Summary.
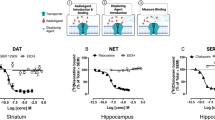
This purpose of this review will be to summarize the interactions between the endogenous amino acid taurine and ethyl alcohol (ethanol) in the central nervous system (CNS). Taurine is one of the most abundant amino acids in the CNS and plays an integral role in physiological processes such as osmoregulation, neuroprotection and neuromodulation. Both taurine and ethanol exert positive allosteric modulatory effects on neuronal ligand-gated chloride channels (i.e., GABAA and glycine receptors) as well as inhibitory effects on other ligand- and voltage-gated cation channels (i.e., NMDA and Ca2+ channels). Behavioral evidence suggests that taurine can alter the locomotor stimulatory, sedating, and motivational effects of ethanol in a strongly dose-dependent manner. Microdialysis studies have revealed that ethanol elevates extracellular levels of taurine in numerous brain regions, although the functional consequences of this phenomenon are currently unknown. Finally, taurine and several related molecules including the homotaurine derivative acamprosate (calcium acetylhomotaurinate) can reduce ethanol self-administration and relapse to drinking in both animals and humans. Taken together, these data suggest that the endogenous taurine system may be an important modulator of effects of ethanol on the nervous system, and may represent a novel therapeutic avenue for the development of medications to treat alcohol abuse and alcoholism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received November 21, 2001 Accepted January 4, 2002 Published online August 20, 2002
Acknowledgements This work was supported by funds from the State of California for medical research on alcohol and substance abuse through the University of California at San Francisco. The author wishes to thank Drs. C. W. Hodge and P. H. Janak for their support and helpful discussions.
Author's address: Dr. M. Foster Olive, Ernest Gallo Clinic and Research Center, Department of Neurology, University of California at San Francisco, 5858 Horton Street, Suite 200, Emeryville, California, U.S.A., Fax +1/510/985 3101, E-mail: folive@itsa.ucsf.edu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olive, M. Interactions between taurine and ethanol in the central nervous system. Amino Acids 23, 345–357 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0203-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0203-1