Abstract
Background
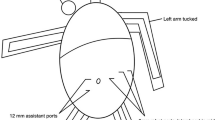
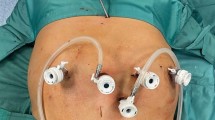
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure (RYGBP) is in many countries the gold standard for obtaining long-lasting weight reduction and improvement of obesity-related comorbidities. However, performing this operation by standard laparoscopic techniques requires important surgical skills because of the anastomoses involved. The da Vinci surgical robot system with its enhanced degrees of freedom in motion and three-dimensional vision is designed to overcome the difficulties encountered in traditional laparoscopic surgery with suturing and delicate tissue handling.
Methods
For this study, 45 patients (9 men) with a mean body mass index (BMI) of 44.2 (range, 35.1–55.4) underwent RYGBP with the aid of the da Vinci robot system. They were compared with 45 consecutive patients with a mean BMI of 43.9 (range, 35.1–56.2) who underwent a laparoscopic RYGBP by the same surgeon during the same period.
Results
Overall, the total operating time was shorter for the laparoscopic cases (127 vs 212 min; p < 0.05). However, the last 10 robotic cases were performed in the same time span as the laparoscopic cases (136 vs 127 min). The total robotic setup time remained constant at about 30 min. There were no differences in postoperative complications between the two groups in terms of anastomotic leakage or stenosis. In the robotic group, more conversions to open surgery were noted. Early in the study, four patients (9%) had to undergo conversion to standard laparoscopic techniques due to inadequate setup of the robotic arms. Five patients (11%), however, had to undergo conversion to open surgery because of intestinal laceration during manipulation of the intestines with the robotic instruments. The costs were higher for robotic surgery than for standard laparoscopic RYGBP, mainly because of the extra equipment used, such as ultrasonic devices.
Conclusion
The RYGBP procedure can be performed safely with the da Vinci robot after a learning curve of about 35 cases. At this writing, however, it is not clear whether the da Vinci system offers a real advantage over standard laparoscopic techniques.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinbrook R (2004) Surgery for severe obesity. New Eng J Med 350:1075–1079
Schauer P (2005) Gastric bypass for severe obesity: approaches and outcomes. Surg Obes Rel Dis 1:297–300
Wittgrove AC, Clark GW (1999) Laparoscopic gastric bypass: a five-year prospective study of 500 patients followed from 3–60 months. Obes Surg 9:123–143
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S, Hammad G, Gourash W (2003) The learning curve for laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in 100 cases. Surg Endosc 17:212–218
Oliak D, Ballantyne GH, Weber P, Wasielewski A, Davies RJ, Schmidt HJ (2003) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: defining the learning curve. Surg Endosc 17:405–408
Champion JK, Hunt T, DeLisle N (1999) Laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in morbid obesity. Obes Surg 9:123–144
Higa K, Ho T, Boone K (2001) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: technique and 3-year follow-up. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 11:377–382
Higa K, Boone K (2005) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: hand-sewn gastrojejunostomy technique. In: Inabnet W, Demaria E, Ikkramuddin S (eds) Laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia pp 107–115
Jacobsen G, Berger R, Horgan S (2003) The role of robotic surgery in morbid obesity. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 13:279–283
Muhlmann G, Klaus A, Kirchmayr W, Wykypiel H, Unger A, Holler E, Nehoda H, Aigner F, Weiss HG (2003) Da Vinci robotic-assisted laparoscopic bariatric surgery: is it justified in a routine setting? Obes Surg 13:848–854
Ali MR, Bhaskerrao B, Wolfe BM (2005) Robot-assisted laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 19:468–472
Mohr C, Nadzam G, Curet M ( 2005) Totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Arch Surg 140:779–785
Moser F, Horgan S (2004) Robotically assisted bariatric surgery. Am J Surg 188:38S–44S
Olbers T, Lonroth H, Fagevik-Olsen M, Lundell L (2003) Laparoscopic gastric bypass: development of technique, respiratory function, and long-term outcome. Obes Surg 13:364–370
Tichansky D, DeMaria E (2005) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: linear stapled technique In: Inabnet W, Demaria E, Ikkramuddin S (eds) Laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia pp 102–105
De La Torre R, Scott JS (2005) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y divided gastric bypass with transgastric anvil placement. In: Inabnet W, Demaria E, Ikkramuddin S (eds) Laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia pp 116–122
Hubens G, Coveliers J, Balliu L, Ruppert M, Vaneerdeweg W (2003) A performance study comparing manual and robotically assisted laparoscopic surgery using the da Vinci system. Surg Endosc 18:1595–1599
Dakin GF, Gagner M (2003) Comparison of laparoscopic skills performance between standard instruments and two surgical robotic systems. Surg Endosc 17:574–579
Nio D, Bemelman W, Boer K, Dunker M, Gouma D, Gulik T (2002) Efficiency of manual versus robotical (Zeus) assisted laparoscopic surgery in the performance of standardized tasks. Surg Endosc 16:412–415
Giulianotti PC, Coratti A, Angelini M, Stranar F, Cecconi S, Bakstracci T, Caravaglios C (2003) Robotics in general surgery: personal experience in a large community hospital. Arch Surg 138:777–784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hubens, G., Balliu, L., Ruppert, M. et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure performed with the da Vinci robot system: is it worth it?. Surg Endosc 22, 1690–1696 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9698-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9698-6