:797–800
Calabresi P, Pisani A, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G (1995) On the mechanisms underlying hypoxia-induced membrane depolarization in striatal neurons. Brain 118:1027–1038
Abe K (2004) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Intern Med 43:900–901
Edvinsson L, Owman C, Sjoberg NO (1976) Autonomic nerves, mast cells, and amine receptors in human brain vessels. A histochemical and pharmacological study. Brain Res 115:377–393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasayama, D., Shimojima, Y., Gono, T. et al. Henoch–Schönlein purpura nephritis complicated by reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 26, 1761–1763 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0502-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0502-0