Summary
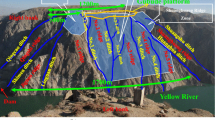
A study is presented of the slow time dependent movement of the deep-seated deformation of Rosone. This rock slope, which mainly consists of gneiss, is located on the Italian side of Western Alps and has been affected by recurrent instability phenomena. Due to these, and also to the presence of various villages and man-made structures (such as a hydroelectric power plant), a significant amount of geological and geomechanical data has been collected in this area. They have led to the assumption that the slow movement develops along a deep-seated sliding surface, involving a volume of rock between 22 and 35 million cubic meters. To check these hypotheses, and to get some insight into the causes of the phenomenon, a series of non-linear, time-dependent analyses has been carried out through the finite element method. The slow movement of the rock mass, and the gradual loss of its mechanical properties with increasing deformation, has been accounted for in the calculations by means of a visco-plastic constitutive law, allowing for strain softening effects. The results of analyses lead to some conclusions on the causes of the observed movements, among which the possible influence of the groundwater pore pressure is likely to play an important role.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forlati, F., Gioda, G. & Scavia, C. Finite Element Analysis of a Deep-seated Slope Deformation. Rock Mech Rock Engng 34, 135–159 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006030170019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006030170019