Abstract
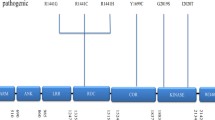
Mutations in the leucine rich repeat kinase 2 gene (LRRK2) are recognized as the most common cause of genetic Parkinsonism to date. The G2019S mutation has been implicated as an important determinant of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in both Ashkenazi Jewish and North African Arab populations with carrier frequency of 29.7% among familial and 6% in sporadic Ashkenazi Jewish PD cases. PD patients with the G2019S mutation display similar clinical characteristics to patients with sporadic PD. While the function of the LRRK2 protein has yet to be fully determined, its distribution coincides with brain areas most affected by PD. The G2019S mutation is believed to be responsible for up-regulation of LRRK2 kinase activity, which may ultimately play a role in neuronal loss. The utility of LRRK2 G2019S screening in family members of Ashkenazi PD patients is discussed. LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers without PD may be an ideal population for the study of possible neuroprotective strategies as they become available, and for furthering the understanding of the pathogenesis and long-term clinical outcomes of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasly JO, Toft M, Fernandez-Mata I et al (2005) Clinical features of LRRK2 associated Parkinson’s disease in central Norway. Ann Neurol 57:762–765
Adams RJ, Van Netten H, Schulzer M, Mak E et al (2005) PET in LRRK2 mutations: comparison to sporadic Parkinson’s disease and evidence for presymptomatic compensation. Brain 128:2777–2785
Bar-Shira A, Hutter C, Giladi N et al (2009) Ashkenazi Parkinson’s disease patients with the LRRK2 G2019S mutation share a common founder dating from the 2nd to 5th centuries. Neurogenetics (ahead of print)
Behar DM, Garrigan D, Kaplan ME, Mobasher Z et al (2004) Contrasting patterns of Y-chromosome variation in Ashkenazi Jewish and host non-Jewish European populations. Hum Genet 114:354–365
Bialecka M, Hui S, Klodowska-Duda G, Opala G et al (2005) Analysis of LRRK2 G2019S mutation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 390(1):1–3
Bonifati V (2007) LRRK2 low-penetrance mutations (Gly2019Ser) and risk alleles (Gly2385Arg)-linking familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 32:1700–1708
Bosgraaf L, Van Haastert PJM (2003) Roc, a Ras/GTPase domain in complex proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1643:5–10
Bras JM, Guerreiro RJ, Ribeiro MH, Januario C et al (2005) G2019S dardarin substitution is a common cause of Parkinson’s disease in a Portuguese cohort. Mov Disord 20(12):1653–1655
Brice A (2005) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease: LRRK2 on the rise. Brain 128:2760–2762
Carmine Belin A, Westerlund M, Sydow O, Lundströmer K et al (2006) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) mutations in a Swedish Parkinson cohort and a healthy nonagenarian. Mov Disord 10:1731–1734
Change N, Mercier G, Lucotte G (2007) Genetic screening of the G2019S mutation of the LRRK2 gene in Southwest European, North African and Sepharadi Jew subjects. Genet Test 12:1–8
Chen-Plotkin AS, Yuan W, Anderson BS, McCarty C (2008) Corticobasal syndrome and primary progressive aphasia as manifestations of LRRK2 gene mutations. Neurology 70:521–527
Cho JW, Kim SY, Park SS, Kim HJ et al (2009) The G2019S LRRK2 mutation is rare in Korean patients with Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 34(1):53–55
Clark LN, Wang Y, Karlins E, Saito L et al (2006) Frequency of LRRK2 mutations in early and late onset Parkinson disease. Neurology 67:1786–1791
Colombo R (2000) Age estimate of the N370S mutation causing Gaucher disease in Ashkenazi Jews and European populations: a reappraisal of haplotype data. Am J Hum Gent 66:692–697
De Rosa A, Criscuolo C, Mancini P, De Martino M et al (2009) Genetic screening for LRRK2 gene G2019S mutation in Parkinson’s disease patients from Southern Italy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(3):242–244
Deng H, Le W, Guo Y, Hunter CB (2005) Genetic and clinical identification of Parkinson’s disease patients with LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Ann Neurol 57(6):933–934
Deng H, Le W, Guo Y, Hunter CB et al (2006) Genetic analysis of LRRK2 mutations in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 251:102–106
Deng J, Lewis PA, Greggio E, Sluch E et al (2008) Structure of the ROC domain from the Parkinson’s disease-associated leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 reveals a dimeric GTPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(5):1499–1504
Djaldetti R, Hassin-Baer S, Farrer MJ, Vilariño–Güell C et al (2008) Clinical characteristics of Parkinson’s disease among Jewish Ethnic groups in Israel. J Neural Transm 115(9):1279–1284
Dupré N, Rivière JB, Myers RH, Provencher P et al (2007) LRRK2 is not a significant cause of Parkinson’s disease in French-Canadians. Can J Neurol Sci 34(3):333–335
Farrer M, Stone J, Mata IF, Lincoln S et al (2005) LRRK2 mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 65:738–740
Ferreira JJ, Guedes LC, Rosa MM, Coelho M et al (2007) High prevalence of LRRK2 mutations in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Portugal. Mov Disord 22(8):1194–1201
Floris G, Cannas A, Solla P, Murro MR et al (2008) Genetic analysis for five LRRK2 mutations in a Sardinian parkinsonian population: Importance of G2019S and R1441C mutations in sporadic Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord (ahead of print)
Funalot B, Nichols WC, Pérez-Tur J, Mercier G, Lucotte G (2006) Genetic screening for two LRRK2 mutations in French patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Genet Test 10(4):290–293
Gaig C, Ezquerra M, Marti MJ, Munoz E (2006) LRRK2 mutations in Spanish patients with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 63:377–382
Gaig C, Ezquerra M, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F (2008) Screening for the LRRK2 G2019S mutation and codon-1441 mutations in a pathological series of parkinsonian syndromes and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Neurol Sci 270(1–2):94–98
Gandhi PN, Chen SG, Wilson-Delfosse AL (2009) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2): a key player in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 87:1283–1295
Gan-Or Z, Giladi N, Rozovski U et al (2008) Genotype-phenotype correlations between GBA mutations and Parkinson disease risk and onset. Neurology 70:2277–2283
Gan-Or Z, Bar-Shira A, Mirelman A, Gurevich T et al (2009) LRRK2 and GBA mutations differentially affect the initial presentation of Parkinson disease. Neurogenetics (ahead of print)
Gao L, Gómez-Garre P, Díaz-Corrales FJ, Carrillo F et al (2009) Prevalence and clinical features of LRRK2 mutations in patients with Parkinson’s disease in southern Spain. Eur J Neurol (ahead of print)
Gilks WP, Abou-Sleiman PM, Gandhi S, Jain S et al (2005) A common LRRK2 mutation in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 365:415–416
Goldwurm S, Di Fonzo A, Simons EJ, Rohe CF et al (2005) The G6055A (G2019S) mutation in LRRK2 is frequent in both early and late onset Parkinson’s disease and originates from a common ancestor. J Med Genet 42:e65
Goldwurm S, Zini M, Di Fonzo A, De Gaspari D et al (2006) LRRK2 G2019S mutation and Parkinson’s disease: a clinical, neuropsychological and neuropsychiatric study in a large Italian sample. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:410–419
Goldwurm S, Zini M, Mariani L, Tesei S et al (2007) Evaluation of LRRK2 G2019S penetrance. Neurology 68:1141–1143
Gorostidi A, Ruiz-Martínez J, de Munain AL, Alzualde A, Massó JF (2009) LRRK2 G2019S and R1441G mutations associated with Parkinson’s disease are common in the Basque Country, but relative prevalence is determined by ethnicity. Neurogenetics 10(2):157–159
Gosal D, Ross OA, Wiley J, Brent Irvine J et al (2005) Clinical traits of LRRK2 associated Parkinson’s disease in Ireland: a link between familial and idiopathic PD. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:349–352
Greggio E, Cookson MR (2009) Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 mutations and Parkinson’s disease: three questions. ASN Neuro 14(1):13–24
Greggio E, Zambrano I, Kaganovich A, Beilina A et al (2008) The Parkinson disease associated Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK) is a dimmer that undergoes intramolecular autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem 283(24):16906–16914
Hardy J, Huabian C, Cookson MR, Gwinn-Hardy K et al (2006) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 60:389–398
Hassin-Baer S, Laitman Y, Azizi E, Molchadski I (2009) The leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) G2019S substitution mutation. J Neurol 256:483–487
Healy DG, Falchi M, O’Sullivan SS, Borifati V (2008) Phenotype, genotype and worldwide genetic penetrance of LRRK2 associated Parkinson’s disease: a case control study. Lancet Neurol 7:583–590
Huang Y, Halliday GM, Vandebona H, Mellick GD et al (2007) Prevalence and clinical features of common LRRK2 mutations in Australians with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22(7):982–989
Hulihan MM, Ishihara-Paul L, Kachergus J, Warren L et al (2008) LRRK2 Gly2019Ser penetrance in Arab-Berber patients from Tunisia: a case control genetic study. Lancet Neurol 7:591–594
Illarioshkin SN, Shadrina MI, Slominsky PA, Bespalova EV et al (2007) A common leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene mutation in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Russia. Eur J Neurol 14(4):413–417
Infante J, Rodríguez E, Combarros O, Mateo I et al (2006) LRRK2 G2019S is a common mutation in Spanish patients with late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 395(3):224–226
Isaias IU, Benti R, Goldwurm S, Zini M et al (2006) Striatal dopamine transporter binding in Parkinson’s disease associated with LRRK2 Gly2019Ser mutation. Mov Disord 21(8):1144–1147
Ishihara L, Gibson RA, Warre L, Amour R et al (2006a) Screening for LRRK2 G2019S and clinical comparison of Tunisian and North American Caucasian Parkinson’s disease families. Mov Disord 22:55–61
Ishihara L, Warren L, Gibson R, Amouri R et al (2006b) Clinical features of Parkinson disease patients with homozygous Leucin-rich repeat kinase 2 G2019S mutations. Arch Neurol 63:1250–1254
Johnson J, Paisán-Ruíz C, Lopez G, Crews C et al (2007) Comprehensive screening of a North American Parkinson’s disease cohort for LRRK2 mutation. Neurodegener Dis 4(5):386–391
Kachergus J, Mata IF, Hulihan M, Taylor JP et al (2005) Identification of a novel LRRK2 mutation linked to autosomal dominant Parkinsonism: evidence of a common founder across European populations. Am J Hum Genet 76:672–680
Kalinderi K, Fidani L, Bostantjopoulou S, Katsarou Z, Kotsis A (2007) The G2019S LRRK2 mutation is uncommon amongst Greek patients with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 14(10):1088–1090
Kay DM, Zabetian CP, Factor SA, Nutt JG et al (2006a) Parkinson’s disease and LRRK2: frequency of a common mutation in US movement disorder clinics. Mov Disord 21(4):519–523
Kay DM, Bird TD, Zabetian CP, Factor SA et al (2006b) Validity and utility of a LRRK2 G2019S mutation test for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Genet Test 3:221–227
Khan NL, Jain S, Lynch JM, Pavese N et al (2005) Mutations in the gene LRRK2 encoding dardarin (PARK8) cause familial Parkinson’s disease: clinical, pathological, olfactory and functional imaging and genetic data. Brain 128:2786–2796
Klein C, Schlossmacher MG (2007) Parkinson disease, 10 years after its genetic revolution. Neurology 69:2093–2104
Klein C, Lohmann-Hedrich K, Rogavena E, Schlossmacher MG, Lang AE (2007) Deciphering the role of heterozygous mutations in genes associated with Parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol 6:652–662
Latourelle J, Sun M, Lew MF, Suchowersky O et al (2008) The Gly2019Ser mutation in LRRK2 is not fully penetrant in familial Parkinson’s disease: the GenePD study. BMC Med; 5; 6; 32
Lesage S, Ibanez P, Lohmann E, Pollak P et al (2005a) G2019S LRRK2 mutation in French and North African families with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 58:784–787
Lesage S, Leutenegger AL, Ibanez P, Janin S et al (2005b) LRRK2 haplotype analysis in European and North African families with Parkinson disease: a common founder for the G2019S mutation dating from the 13th century. Am J Hum Genet 77:330–332
Lesage S, Durr A, Tazir M, Lohmann E et al (2006) LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson’s disease in North African Arabs. N Engl J Med 354:422–423
Lesage S, Belarbi S, Troiano A, Condroyer C et al (2008) Is the common LRRK2 G2019S mutation related to dyskinesias in North African Parkinson disease? Neurology 71:1550–1552
Lin CH, Tzen KY, Yu CY, Tai CH et al (2008) LRRK2 mutation in familial Parkinson’s disease in a Taiwanese population: clinical, PET, and functional studies. J Biomed Sci 15(5):661–667
Lu YW, Tan EK (2008) Molecular biology changes associated with LRRK2 mutations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 86:1895–1901
MacLeod D, Dowman J, Hammond R, Leete T et al (2006) The familial Parkinsonism gene LRRK2 regulates neurite process morphology. Neuron 52(4):587–593
Marongiu R, Ghezzi D, Ialongo T, Soleti F et al (2006) Frequency and phenotypes of LRRK2 G2019S mutation in Italian patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21(8):1232–1235
Mata IF, Kachergus JM, Taylor JP, Lincoln S et al (2005) LRRK2 pathogenic substitutions in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 6:171–177
Mata IF, Ross OA, Kachergus J, Huerta C et al (2006) LRRK2 mutations are a common cause of Parkinson’s disease in Spain. Eur J Neurol 13:391–394
Mata IF, Cosentino C, Marca V, Torres L et al (2009) LRRK2 mutations in patients with Parkinson’s disease from Peru and Uruguay. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(5):370–373
Melrose H (2008) Update on functional biology of LRRK2. Future Neurol 3(6):669–681
Miklossy J, Arai T, Guo JP, Klegeris A et al (2006) LRRK2 expression in normal and pathological human brain and in human cell lines. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:953–963
Möller JC, Rissling I, Mylius V, Höft C et al (2008) The prevalence of the G2019S and R1441C/G/H mutations in LRRK2 in German patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 15(7):743–745
Munhoz RP, Wakutani Y, Marras C, Helio TA et al (2008) The G2019S LRRK2 mutation in Brazilian patients with Parkinson’s disease: phenotype in monozygotic twins. Mov Disord 23:290–294
Nandhagopal R, Mak E, Schulzer M, McKenzie J et al (2008) Progression of dopaminergic dysfunction in LRRK2 kindred. A multitracer PET study. Neurology 71:1790–1795
Nichols WC, Pankratz N, Hernandez D, Paisan-Ruiz C et al (2005) Genetic screening for a single common LRRK2 mutation in familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 365:410–412
Orr-Urtreger A, Shifrin C, Rozovski U, Rosner S et al (2007) The LRRK2 G2019S mutation in Ashkenazi Jews with Parkinson disease. Neurology 69:1595–1602
Ozelius LJ, Senthil G, Saunders-Pullman R, Ohmann E et al (2006) LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med 354:424–425
Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP et al (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44(4):595–600
Papapetropoulos S, Adi N, Shehadeh L, Bishopric N et al (2008) Is the G2019S LRRK2 mutation common in all southern European populations? J Clin Neurosci 15(9):1027–1030
Papaptropoulos S, Singer C, Ross OA, Toft M et al (2006) Clinical heterogeneity of the LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Arch Neurol 63:1242–1246
Patra B, Parsian A, Racette BA et al (2009) LRRK2 gene G2019S mutation and SNP’s (haplotypes) in subtypes of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15:175–180
Pavese N, Brooks DJ (2008) Imaging neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (ahead of print)
Pchelina SN, Yakimovski AF, Ivanova ON, Emelianov AK et al (2006) G2019S LRRK2 mutation in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Russia. Mov Disord 21(12):2234–2236
Pchelina SN, Yakimovski AF, Emelyanov AK, Ivanova ON et al (2008) Screening for LRRK2 mutations in patients with Parkinson’s disease in Russia: identification of a novel LRRK2 variant. Eur J Neurol 15:692–696
Perez-Pastene C, Cobb SA, Díaz-Grez F, Hulihan MM et al (2007) LRRK2 mutations in South America: a study of Chilean Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 422(3):193–197
Perry G, Zhu X, Babar AK, Siedlak SL et al (2008) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 colocalizes with α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease, but not Tau-containing deposits in Tauopathies. Neurodegener Dis 5:222–224
Pimentel MM, Moura KC, Abdalla CB, Pereira JS et al (2008) A study of LRRK2 mutations and Parkinson’s disease in Brazil. Neurosci Lett 433(1):17–21
Punia S, Behari M, Govindappa ST, Swaminath PV et al (2006) Absence/rarity of commonly reported LRRK2 mutations in Indian Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 409:83–88
Rajput A, Dickson DW, Robinson CA, Ross OA et al (2006) Parkinsonism, LRRK2 G2019S, and tau neuropathology. Neurology 67:1506–1508
Ross OA, Toft M, Whittle AJ et al (2006) LRRK2 and Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 59:388–393
Santpere G, Ferrer I (2009) LRRK2 and neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 117:227–246
Saunders-Pullman R, Lipton RB, Senthil G, Katz M et al (2006) Increased frequency of the LRRK2 G2019S mutation in an elderly Ashkenazi Jewish population is not associated with dementia. Neurosci Lett 402:92–96
Shojaee S, Sina F, Farboodi N, Fazlali Z et al (2009) A clinic-based screening of mutations in exons 31, 34, 35, 41, and 48 of LRRK2 in Iranian Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 24(7):1023–1027
Silveita-Moriyama L, Guedes LC, Kingsbury A, Ayling H et al (2008) Hyposmia in G2019S LRRK2-related Parkinsonism. Neurology 71:1021–1026
Spanaki C, Latsoudis H, Plaitakis A (2006) LRRK2 mutations on Crete: R1441H associated with PD evolving to PSP. Neurology 67(8):1518–1519
Squillaro T, Cambi F, Ciacci G, Rossi S et al (2007) Frequency of the LRRK2 G2019S mutation in Italian patients affected by Parkinson’s disease. J Hum Genet 52(3):201–204
Tan EK, Shen H, Tan LC, Farrer M et al (2005) The G2019S LRRK2 mutation is uncommon in an Asian cohort of Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 384(3):327–329
Tanner CM, Ottman R, Goldman SM, Ellen J et al (1999) Parkinson disease in twins. FAMA 281:341–346
Tomiyama H, Li Y, Funayama M, Hasegawa K (2006) Clinicogenetic study of mutations in LRRK2 exon 41 in Parkinson’s disease patients from 18 countries. Mov Disord 8:1102–1108
Tompkins MM, Hill WD (1997) Contribution of somal Lewy bodies to neuronal death. Brain Res 24:24–29
Warren L, Gibson R, Ishihara L, Elango R et al (2008) A founding LRRK2 haplotype shared by Tunisian, US, European and Middle Eastern families with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:77–80
West AB, Moore DJ, Biskup S, Bugayenko A et al (2005) Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity. PNAS 102(46):16842–16847
Williams-Gray CH, Goris A, Foltynie T, Brown J et al (2006) Prevalence of the LRRK2 G2019S mutation in a UK community based idiopathic Parkinson’s disease cohort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(5):665–667
Zabetian C, Samii A, Mosely AD, Roberts AW et al (2005) A clinical based study of the LRRK2 gene in Parkinson’s disease yields new mutations. Neurology 65:741–744
Zabetian C, Hutter CM, Yearout D, Lopez AN et al (2006a) LRRK2 G2019S in families with Parkinson disease who originated from Europe and the Middle East: evidence of two distinct founding events beginning two millennia ago. Am J Hum Genet 79:752–758
Zabetian CP, Morino H, Ujike H, Yamamoto M et al (2006b) Identification and haplotype analysis of LRRK2 G2019S in Japanese with Parkinson disease. Neurology 67:697–699
Zhu X, Babar A, Siedlak SL, Yang Q et al (2006) LRRK2 in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Mol Neurodegener 1:17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thaler, A., Ash, E., Gan-Or, Z. et al. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation as the cause of Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi Jews. J Neural Transm 116, 1473–1482 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0303-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0303-0