Abstract
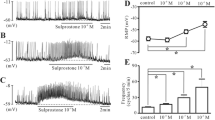
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) are the pacemaker cells that generate the rhythmic oscillation responsible for the production of slow waves in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Spingolipids are known to present in digestive system and are responsible for multiple important physiological and pathological processes. In this study, we are interested in the action of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) on ICC. S1P depolarized the membrane and increased tonic inward pacemaker currents. FTY720 phosphate (FTY720P, an S1P1,3,4,5 agonist) and SEW 2871 (an S1P1 agonist) had no effects on pacemaker activity. Suramin (an S1P3 antagonist) did not block the S1P-induced action on pacemaker currents. However, JTE-013 (an S1P2 antagonist) blocked the S1P-induced action. RT-PCR revealed the presence of the S1P2 in ICC. Calphostin C (a protein kinase C inhibitor), NS-398 (a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor), PD 98059 (a p42/44 inhibitor), or SB 203580 (a p38 inhibitor) had no effects on S1P-induced action. However, c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor II suppressed S1P-induced action. External Ca2+-free solution or thapsigargin (a Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum) suppressed action of S1P on ICC. In recording of intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) concentration using fluo-4/AM S1P increased intensity of spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations in ICC. These results suggest that S1P can modulate pacemaker activity of ICC through S1P2 via regulation of external and internal Ca2+ and mitogenactivated protein kinase activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemany, R., Sichelschmidt, B., Zu Heringdorf, D.M., Lass, H., Van Koppen, C.J., and Jakobs, K.H. (2000). Stimulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate formation by the P2Y2 receptor in HL-60 cells: Ca2+ requirement and implication in receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization, but not MAP kinase activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 58, 491–497.
Alvarez, S.E., Milstien, S., and Spiegel, S. (2007). Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrin. Metab. 18, 300–307.
Anliker, B., and Chun, J. (2004). Lysophospholipid G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 20555–20558.
Bischoff, A., Czyborra, P., Fetscher, C., Meyer Zu Heringdorf, D., Jakobs, K.H., and Michel, M.C. (2000). Sphingosine 1 phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine constrict renal and mesenteric microvessels in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 130, 1871–1877.
Blom, T., Slotte, J.P., Pitson, S.M., and Törnquist, K. (2005). Enhan-cement of intracellular sphingosine-1-phosphate production by inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate-evoked calcium mobilisation in HEK-293 cells: endogenous sphingosine-1-phosphate as a modulator of the calcium response. Cell. Signal. 17, 827–836.
Choi, S., Yeum, C.H., Kim, Y.D., Park, C.G., Kim, M.Y., Park, J.S., Jeong, H.S., Kim, B.J., So, I., and Kim, K.W. (2010). Receptor tyrosine and MAP kinase are involved in effects of H2O2 on interstitial cells of Cajal in murine intestine. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 14, 257–266.
Dragusin, M., Wehner, S., Kelly, S., Wang, E., Merrill Jr, A.H., Kalff, J.C., and Van Echten-Deckert, G. (2006). Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate and ceramide-1-phosphate on rat intestinal smooth muscle cells: implications for postoperative ileus. FASEB J. 20, 1930–1932.
Fukata, Y., Kaibuchi, K., and Amano, M. (2001). Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 32–39.
Furness, J.B., Hind, A.J., Ngui, K., Robbins, H.L., Clerc, N., Merrot, T., Tjandra, J.J., and Poole, D.P. (2006). The distribution of PKC isoforms in enteric neurons, muscle and interstitial cells of the human intestine. Histochem. Cell Biol. 126, 537–548.
Hemmings, D.G. (2006). Signal transduction underlying the vascular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 373, 18–29.
Hla, T. (2004). Physiological and pathological actions of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 513–520.
Huizinga, J.D., Thuneberg, L., Kluppel, M., Malysz, J., Mikkelsen, H.B., and Bernstein, A. (1995). W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 373, 347–349.
Huizinga, J.D., Zhu, Y., Ye, J., and Molleman, A. (2002). Highconductance chloride channels generate pacemaker currents in interstitial cells of Cajal. Gastroenterology 123, 1627–1636.
Kim, B.J., Lim, H.H., Yang, D.K., Jun, J.Y., Chang, I.Y., Park, C.S., So, I., Stanfield, P.R., and Kim, K.W. (2005). Melastatin-type transient receptor potential channel 7 is required for intestinal pacemaking activity. Gastroenterology 129, 1504–1517.
Mostafa, R.M., Moustafa, Y.M., and Hamdy, H. (2010). Interstitial cells of Cajal, the Maestro in health and disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 3239.
Murata, N., Sato, K., Kon, J., Tomura, H., Yanagita, M., Kuwabara, A., Ui, M., and Okajima, F. (2000). Interaction of sphingosine 1-phosphate with plasma components, including lipoproteins, regulates the lipid receptor-mediated actions. Biochem. J. 352, 809–815.
Nakayama, S., Kajioka, S., Goto, K., Takaki, M., and Liu, H.N. (2007). Calcium associated mechanisms in gut pacemaker activity. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 11, 958–968.
Nodai, A., Machida, T., Izumi, S., Hamaya, Y., Kohno, T., Igarashi, Y., Iizuka, K., Minami, M., and Hirafuji, M. (2007). Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces cyclooxygenase-2 via Ca2+-dependent, but MAPK-independent mechanism in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 80, 1768–1776.
Pfaff, M., Powaga, N., Akinci, S., Schütz, W., Banno, Y., Wiegand, S., Kummer, W., Wess, J., and Haberberger, R.V. (2005). Activation of the SPHK/S1P signalling pathway is coupled to muscarinic receptor-dependent regulation of peripheral airways. Respir. Res. 6, 48.
Porcher, C., Horowitz, B., Bayguinov, O., Ward, S.M., and Sanders, K.M. (2002). Constitutive expression and function of cyclooxygenase-2 in murine gastric muscles. Gastroenterology 122, 1442–1454.
Rosenfeldt, H.M., Amrani, Y., Watterson, K.R., Murthy, K.S., Panettieri, R.A.Jr., and Spiegel, S. (2003). Sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulates contraction of human airway smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 17, 1789–1799.
Salomone, S., Potts, E., Tyndall, S., Ip, P., Chun, J., Brinkmann, V., and Waeber, C. (2008). Analysis of sphingosine 1 phosphate receptors involved in constriction of isolated cerebral arteries with receptor null mice and pharmacological tools. Br. J. Pharmacol. 153, 140–147.
Sanchez, T., and Hla, T. (2004). Structural and functional charac teristics of S1P receptors. J. Cell. Biochem. 92, 913–922.
Sanders, K.M. (1996). A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 111, 492–515.
Song, H.J., Choi, T.S., Chung, F.Y., Park, S.Y., Ryu, J.S., Woo, J.G., Min, Y.S., Shin, C.Y., and Sohn, U.D. (2006). Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced signal transduction in cat esophagus smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cells 21, 42–51.
Spiegel, S., and Merrill, Jr. A. (1996). Sphingolipid metabolism and cell growth regulation. FASEB J. 10, 1388–1397.
Takuwa, Y., Okamoto, H., Takuwa, N., Gonda, K., Sugimoto, N., and Sakurada, S. (2001). Subtype-specific, differential activities of the EDG family receptors for sphingosine-1-phosphate, a novel lysophospholipid mediator. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 177, 3–11.
Van Koppen, C.J., Meyer zu Heringdorf, D., Alemany, R., and Jakobs, K.H. (2001). Sphingosine kinase-mediated calcium signaling by muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Life Sci. 68, 2535–2540.
Ward, S.M., Burns, A.J., Torihashi, S., and Sanders, K.M. (1994). Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J. Physiol. 480, 91–97.
Ward, S., Ordög, T., Koh, S., Baker, S.A., Jun, J., Amberg, G., Monaghan, K., and Sanders, K.M. (2000). Pacemaking in interstitial cells of Cajal depends upon calcium handling by endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. J. Physiol. 525, 355–361.
Watterson, K.R., Ratz, P.H., and Spiegel, S. (2005). The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in smooth muscle contraction. Cell. Signal. 17, 289–298.
Young, K., and Nahorski, S. (2002). Sphingosine 1-phosphate: a Ca2+ release mediator in the balance. Cell Calcium 32, 335–341.
Zhou, H., and Murthy, K.S. (2004). Distinctive G protein-dependent signaling in smooth muscle by sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors S1P1 and S1P2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 286, C1130–C1138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.D., Han, K.T., Lee, J. et al. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate on pacemaker activity of interstitial cells of Cajal from mouse small intestine. Mol Cells 35, 79–86 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-2282-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-2282-0