Abstract
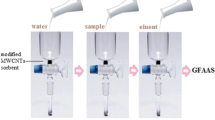
Ion pair solid phase extraction was applied to the simultaneous preconcentration of iron and antimony. The ion pairs consisting of FeCl4 − or SbCl4 − anions and the benzyldimethyltetradecyl ammonium cation were formed on the surface of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, then eluted with nitric acid, and the elements finally quantified by ETAAS. The adsorption capacities of the impregnated MWCNTs are 9.2 mg g−1 for iron and 27.5 mg g−1 for antimony. The following analytical figures of merit were determined for iron and antimony, respectively: Enrichment factors of 210 and 230, assay precisions of ±5.3 % and ±4.8 %, linear calibration plots from 0.7 to 9.4 and 13.0 to 190 ng L−1, and detection limits of 0.17 and 3.5 ng L−1. The method was applied to the determination of iron and antimony in human hair, synthetic sample, and to the certified reference materials gold ore (MA-1b) and trace elements in water (SRM 1643d).

ᅟ


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shakerian F, Dadfarnia S, Shabani AMH (2009) Separation, preconcentration and measurement of inorganic iron species by cloud point extraction and flow injection flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Iran Chem Soc 6:594–601
Tašev K, Karadjova I, Arpadjan S, Cvetković J, Stafilov T (2006) Liquid/liquid extraction and column solid phase extraction procedures for iron species determination in wines. Food Control 17:484–488
Lepp NW, Edwards R, Jones KC (1995) Heavy metal in soil, 2nd ed. Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow
Toghill KE, Lu M, Compton RG (2011) Electroanalytical determination of antimony. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:3057–3076
Jahandari S, Taher MA, Fazelirad H, Sheikhshoai I (2013) Anodic stripping voltammetry of silver(I) using a carbon paste electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 180:347–354
Fazelirad H, Taher MA (2013) Ligandless, ion pair-based and ultrasound assisted emulsification solidified floating organic drop microextraction for simultaneous preconcentration of ultra-trace amounts of gold and thallium and determination by GFAAS. Talanta 103:375–383
Yalcinkaya O, Kalfa OM, Turker AR (2010) Chelating agent free solid phase extraction (CAF-SPE) method for separation and/or preconcentration of iron(III) ions. Turk J Chem 34:207–217
Mirzajani R, Pourreza N, Kiasat A, Abdollahzadeh R (2013) Solid phase extraction and determination of Fe(III) in some vegetables and natural water samples using a new inorganic/organic hybrid adsorbent. Int J Environ Anal Chem. doi:10.1080/03067319.2013.823490
Pourreza N, Rastegarzadeh S, Kiasat AR, Yahyavi H (2012) Spectrophotometric determination of iron(II) after solid phase extraction of its 2,2′ bipyridine complex on silica gel-polyethylene glycol. J Spectrosc 2013:1–6
Khayatian G, Kolaie HRAV, Nasiri F, Atashkar B, Hassanpoor S (2010) Determination of total iron in environmental samples by solid phase extraction with dimethyl(E)-2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-butenedioate. J Chin Chem Soc 57:118–123
Kassem MA, Amin AS (2013) Spectrophotometric determination of iron in environmental and food samples using solid phase extraction. Food Chem 141:1941–1946
Cui Y, Hu Z-J, Yang J-X, Gao H-W (2012) Novel phenyl-iminodiacetic acid grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes for solid phase extraction of iron, copper and lead ions from aqueous medium. Microchim Acta 176:359–366
Shakerian F, Dadfarnia S, Shabani A, Rohani M (2008) MultiSimplex optimization of on-line sorbent proconcentration and determination of iron by FI-AAS and microcolumn of immobilized ferron. Talanta 77:551–555
Amin AS, Gouda AA (2008) Utility of solid-phase spectrophotometry for determination of dissolved iron(II) and iron(III) using 2,3-dichloro-6-(3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)quinoxaline. Talanta 76:1241–1245
Zeng C, Yang F, Zhou N (2011) Hollow fiber supported liquid membrane extraction coupled with thermospray flame furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of Sb(III) and Sb(V) in environmental and biological samples. Microchem J 98:307–311
Ozdemir N, Soylak M, Elci L, Dogan M (2004) Speciation analysis of inorganic Sb(III) and Sb(V) ions by using mini column filled with Amberlite XAD-8 resin. Anal Chim Acta 505:37–41
Zhang L, Morita Y, Sakuragawa A, Isozaki A (2007) Inorganic speciation of As(III, V), Se(IV, VI) and Sb(III, V) in natural water with GF-AAS using solid phase extraction technology. Talanta 72:723–729
Zhang L, Ishi D, Shitou K, Morita Y, Isozaki A (2005) Simultaneous multi-element analysis of total As, Se and Sb on titanium dioxide by slurry sampling-graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 68:336–342
Garbos S, Rzepecka M, Bulska E, Hulanicki A (1999) Microcolumn sorption of antimony(III) chelate for antimony speciation studies. Spectrochim Acta B 54:873–881
Menegário AA, Smichowski P, Tonello PS, Polla G, Oliveira EP, Santelli RE (2008) On-line redox speciation analysis of antimony using l-proline immobilized on controlled pore glass and hydride generation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry for detection. Anal Chim Acta 625:131–136
Rojas FS, Ojeda CB, Pavón JMC (2007) Preconcentration of inorganic antimony(III) in environmental samples by PSTH-Dowex microcolumn and determination by FI-ETAAS. Talanta 72:951–956
Menegário AA, Silva AJ, Pozzi E, Durrant SF, Abreu CH (2006) On-line determination of Sb(III) and total Sb using baker’s yeast immobilized on polyurethane foam and hydride generation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 61:1074–1079
Wu H, Wang X, Liu B, Liu Y, Li S, Lu J, Tian J, Zhao W, Yang Z (2011) Simultaneous speciation of inorganic arsenic and antimony in water samples by hydride generation-double channel atomic fluorescence spectrometry with on-line solid-phase extraction using single-walled carbon nanotubes micro-column. Spectrochim Acta B 66:74–80
Yu C, Cai Q, Guo Z-X, Yang Z, Khoo SB (2002) Antimony speciation by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using solid phase extraction cartridges. Analyst 127:1380–1385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazelirad, H., Taher, M.A. Preconcentration of ultra-trace amounts of iron and antimony using ion pair solid phase extraction with modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 181, 655–662 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1169-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1169-x