Abstract
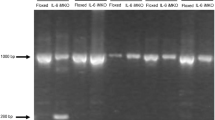
It is well known that exhaustive exercise increases serum and skeletal muscle IL-6 concentrations. However, the effect of exhaustive exercise on the concentrations of other cytokines in the muscle and in the adipose tissue is controversial. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of exhaustive exercise on mRNA and protein expression of IL-10, TNF-α and IL-6 in different types of skeletal muscle (EDL, soleus) and in two different depots of white adipose tissue (mesenteric–MEAT and retroperitoneal–RPAT). Rats were killed by decapitation immediately (E0 group, n = 6), 2 (E2 group, n = 6) and 6 (E6 group, n = 6) hours after the exhaustion protocol, which consisted of running on a treadmill (approximately 70% VO2max for 50 min and then subsequently at an elevated rate that increased at 1 m/min every minute, until exhaustion). The control group (C group, n = 6) was not subjected to exercise. Cytokine protein expression increased in EDL, soleus, MEAT and RPAT from all exercised groups, as detected by ELISA. EDL IL-10 and TNF-α expression was higher than that of the soleus. The IL-10/TNF-α ratio was increased in the skeletal muscle, especially in EDL, but it was found to be decreased in the adipose tissue. These results show that exhaustive exercise presents a different effect depending on the tissue which is analysed: in the muscle, it induces an anti-inflammatory effect, especially in type 2 fibres, while the pro-inflammatory effect prevails in adipose tissue, possibly contributing to increased lipolysis to provide energy for the exercising muscle.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banzet S, Koulmann N, Simler N, Birot O, Sanchez H, Chapot R, Peinnequin A, Bigard X (2005) Fiber-type specificity of interleukin-6 gene transcription during muscle contraction in rat: association with calcineurin activity. J Physiol 566:839–847. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089193
Banzet S, Koulmann N, Sanchez H, Serrurier B, Peinnequin A, Alonso A, Bigard X (2007) Contraction-induced interleukin-6 transcription in rat slow-type muscle is partly dependent on calcineurin activation. J Cell Physiol 210:596–601. doi:10.1002/jcp.20854
Beutler B, Greenwald D, Hulmes JD, Chang M, Pan YC, Mathison J, Ulevitch R, Cerami A (1985) Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature 316(6028):552–554
Bury TB, Louis R, Radermecker MF, Pirnay F (1996) Blood mononuclear cells mobilization and cytokines secretion during prolonged exercises. Int J Sports Med 17:156–160. doi:10.1055/s-2007-972825
Camus G, Nys M, Poortmans JR, Venneman I, Monfils T, Deby-Dupont G, Juchmès-Ferir A, Deby C, Lamy M, Duchateau J (1998) Endotoxaemia, production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation following strenuous exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 79:62–68. doi:10.1007/s004210050474
Cawthorn WP, Sethi JK (2008) TNF-alpha and adipocyte biology. FEBS Lett 582:117–131. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.051
Chan MH, Carey AL, Watt MJ, Febbraio MA (2004) Cytokine gene expression in human skeletal muscle during concentric contraction: evidence that IL-8, like IL-6, is influenced by glycogen availability. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R322–R327. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00030.2004
Dokka S, Shi X, Leonard S, Wang L, Castranova V, Rojanasakul Y (2001) Interleukin-10-mediated inhibition of free radical generation in macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280:L1196–L1202
Enevoldsen LH, Stallknecht B, Langfort J, Petersen LN, Holm C, Ploug T, Galbo H (2001) The effect of exercise training on hormone-sensitive lipase in rat intra-abdominal adipose tissue and muscle. J Physiol 536(Pt 3):871–877. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00871.x
Febbraio MA, Pedersen BK (2002) Muscle-derived interleukin-6: mechanisms for activation and possible biological roles. FASEB J 16:1335–1347. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0876rev
Febbraio MA, Ott P, Nielsen HB, Steensberg A, Keller C, Krustrup P, Secher NH, Pedersen BK (2003) Hepatosplanchnic clearance of interleukin-6 in humans during exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E397–E402
Fischer CP (2006) Interleukin-6 in acute exercise and training: what is the biological relevance? Exerc Immunol Rev 12:6–33
Gesta S, Blüher M, Yamamoto Y, Norris AW, Berndt J, Kralisch S, Boucher J, Lewis C, Kahn CR (2006) Evidence for a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6676–6681. doi:10.1073/pnas.0601752103
Gomez-Merino D, Drogou D, Guezennec CY, Chennaoui M (2007) Effects of chronic exercise on cytokine production in white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of rats. Cytokine 40:23–29. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2007.07.188
Helge JW, Stallknecht B, Pedersen BK, Galbo H, Kiens B, Richter EA (2003) The effect of graded exercise on IL-6 release and glucose uptake in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 546:299–305. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030437
Hirose L, Nosaka K, Newton M, Laveder A, Kano M, Peake J, Suzuki K (2004) Changes in inflammatory mediators following eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Exerc Immunol Rev 10:75–90
Hiscock N, Chan MH, Bisucci T, Darby IA, Febbraio MA (2004) Skeletal myocytes are a source of interleukin-6 mRNA expression and protein release during contraction: evidence of fiber type specificity. FASEB J 18:992–994
Ikeda M, Ohira H, Toyama Y, Katagiri T, Sakakibara B (2007) Effect of intestinal microflora on the production of interleukin 10 and prostaglandin E(2) in serum and Kupffer cells from germ free and conventional mice. J Clin Biochem Nutr 41:169–174. doi:10.3164/jcbn.2007023
Jonsdottir IH, Schjerling P, Ostrowski K, Asp S, Richter EA, Pedersen BK (2000) Muscle contractions induce interleukin-6 mRNA production in rat skeletal muscles. J Physiol 528:157–163. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00157.x
Kaur K, Sharma AK, Dhingra S, Singal PK (2006) Interplay of TNF-alpha and IL-10 in regulating oxidative stress in isolated adult cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41:1023–1030. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.005
Kim HJ, Higashimori T, Park SY, Choi H, Dong J, Kim YJ, Noh HL, Cho YR, Cline G, Kim YB, Kim JK (2004) Differential effects of interleukin-6 and -10 on skeletal muscle and liver insulin action in vivo. Diabetes 53:1060–1067. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.4.1060
Lafontan M, Berlan M (2003) Do regional differences in adipocyte biology provide new pathophysiological insights? Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:276–283. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00132-9
Leonidou L, Mouzaki A, Michalaki M, DeLastic AL, Kyriazopoulou V, Bassaris HP, Gogos CA (2007) Cytokine production and hospital mortality in patients with sepsis induced stress hyperglycemia. J Infect 55:340–346. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2007.05.177
Lira F, Rosa J, Yamashita A, Koyama C, Batista M Jr, Seelaender M (2009) Endurance training induces depot-specific changes in IL-10/TNF-alpha ratio in rat. Cytokine 45:80–85. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.10.018
Mastorakos G, Pavlatou M (2005) Exercise as a stress model and the interplay between the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal and the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axes. Horm Metab Res 37:577–584. doi:10.1055/s-2005-870426
Mathur N, Pedersen BK (2008) Exercise as a mean to control low-grade systemic inflammation. Mediat Inflamm Epub 2009(Jan)
Meador BM, Krzyszton CP, Johnson RW, Huey KA (2008) Effects of IL-10 and age on IL-6, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha responses in mouse skeletal and cardiac muscle to an acute inflammatory insult. J Appl Physiol 104:991–997. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01079.2007
Nieman DC, Davis JM, Henson DA, Gross SJ, Dumke CL, Utter AC, Vinci DM, Carson JA, Brown A, McAnulty SR, McAnulty LS, Triplett NT (2005) Muscle cytokine mRNA changes after 2.5 h of cycling: influence of carbohydrate. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:1283–1290. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000175054.99588.b1
Northoff H, Berg A (1991) Immunologic mediators as parameters of the reaction to strenuous exercise. Int J Sports Med 12:S9–S15. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1024743
Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Asp S, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK (1999) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol 515:287–291. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.287ad.x
Park PH, Huang H, McMullen MR, Bryan K, Nagy LE (2008) Activation of cyclic-AMP response element binding protein contributes to adiponectin-stimulated interleukin-10 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 83:1258–1266. doi:10.1189/jlb.0907631
Pedersen BK (2007) IL-6 signalling in exercise and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1295–1297. doi:10.1042/BST0351295
Pedersen BK, Fischer CP (2007) Physiological roles of muscle-derived interleukin-6 in response to exercise. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 10(3):265–271. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e3280ebb5b3
Penkowa M, Keller C, Keller P, Jauffred S, Pedersen BK (2003) Immunohistochemical detection of interleukin-6 in human skeletal muscle fibers following exercise. FASEB J 17:2166–2168
Peterson JM, Feeback KD, Baas JH, Pizza FX (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 101:1394–1399. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01453.2005
Plomgaard P, Penkowa M, Pedersen BK (2005) Fiber type specific expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-18 in human skeletal muscles. Exerc Immunol Rev 11:53–63
Pond C (1999) Physiological specialisation of adipose tissue. Prog Lipid Res 38:225–248. doi:10.1016/S0163-7827(99)00003-X
Raue U, Slivka D, Jemiolo B, Hollon C, Trappe S (2007) Proteolytic gene expression differs at rest and after resistance exercise between young and old women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62:1407–1412
Roher N, Samokhvalov V, Díaz M, MacKenzie S, Klip A, Planas JV (2008) The proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases the amount of glucose transporter-4 at the surface of muscle cells independently of changes in interleukin-6. Endocrinology 149:1880–1889. doi:10.1210/en.2007-1045
Ruan H, Lodish HF (2003) Insulin resistance in adipose tissue: direct and indirect effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:447–455. doi:10.1016/S1359-6101(03)00052-2
Schottelius AJ, Mayo MW, Sartor RB, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) Interleukin-10 signaling blocks inhibitor of kappaB kinase activity and nuclear factor kappaB DNA binding. J Biol Chem 274:31868–31874. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.45.31868
Schulz KH, Gold SM, Witte J, Bartsch K, Lang UE, Hellweg R, Reer R, Braumann KM, Heesen C (2004) Impact of aerobic training on immune-endocrine parameters, neurotrophic factors, quality of life and coordinative function in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 225:11–18. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2004.06.009
Sjorgreen B,Nordenskjold T, Holmgren H, Wollestron J (1938) Beitrag zur kentnis des lebenrhythmik. Pflugers Arch Ges Phys 240–247
Sprenger H, Jacobs C, Nain M, Gressner AM, Prinz H, Wesemann W, Gemsa D (1992) Enhanced release of cytokines, interleukin-2 receptors, and neopterin after long-distance running. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 63:188–195. doi:10.1016/0090-1229(92)90012-D
Starkie RL, Angus DJ, Rolland J, Hargreaves M, Febbraio MA (2000) Effect of prolonged, submaximal exercise and carbohydrate ingestion on monocyte intracellular cytokine production in humans. J Physiol 528:647–655. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00647.x
Steensberg A, Fischer CP, Keller C, Moller K, Pedersen BK (2003) IL-6 enhances plasma IL-1ra, IL-10, and cortisol in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E433–E437
Suganami T, Tanimoto-Koyama K, Nishida J, Itoh M, Yuan X, Mizuarai S, Kotani H, Yamaoka S, Miyake K, Aoe S, Kamei Y, Ogawa Y (2007) Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:84–91. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000251608.09329.9a
Suzuki K, Yamada M, Kurakake S, Okamura N, Yamaya K, Liu Q, Kudoh S, Kowatari K, Nakaji S, Sugawara K (2000) Circulating cytokines and hormones with immunosuppressive but neutrophil-priming potentials rise after endurance exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 81:281–287. doi:10.1007/s004210050044
Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, Liu Q, Kurakake S, Okamura N, Kumae T, Umeda T, Sugawara K (2003) Impact of a competitive marathon race on systemic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:348–355. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000048861.57899.04
Suzuki K, Peake J, Nosaka K, Okutsu M, Abbiss CR, Surriano R, Bishop D, Quod MJ, Lee H, Martin DT, Laursen PB (2006) Changes in markers of muscle damage, inflammation and HSP70 after an Ironman triathlon race. Eur J Appl Physiol 98:525–534. doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0296-4
Torti FM, Dieckmann B, Beutler B, Cerami A, Ringold GM (1985) A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science 229(4716):867–869
Trujillo ME, Sullivan S, Harten I, Schneider SH, Greenberg AS, Fried SK (2004) Interleukin-6 regulates human adipose tissue lipid metabolism and leptin production in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5577–5582. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0603
Vohl MC, Sladek R, Robitaille J, Gurd S, Marceau P, Richard D, Hudson TJ, Tchernof A (2004) A survey of genes differentially expressed in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in men. Obes Res 12:1217–1222. doi:10.1038/oby.2004.153
Zaldivar F, Wang-Rodriguez J, Nemet D, Schwindt C, Galassetti P, Mills PJ, Wilson LD, Cooper DM (2006) Constitutive pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine and growth factor response to exercise in leukocytes. J Appl Physiol 100:1124–1133. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00562.2005
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Emilia Ribeiro for her technical assistance. This work was supported by Grant No. 04/11588-0 and 05/01445-0 from the FAPESP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosa Neto, J.C., Lira, F.S., Oyama, L.M. et al. Exhaustive exercise causes an anti-inflammatory effect in skeletal muscle and a pro-inflammatory effect in adipose tissue in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 106, 697–704 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1070-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1070-1