Abstract
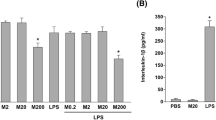
CD38, an ADP ribosyl cyclase, is a 45 kDa type II transmembrane protein having a short N-terminal cytoplasmic domain and a long C-terminal extracellular domain, expressed on the surface of various cells including macrophages, lymphocytes, and pancreatic β cells. It is known to be involved in cell adhesion, signal transduction and calcium signaling. In addition to its transmembrane form, CD38 is detectable in biological fluids in soluble forms. The mechanism by which CD38 is solubilized from the plasma membrane is not yet clarified. In this study, we found that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced CD38 upregulation and its extracellular release in J774 macrophage cells. Furthermore, it also increased CD38 expression at the mRNA level by activating the Janus kinase-signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway. However, LPS decreased the levels of CD38 in the plasma membrane by releasing CD38 into the culture supernatant. LPS-induced CD38 release was blocked by the metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor indicating that MMP-9 solubilizes CD38. In conclusion, the present findings demonstrate a potential mechanism by which C38 is solubilized from the plasma membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Flora, A., Franco, L., Guida, L., Bruzzone, S., Usai, C., and Zocchi, E. (2000). Topology of CD38. Chem. Immunol. 75, 79–98.
Deaglio, S., Dianzani, U., Horenstein, A.L., Fernandez, J.E., van Kooten, C., Bragardo, M., Funaro, A., Garbarino, G., Di Virgilio, F., Banchereau, J., et al. (1996). Human CD38 ligand. A 120-kDa protein predominantly expressed on endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 156, 727–734.
Deaglio, S., Morra, M., Mallone, R., Ausiello, C.M., Prager, E., Garbarino, G., Dianzani, U., Stockinger, H., and Malavasi, F. (1998). Human CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase) is a counter-receptor of CD31, an Ig superfamily member. J. Immunol. 160, 395–402.
Deryugina, E.I., and Quigley, J.P. (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25, 9–34.
Dianzani, U., Funaro, A., DiFranco, D., Garbarino, G., Bragardo, M., Redoglia, V., Buonfiglio, D., De Monte, L.B., Pileri, A., and Malavasi, F. (1994). Interaction between endothelium and CD4+CD45 RA+ lymphocytes. Role of the human CD38 molecule. J. Immunol. 153, 952–959.
Funaro, A., Spagnoli, G.C., Ausiello, C.M., Alessio, M., Roggero, S., Delia, D., Zaccolo, M., and Malavasi, F. (1990). Involvement of the multilineage CD38 molecule in a unique pathway of cell activation and proliferation. J. Immunol. 145, 2390–2396.
Funaro, A., Horenstein, A.L., Calosso, L., Morra, M., Tarocco, R.P., Franco, L., De Flora, A., and Malavasi, F. (1996). Identification and characterization of an active soluble form of human CD38 in normal and pathological fluids. Int. Immunol. 8, 1643–1650.
Horvath, C.M. (2004). The Jak-STAT pathway stimulated by interferon α or interferon β. Sci. STKE 2004, tr10.
Howard, M., Grimaldi, J.C., Bazan, J.F., Lund, F.E., Santos-Argumedo, L., Parkhouse, R.M., Walseth, T.F., and Lee, H.C. (1993). Formation and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose catalyzed by lymphocyte antigen CD38. Science 262, 1056–1059.
Inoue, S., Kontani, K., Tsujimoto, N., Kanda, Y., Hosoda, N., Hoshino, S., Hazeki, O., and Katada, T. (1997). Protein-tyrosine phosphorylation by IgG1 subclass CD38 monoclonal antibodies is mediated through stimulation of the FcgammaII receptors in human myeloid cell lines. J. Immunol. 159, 5226–5232.
Lee, H.C., and Aarhus, R. (1991). ADP-ribosyl cyclase: an enzyme that cyclizes NAD+ into a calcium-mobilizing metabolite. Cell Regul. 2, 203–209.
Lee, C., An, H.J., Kim, J.L., Lee, H., and Paik, S.G. (2009). Inhibitory effect of a phosphatidyl ethanolamine derivative on LPSinduced sepsis. Mol. Cells 27, 251–255.
Mallone, R., Ferrua, S., Morra, M., Zocchi, E., Mehta, K., Notarangelo, L.D., and Malavasi, F. (1998). Characterization of a CD38-like 78-kilodalton soluble protein released from B cell lines derived from patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 2821–2830.
Opdenakker, G., Van den Steen, P.E., and Van Damme, J. (2001). Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol. 22, 571–579.
Parks, W.C., Wilson, C.L., and Lopez-Boado, Y.S. (2004). Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 617–629.
Partida-Sanchez, S., Cockayne, D.A., Monard, S., Jacobson, E.L., Oppenheimer, N., Garvy, B., Kusser, K., Goodrich, S., Howard, M., Harmsen, A., et al. (2001). Cyclic ADP-ribose production by CD38 regulates intracellular calcium release, extracellular calcium influx and chemotaxis in neutrophils and is required for bacterial clearance in vivo. Nat. Med. 7, 1209–1216.
Sakaguchi, S., Negishi, H., Asagiri, M., Nakajima, C., Mizutani, T., Takaoka, A., Honda, K., and Taniguchi, T. (2003). Essential role of IRF-3 in lipopolysaccharide-induced interferon-β gene expression and endotoxin shock. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 306, 860–866.
Song, E.K., Lee, Y.R., Yu, H.N., Kim, U.H., Rah, S.Y., Park, K.H., Shim, I.K., Lee, S.J., Park, Y.M., Chung, W.G., et al. (2008). Extracellular NAD is a regulator for FcgR-mediated phagocytosis in murine macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 367, 156–161.
Song, E.K., Rah, S.Y., Lee, Y.R., Yoo, C.H., Kim, Y.R., Yeom, J.H., Park, K.H., Kim, J.S., Kim, U.H., and Han, M.K. (2011). Connexin-43 hemichannels mediate cyclic ADP-ribose generation and its Ca2+-mobilizing activity by NAD+/cyclic ADP-ribose transport. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 44480–44490.
Zielinska, W., Barata, H., and Chini, E.N. (2004). Metabolism of cyclic ADP-ribose: Zinc is an endogenous modulator of the cyclase/NAD glycohydrolase ratio of a CD38-like enzyme from human seminal fluid. Life Sci. 74, 1781–1790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CU., Song, EK., Yoo, CH. et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces CD38 expression and solubilization in J774 macrophage cells. Mol Cells 34, 573–576 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0263-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0263-3