Abstract
Background
Rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance was determined in 2,112 Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis B who were followed up for at least 15 years.
Methods
Patients had a median age of 37 years and included 1,431 (67.8 %) men. Median values were AST/ALT, 43/62 IU/L; platelet counts, 182 × 103/mm3; HBsAg, 3,400 IU/mL; and hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, 6.2 log copies/mL. Factors influencing HBsAg seroclearance were evaluated by the Cox proportional model and annual rate of HBsAg seroclearance by the Kaplan–Meier life table method.
Results
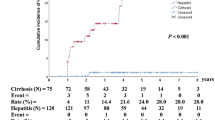
The overall annual rate of HBsAg seroclearance was 1.75 % in 2,112 patients; it was 1.65 % in 1,130 untreated and 2.05 % in 982 treated patients (p = 0.289). In untreated patients, seroclearance was influenced by age, no HBV infections in third-degree or closer relatives, and HBsAg levels in univariate analysis. Seroclearance was influenced by a median age ≥50 years [relative risk (RR) 1.61 (p = 0.018)] and HBsAg ≤2,000 IU/mL [RR 1.77 (p = 0.014)] in multivariate analysis. In treated patients, age, male gender, no HBV infections in third-degree or closer relatives, interferon therapy, chronic hepatitis, high AST and γ-GTP levels, low platelet counts, hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-negative status, low HBsAg levels and the wild-type precore sequence significantly influenced HBsAg seroclearance. In multivariate analysis, no family history [RR 2.22 (p = 0.006)], interferon treatment [RR 3.15 (p < 0.001)], and HBeAg-negative status [RR 3.75 (p < 0.001)] significantly influenced HBsAg seroclearance.
Conclusions
In this retrospective cohort study, the annual rate of HBsAg seroclearance was 1.65 % in untreated patients and 2.05 % in treated patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ETV:
-
Entecavir
- HBeAg:
-
Hepatitis B e antigen
- HBcrAg:
-
Hepatitis B core-related antigen
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HBV DNA:
-
Hepatitis B virus DNA
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- LAM:
-
Lamivudine
References
Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1118–29.
Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–45.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73.
Huo TI, Wu JC, Lee PC, Chau GY, Lui WY, Tsay SH, et al. Sero-clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen in chronic carriers does not necessarily imply a good prognosis. Hepatology. 1998;28:231–6.
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:678–86.
Arase Y, Ikeda K, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, et al. Long-term outcome after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Am J Med. 2006;119:71.e9–16.
Chen YC, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1084–9.
Chu CM, Liaw YF. HBsAg seroclearance in asymptomatic carriers of high endemic areas: appreciably high rates during a long-term follow-up. Hepatology. 2007;45:1187–92.
Yuen MF, Wong DK, Fung J, Ip P, But D, Hung I, et al. HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in Asian patients: replicative level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1192–9.
Suzuki F, Arase Y, Suzuki Y, Akuta N, Sezaki H, Seko Y, et al. Long-term efficacy of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:814–22.
Kobayashi M, Suzuki F, Akuta N, Hosaka T, Sezaki H, Yatsuji H, et al. Loss of hepatitis B surface antigen from the serum of patients with chronic hepatitis treated with lamivudine. J Med Virol. 2007;79:1472–7.
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Sezaki H, Hosaka T, Someya T, et al. Favorable efficacy of long-term lamivudine therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: an 8-year follow-up study. J Med Virol. 2005;75:491–8.
Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, Seko Y, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen during long-term nucleot(s)ide analog treatment in chronic hepatitis B: results from a nine-year longitudinal study. J Gastroenterol. 2012. doi:10.1007/s00535-012-0688-7.
Ahn SH, Park YN, Park JY, Chang HY, Lee JM, Shin JE, et al. Long-term clinical and histological outcomes in patients with spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. J Hepatol. 2005;42:188–94.
Kim JH, Lee JH, Park SJ, Bae MH, Kim JH, Kim do Y, et al. Factors associated with natural seroclearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and prognosis after seroclearance: a prospective follow-up study. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008;55:578–81.
Liaw YF, Leung N, Kao JH, Piratvisuth T, Gane E, Han KH, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2008 update. Hepatol Int. 2008;2:263–83.
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lu SN, Jen CL, Wang LY, et al. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:474–82.
Kato Y, Nakao K, Hamasaki K, Kato H, Nakata K, Kusumoto Y, et al. Spontaneous loss of hepatitis B surface antigen in chronic carriers, based on a long-term follow-up study in Goto Islands, Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2000;35:201–5.
McMahon BJ, Holck P, Bulkow L, Snowball M. Serologic and clinical outcomes of 1536 Alaska natives chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:759–68.
Simonetti J, Bulkow L, McMahon BJ, Homan C, Snowball M, Negus S, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 2010;51:1531–7.
Shiraki K, Yoshihara N, Sakurai M, Eto T, Kawana T. Acute hepatitis B in infants born to carrier mothers with the antibody to hepatitis B e antigen. J Pediatr. 1980;97:768–70.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan.
Conflict of interest
These authors disclose the following: Dr. Kumada reports having received investigator, lecture, and consulting fees from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., MSD KK, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharma International, Dentsu Sudler, and Hennessey Inc. Dr. Ikeda reports having received investigator, lecture, and consulting fees from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, M., Hosaka, T., Suzuki, F. et al. Seroclearance rate of hepatitis B surface antigen in 2,112 patients with chronic hepatitis in Japan during long-term follow-up. J Gastroenterol 49, 538–546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0821-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0821-2