Abstract.
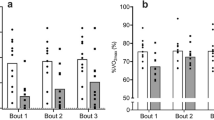
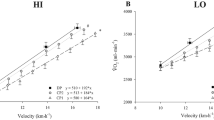
The purpose of the study was to compare selected physiological responses during singles tennis match play and continuous running at a similar mean oxygen uptake (\(\dot V{\rm O}_{\rm 2} \) ). The study consisted of two main parts, which were separated by 1 week. In the first part, 12 nationally ranked senior tennis players [six females and six males; 47.2 (6.6) years old and 47.0 (5.4) years old, respectively] each completed a 2-h singles tennis match (TE). Mean \(\dot V{\rm O}_{\rm 2} \) during TE [23.1 (3.1) ml·kg–1·min–1 for the women and 25.6 (2.8) ml·kg–1·min–1 for the men] was measured by a portable spirometry-telemetry system and corresponded to 56% (women) or 54% (men) of their respective maximum \(\dot V{\rm O}_{\rm 2} \) . In the second part, the relative \(\dot V{\rm O}_{\rm 2} \) data measured during TE were used to set a similar workload during a 2-h treadmill run at a constant level (RU). At the measured time points, heart rate [140.1 (15.5) beats·min–1 vs 126.4 (15.1) beats·min–1], lactate concentration [1.53 (0.65) mmol·l–1 vs 1.01 (0.38) mmol·l–1] and glucose concentration [5.45 (0.84) mmol·l–1 vs 4.34 (0.56) mmol·l–1] in capillary blood, as well as the respiratory exchange ratio [0.93 (0.03) vs 0.88 (0.03)], were higher (P<0.05) in TE compared to RU. Serum concentrations of free fatty acids increased (P<0.05) during both work loads [from 0.25 (0.15) mmol·l–1 to 1.31 (0.44) mmol·l–1 in TE and from 0.22 (0.17) mmol·l–1 to 1.24 (0.35) mmol·l–1 in RU]. Post-exercise urine concentrations of epinephrine [0.17 (0.14) µmol·l–1 vs 0.08 (0.04) µmol·l–1] and norepinephrine [1.27 (0.59) µmol·l–1 vs. 0.55 (0.33) µmol·l–1] were higher in TE (P<0.05). These results indicate a stronger metabolic emphasis on glycolysis and glycogenolysis and an overall enhanced sympathoadrenal activity during tennis match play compared to continuous running exercise at a similar mean \(\dot V{\rm O}_{\rm 2} \) .
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrauti, A., Bergeron, M.F., Pluim, B.M. et al. Physiological responses in tennis and running with similar oxygen uptake. Eur J Appl Physiol 85, 27–33 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100425
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100425