Abstract
Background
Increased intraabdominal pressure can be found after major abdominal trauma and necrotizing pancreatitis and is used during laparoscopic surgery. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of the aldosterone receptor antagonist (potassium canrenoate) on renal hemodynamics and urinary output in pigs during increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP).
Methods
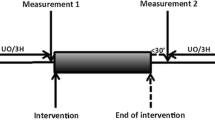
The IAP was kept at 30 mmHg for 3 h by instillation of Ringer’s solution into the peritoneal cavity. Eight animals were treated with potassium canrenoate and eight animals served as controls. Renal blood flow, hormones in femoral artery blood, and the urinary output were measured.
Results
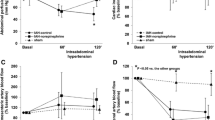
The administration of potassium canrenoate was followed by increased aldosterone concentrations in arterial blood, increased blood concentration of potassium, and increased concentration of sodium in the urine, indicating satisfactory inhibition of aldosterone. Potassium canrenoate did not cause changes in cardiac output and arterial pressure. It did not affect the renal vascular resistance that increased at an IAP of 30 mmHg, or the renal blood flow that remained constant during the experiments. The group treated with potassium canrenoate had higher mean urinary output than the controls, but the difference was not significant.
Conclusion
Increased IAP in pigs is associated with markedly reduced urinary output and increased serum concentrations of aldosterone. Although the urinary output did not increase significantly, the increased sodium concentration in the urine of canrenoate-treated animals suggests that the high blood level of aldosterone contributes to the oliguria under increased IAP.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
GL Bloomfield CR Blocher IF Fakhry DA Sica HJ Sugerman (1997) ArticleTitleElevated intraabdominal pressure increases plasma renin activity and aldosterone levels J Trauma 42 997–1005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkslCntLY%3D Occurrence Handle9210531
SE Bradley GP Bradley (1947) ArticleTitleThe effect of increased intraabdominal pressure renal function in man J Clin Invest 26 1010–1022
CB Caldwell JJ Ricotta (1987) ArticleTitleChanges in visceral blood flow with elevated intraabdominal pressure J Surg Res 43 14–20 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiB2MrpsFc%3D Occurrence Handle3599981
CB Caldwell JJ Ricotta (1986) ArticleTitleEvaluation of intraabdominal pressure and renal hemodynamics Curr Surg 43 495–498 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiC3cvjs1Y%3D Occurrence Handle3802901
HC Coombs (1922) ArticleTitleThe mechanism of the regulation of intraabdominal pressure Am J Physiol 61 159–170
DJ Cullen JP Coyle R Teplick MC Long (1989) ArticleTitleCardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal effects of massively increased intraabdominal pressure in critically ill patients Crit Care Med 17 118–121 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC38%2FhsVM%3D Occurrence Handle2914444
LN Diebel RF Wilson SA Dulchavsky J Saxe (1992) ArticleTitleEffect of increased intraabdominal pressure on hepatic arterial, portal venous, and hepatic microcirculatory blood flow J Trauma 33 279–282 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A2szotlw%3D Occurrence Handle1507294
FF Gudmundsson HG Gislason A Dicko A Horn A Viste K Grong K Svanes (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure on gastrointestinal blood flow in pigs Surg Endosc 15 854–860 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004640090090 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrksFSiuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11443466
FF Gudmundsson HG Gislason OL Myking A Viste K Grong K Svanes (2002) ArticleTitleHormonal changes related to decreased renal blood flow and low urine output under prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure in pigs Eur J Surg 168 178–186 Occurrence Handle10.1080/110241502320127801 Occurrence Handle12182244
FF Gudmundsson A Viste OL Myking L Bostad K Grong K Svanes (2003) ArticleTitleRole of angiotensin-II under prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP) in pigs Surg Endosc 17 1092–1097 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00464-002-9123-0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2czos1Cgtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12632126
ME Gunning JR Ingelfinger AJ King BM Brenner (1995) Vasoactive peptides and the kidney Brenner and Rector’s The Kidney WB Saunders Philadelphia 242–244
PK Harman IL Kron HD McLachlan AE Freedlender SP Nolan (1982) ArticleTitleElevated intraabdominal pressure and renal function Ann Surg 196 594–597 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyD387ksV0%3D Occurrence Handle7125746
MA Heymann BD Payne JI Hoffman AM Rudolph (1977) ArticleTitleBlood flow measurements with radionuclide-labelled particles Prog Cardiovasc Dis 20 55–79 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXkvFyht74%3D Occurrence Handle877305
AD Ivankovich DJ Miletich RF Albrecht HJ Heyman RF Bonnet (1975) ArticleTitleCardiovascular effects of intraperitoneal insufflation with carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide in the dog Anesthesiology 42 281–287 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSqC3cjitl0%3D Occurrence Handle123134
A Karim (1978) ArticleTitleSpironolactone: disposition, metabolism, pharmacodynamics and bioavailability Drug Metab Rev 8 151–188 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXkvF2gtbc%3D Occurrence Handle363379
J Kashtan JF Green EQ Parsons JW Holcroft (1981) ArticleTitleHemodynamic effect of increased abdominal pressure J Surg Res 30 249–255 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-4804(81)90156-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6C1MrnvFE%3D Occurrence Handle7230773
K Kojima K Yamamoto H Fujioka H Kaneko (1985) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of spironolactone and potassium canrenoate in humans J Pharmacobiodynam 8 161–166 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXitFGntrY%3D
W Krause J Karras W Seifert (1983) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of canrenone after oral administration of spironolactone and intravenous injection of canrenoate-K in healthy man Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25 449–453 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXksVyksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle6653638
R Mo OL Myking P Lund-Johansen P Omvik (1994) ArticleTitleThe Bergen blood pressure study: in appropriately low levels of circulating atrial natriuretic peptide in offspring of hypertensive families Blood Press 3 223–230 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmt1OktLc%3D Occurrence Handle7661920
JD Richardson JK Trinkle (1976) ArticleTitleHemodynamic and respiratory alterations with increased intraabdominal pressure J Surg Res 20 401–404 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-4804(76)90112-8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSmB3Mflt1M%3D Occurrence Handle933497
BH Saggi HJ Sugerman RR Ivatury GL Bloomfield (1998) ArticleTitleAbdominal compartment syndrome J Trauma 45 597–609 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvit1Wkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9751558
M Sugrue MD Buist F Hourihan S Deane A Bauman K Hillman (1995) ArticleTitleProspective study of intraabdominal hypertension and renal function after laparotomy Br J Surg 82 235–238 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB28fnsl0%3D Occurrence Handle7749700
EC Wendt (1876) ArticleTitleUber den Einfluss des intraabdominalen Druckes auf die Absonderungsgeschwindigkeit des Harnes Arch Heilkunde 17 527
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00464-004-0090-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudmundsson, F.F., Viste, A., Myking, O.L. et al. Effects of the aldosterone receptor antagonist potassium canrenoate on renal blood flow and urinary output during prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP) in pigs. Surg Endosc 18, 1528–1534 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9295-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9295-2