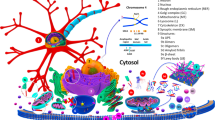
Abstract
The name synphilin-1 comes from its identification as an alpha-synuclein-interacting protein (SNCAIP) in yeast two-hybrid screens. Since alpha-synuclein (PARK1) was the first gene identified as causing inherited forms of Parkinson’s disease (PD), synphilin-1 was quickly implicated in neurodegeneration in PD. Recently, the first genetic evidence for the direct contribution of synphilin-1 in the pathogenesis of PD has been defined with the identification of an R621C mutation as a susceptibility factor for PD in two German patients. Extensive in vitro studies have determined the physiological functions of synphilin-1, identified novel synphilin-1-interacting proteins, and linked synphilin-1 to ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. The present article provides an overview of the current concepts of the role of synphilin-1 in synaptic function and protein degradation and in the molecular mechanisms leading to neurodegeneration in PD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandopadhyay R, de Silva R, Khan N, Graham E, Vaughan J, Engelender S, Ross C, Morris H, Morris C, Wood NW, Daniel S, Lees A (2001) No pathogenic mutations in the synphilin-1 gene in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 307:125–127
Chung KK, Zhang Y, Lim KL, Tanaka Y, Huang H, Gao J, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2001) Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1: implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 7:1144–1150
Engelender S, Kaminsky Z, Guo X, Sharp AH, Amaravi RK, Kleiderlein JJ, Margolis RL, Troncoso JC, Lanahan AA, Worley PF, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ross CA (1999) Synphilin-1 associates with alpha-synuclein and promotes the formation of cytosolic inclusions. Nat Genet 22:110–114
Engelender S, Wanner T, Kleiderlein JJ, Wakabayashi K, Tsuji S, Takahashi H, Ashworth R, Margolis RL, Ross CA (2000) Organization of the human synphilin-1 gene, a candidate for Parkinson’s disease. Mamm Genome 11:763–766
Farrer M, Destee A, Levecque C, Singleton A, Engelender S, Becquet E, Mouroux V, Richard F, Defebvre L, Crook R, Hernandz D, Ross CA, Hardy J, Amouyel P, Chartier-Harlin MC (2001) Genetic analysis of synphilin-1 in familial Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 8:317–323
Fortun J, Dunn WA, Joy S, Li J, Notterpek L (2003) Emerging role for autophagy in the removal of aggresomes in Schwann cells. J Neurosci 23:10672–10680
Gai WP, Yuan HX, Li XQ, Power JTH, Blumbergs PC, Jensen PH (2004) In situ and in vitro study of colocalization and segregation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin and lipids in Lewy bodies. Exp Neurol 166:324–333
Hicks AA, Petursson H, Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Johannsdottir HS, Sainz J, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K, Sveinbjornsdottir S (2002) A susceptibility gene for late-onset idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 52:549–555
Iseki E, Takayama N, Furakawa Y, Marui W, Nakai T, Miura S, Ueda K, Kosaka K (2002) Immunohistochemical study of synphilin-1 in brains of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies—synphilin-1 is non-specifically implicated in the formation of different neuroanl cytoskeletal inclusions. Neurosci Lett 326:211–215
Ito T, Niwa JI, Hishikawa N, Ishigaki S, Doyu M, Sobue G (2003) Dorfin localizes to Lewy bodies and ubiquitylates synphilin-1. J Biol Chem 278:29106–29114
Johnston JA, Ward CL, Kopito RR (1998) Aggresomes: a cellular response to misfolded proteins. J Cell Biol 143:1883–1898
Junn E, Lee SS, Suhr UT, Mouradian MM (2002) Parkin accumulation in aggresomes due to proteasome impairment. J Biol Chem 277:47870–47877
Katsuse O, Iseki E, Marui W, Kosaka K (2003) Developmental stages of cortical Lewy bodies and their relation to axonal transport blockage in brains of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol Sci 211:29–35
Kawamata H, McLean PJ, Sharma N, Hyman BT (2001) Interaction of alpha-synuclein and synphilin-1: effect of Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations. J Neurochem 77:929–934
Kopito RR (2000) Aggresomes, inclusion bodies and protein aggregation. Trends Cell Biol 10:524–530
Krüger R, Riess O, Eberhardt O, Schulz JB (2002) Parkinson’s disease: does one biochemical pathway fit all genes. Trends Mol Med 8:236–240
Krüger R, Marx FP, Strauss KM, Dawson S, Riess O, Schulz JB (2003) Identification of the proteasomal subunit S6-ATPase as a novel synphilin-1 interacting protein. Progr No. 410.3. Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner. Society for Neuroscience, Washington
Lee G, Junn E, Tanaka M, Kim YM, Mouradian MM (2002) Synphilin-1 degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and effects on cell survival. J Neurochem 83:346–352
Lee G, Tanaka M, Park K, Lee SS, Kim YM, Junn E, Lee SH, Mouradian MM (2004) Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation regulates alpha-synuclein/synphilin-1 interaction and inclusion body formation. J Biol Chem 279:6834–6839
Liani E, Eyal A, Shemer R, Berg D, Franck T, Riess O, Ross CA, Rott R, Engelender S (2004) Ubiquitylation of synphilin-1 and alpha-synuclein by SIAH proteins and their presence in Lewy bodies imply a role in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 101:5500–5505
Maraganore DM, Farrer MJ, Lesnick TG, Andrade M de, Bower JH, Hernandez D, Hardy JA, Rocca WA (2003) Case-control study of the alpha-synuclein interacting protein gene and Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:1233–1239
Marx FP, Holzmann C, Strauss KM, Li L, Eberhardt O, Cookson MR, Hernandez D, Farrer MJ, Kachergus J, Engelender S, Ross CA, Berger K, Schöls L, Schulz JB, Riess O, Krüger R (2003) Identification and functional characterization of a novel R621C mutation in the synphilin-1 gene in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 12:1223–1231
McNaught KS, Jenner P (2001) Proteasomal function is impaired in substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 297:191–194
Murray IVJ, Medford MA, Guan HP, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2003) Synphilin in normal human brains and in synucleinopathies: studies with new antibodies. Acta Neuropathol 105:177–184
Nagano Y, Yamashita H, Takahashi T, Kishida S, Nakamura T, Iseki E, Hattori N, Mizuno Y, Kikuchi A, Matsumoto M (2003) Siah-1 facilitates ubiquitination and degradation of synphilin-1. J Biol Chem 278:51504–51514
Neystat M, Rzhetskaya M, Kholodilov N, Burke RE (2002) Analysis of synphilin-1 and synuclein interactions by yeast two-hybrid beta-galactosidase liquid assay. Neurosci Lett 325:119–123
O’Farrell C, Murphy DD, Petrucelli L, Singleton AB, Hussey J, Farrer M, Hardy J, Dickson DW, Cookson MR (2001) Transfected synphilin-1 forms cytoplasmic inclusions in HEK293 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 97:94–102
O’Farrell C, Pickford F, Vink L, McGowan E, Cookson MR (2002) Sequence conservation between mouse and human synphilin-1. Neurosci Lett 322:9–12
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Rudolph A, Shults C, Conneally PM, Foroud T (2002) Genome screen to identify susceptibility genes for Parkinson disease in a sample without parkin mutations. Am J Hum Genet 71:124–135
Ribeiro CS, Carneiro K, Ross CA, Menezes JR, Engelender S (2002) Synphilin-1 is developmentally localized to synaptic terminals, and its association with synaptic vesicles is modulated by alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 277:23927–23933
Schlossmacher MG, Frosch MP, Gai WP, Medina M, Sharma N, Forno L, Ochiishi T, Shimura H, Sharon R, Hattori N, Langston JW, Mizuno Y, Hyman BT, Selkoe DJ, Kosik KS (2002) Parkin localizes to the Lewy bodies of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 160:1655–1667
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH, Goetz CG, Small GW, Masterman D, Mastaglia F, Laing NG, Stajich JM, Slotterbeck B, Booze MW, Ribble RC, Rampersaud E, West SG, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Roses AD, Haines JL, Scott BL, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA (2001) Complete genomic screen in Parkinson disease: evidence for multiple genes. J Am Med Assoc 286:2239–2244
Tanaka M, Kim YM, Lee G, Junn E, Iwatsubo T, Mouradian MM (2003) Aggresomes formed by alpha-synuclein and synphilin-1 are cytoprotective. J Biol Chem 279:4625–4631
Tanji K, Toki T, Tamo W, Imaizumi T, Matsumiya T, Mori F, Takahashi H, Satoh K, Wakabayashi K (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates synphilin-1 in vitro. Neuropathology 23:199–202
Taylor JP, Tanaka F, Robitschek J, Sandoval M, Taye A, Markovic-Plese S, Fischbeck K (2003) Aggresomes protect cells by enhancing the degradation of toxic polyglutamine-containing protein. Hum Mol Genet 12:749–757
Wakabayashi K, Engelender S, Yoshimoto M, Tsuji S, Ross CA, Takahashi H (2000) Synphilin-1 is present in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 47:521–523
Wakabayashi K, Engelender S, Tanaka Y, Yoshimoto M, Mori F, Tsuji S, Ross CA, Takahashi H (2002) Immunocytochemical localization of synphilin-1, an alpha-synuclein-associated protein, in neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol 103:209–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work of R.K. on synphilin-1 is supported by a grant from the Fritz Thyssen Foundation, a grant from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Fö 01KS9602), and the Interdisciplinary Center of Clinical Research Tübingen (IZKF)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krüger, R. The role of synphilin-1 in synaptic function and protein degradation. Cell Tissue Res 318, 195–199 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0953-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0953-z