Abstract
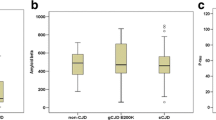
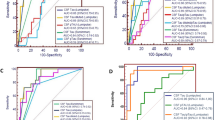
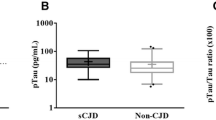
One of the largest clusters of genetic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (gCJD) is found among Jews of Libyan origin in Israel and is linked to the E200K mutation in PRNP (gCJDE200K). The aim of this study was to compare the levels of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers, Tau and 14-3-3 proteins, between gCJDE200K patients, sporadic CJD (sCJD) patients and non-CJD controls in Israel between the years 1996–2006. The levels of Tau and 14-3-3 proteins in CSF were measured by ELISA and immunoblotting, respectively. CSF Tau levels were similar in gCJDE200K and sCJD, both were significantly higher than in controls [1,107 ± 470 pg/ml [33/46 (72%)] of the cases >1,000 pg/ml, 1,280 ± 580 pg/ml [25/30 (83.3%)], and 354 ± 338 pg/ml [17/243 (6.9%)], respectively, p < 0.001]. 14-3-3 was detected in CSF of 41/53 (77%) of each gCJDE200K and sCJD patients tested, but only in 70/417 (16.8%) of controls (p < 0.001). An inverse correlation was found between disease duration and Tau levels in both gCJDE200K and sCJD (r = −0.464 and r = −0.284). No difference was found in Tau or 14-3-3 between the various codon 129 genotypes. We conclude that CSF biomarkers, Tau and 14-3-3, may be used in the diagnosis in both patients’ populations, presenting a similar sensitivity yet Tau assay having higher specificity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alperovitch A, Zerr I, Pocchiari M, Mitrova E, de Pedro Cuesta J, Hegyi I, Collins S, Kretzschmar H, van Duijn C, Will RG (1999) Codon 129 prion protein genotype and sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Lancet 353:1673–1674
Buerger K, Otto M, Teipel SJ, Zinkowski R, Blennow K, DeBernardis J, Kerkman D, Schröder J, Schönknecht P, Cepek L, McCulloch C, Möller HJ, Wiltfang J, Kretzschmar H, Hampel H (2006) Dissociation between CSF total Tau and Tau protein phosphorylated at threonine 231 in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:10–5
Castellani RJ, Colucci M, Xie Z, Zou W, Li C, Parchi P, Capellari S, Pastore M, Rahbar MH, Chen SG, Gambetti P (2004) Sensitivity of 14-3-3 protein test varies in subtypes of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 63:436–442
Cepek L, Steinacker P, Mollenhauer B, Wiese B, Ciesielczyk B, Bibl M, Wiltfang J, Zerr I, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar HA, Poser S, Otto M (2005) Follow-up investigations of Tau protein and S-100B levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19:376–382
Chapman J, Korczyn AD (1991) Genetic and environmental factors determining the development of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Libyan Jews. Neuroepidemiology 10:228–231
Gabizon R, Rosenmann H, Meiner Z, Kahana I, Kahana E, Shugart Y, Ott J, Prusiner SB (1993) Mutation and polymorphism of the prion protein gene in Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). Am J Hum Genet 53:828–835
Geschwind MD, Martindale J, Miller D, DeArmond SJ, Uyehara-Lock J, Gaskin D, Kramer JH, Barbaro NM, Miller BL (2003) Challenging the clinical utility of the 14-3-3 protein for the diagnosis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 60:813–816
Glodzik-Sobanska L, Pirraglia E, Brys M, de Santi S, Mosconi L, Rich KE, Switalski R, Saint Louis L, Sadowski MJ, Martiniuk F, Mehta P, Pratico D, Zinkowski RP, Blennow K, de Leon MJ (2009) The effects of normal aging and ApoE genotype on the levels of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 30:672–681
Goldfarb LG, Korczyn AD, Brown P, Chapman J, Gajdusek DC (1990) Mutation in codon 200 of scrapie amyloid precursor gene linked to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Sephardic Jews of Libyan and non-Libyan origin. Lancet 336:637–638
Green AJ, Thompson EJ, Stewart GE, Zeidler M, McKenzie JM, MacLeod MA, Ironside JW, Will RG, Knight RS (2001) Use of 14-3-3 and other brain-specific proteins in CSF in the diagnosis of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:744–748
Green AJ, Ramljak S, Muller WE, Knight RS, Schroder HC (2002) 14-3-3 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with variant and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease measured using capture assay able to detect low levels of 14-3-3 protein. Neurosci Lett 324:57–60
Green A, Sanchez-Juan P, Ladogana A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Sánchez-Valle R, Mitrová E, Stoeck K, Sklaviadis T, Kulczycki J, Heinemann U, Hess K, Slivarichová D, Saiz A, Calero M, Mellina V, Knight R, van Duijn CM, Zerr I (2007) CSF analysis in patients with sporadic CJD and other transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Eur J Neurol 14:121–124
Hsiao K, Meiner Z, Kahana E, Cass C, Kahana I, Avrahami D, Scarlato G, Abramsky O, Prusiner SB, Gabizon R (1991) Prion protein mutation in Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. N Eng J Med 324:1091–1097
Hsiech G, Kenney K, Gibbs CJ Jr, Lee KH, Harrington MG (1996) The 14-3-3 brain protein in cerebrospinal fluid as a marker for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. N Engl J Med 335:924–930
Kahana E, Alter M, Braham J, Sofer D (1974) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: focus among Libyan Jews in Israel. Science 183:90–91
Kahana E, Zilber N, Abraham M (1991) Do Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients of Jewish Libyan origin have unique clinical features? Neurology 41:1390–1392
Korczyn AD (1991) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease among Libyan Jews. Eur J Epidemiol 7:490–493
Kovács GG, Puopolo M, Ladogana A, Pocchiari M, Budka H, van Duijn C, Collins SJ, Boyd A, Giulivi A, Coulthart M, Delasnerie-Laupretre N, Brandel JP, Zerr I, Kretzschmar HA, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Calero-Lara M, Glatzel M, Aguzzi A, Bishop M, Knight R, Belay G, Will R, Mitrova E (2005) Genetic prion disease: the EUROCJD experience. Hum Genet 118:166–174
Ladogana A, Sanchez-Juan P, Mitrová E, Green A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Sánchez-Valle R, Koscova S, Aguzzi A, Sklaviadis T, Kulczycki J, Gawinecka J, Saiz A, Calero M, van Duijn CM, Pocchiari M, Knight R, Zerr I (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in human genetic transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J Neurol 256:1620–1628
Mead S (2006) Prion disease genetics. Eur J Hum Genet 14:273–281
Meiner Z, Gabizon R, Prusiner SB (1997) Inherited Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Libyan Jews caused by mutation at codon 200 in the prion protein gene. Medicine (Baltimore) 76:227–237
Meissner B, Körtner K, Bartl M, Jastrow U, Mollenhauer B, Schröter A, Finkenstaedt M, Windl O, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA, Zerr I (2004) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: magnetic resonance imaging and clinical findings. Neurology 63:450–456
Mitrová E, Belay G (2002) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with E200K mutation in Slovakia: characterization and development. Acta Virol 46:31–39
Mollenhauer B, Serafin S, Zerr I, Steinhoff BJ, Otto M, Scherer M, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Poser S (2003) Diagnostic problems during late course in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 250:629–630
Otto M, Wiltfang J, Tumani H, Zerr I, Lantsch M, Kornhuber J, Weber T, Kretzschmar HA, Poser (1997) Elevated levels of Tau-protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci Lett 225:210–212
Otto M, Wiltfang J, Cepek L, Neumann M, Mollenhauer B, Steinacker P, Ciesielczyk B, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar HA, Poser S (2002) Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 58:192–197
Prusiner SB (2001) Shattuck lecture—neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N Engl J Med 344:1516–1526
Rosenmann H, Meiner Z, Kahana E, Halimi M, Lenetsky E, Abramsky O, Gabizon R (1997) Detection of 14-3-3 protein in the CSF of genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 49:593–595
Sanchez-Juan P, Green A, Ladogana A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Sáanchez-Valle R, Mitrováa E, Stoeck K, Sklaviadis T, Kulczycki J, Hess K, Bodemer M, Slivarichová D, Saiz A, Calero M, Ingrosso L, Knight R, Janssens AC, van Duijn CM, Zerr I (2006) CSF tests in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 67:637–643
Sanchez-Juan P, Sánchez-Valle R, Green A, Ladogana A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Mitrová E, Stoeck K, Sklaviadis T, Kulczycki J, Hess K, Krasnianski A, Equestre M, Slivarichová D, Saiz A, Calero M, Pocchiari M, Knight R, van Duijn CM, Zerr I (2007) Influence of timing on CSF tests value for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease diagnosis. J Neurol 254:901–906
Satoh K, Shirabe S, Tsujino A, Eguchi H, Motomura M, Honda H, Tomita I, Satoh A, Tsujihata M, Matsuo H, Nakagawa M, Eguchi K (2007) Total Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid and diffusion-weighted MRI as an early diagnostic marker for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 24:207–212
Satoh K, Shirabe S, Eguchi H, Tsujino A, Eguchi K, Satoh A, Tsujihata M, Niwa M, Katamine S, Kurihara S, Matsuo H (2006) 14-3-3 Protein, total Tau and phosphorylated Tau in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and neurodegenerative disease in Japan. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:45–52
Van Everbroeck B, Quoilin S, Boons J, Martin JJ, Cras P (2003) A prospective study of CSF markers in 250 patients with possible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1210–1214
Will RG (1993) Epidemiology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Br Med Bull 49:960–970
World Health Organization (1998) Consensus on criteria for sporadic CJD. WHO, Geneva
Young GS, Geschwind MD, Fischbein NJ, Martindale JL, Henry RG, Liu S, Lu Y, Wong S, Liu H, Miller BL, Dillon WP (2005) Diffusion-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1551–1562
Zerr I, Bodemer M, Gefeller O, Otto M, Poser S, Wiltfang J, Windl O, Kretzschmar HA, Weber T (1998) Detection of 14-3-3 protein in the cerebrospinal fluid supports the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 43:32–40
Zilber N, Kahana E, Abraham M (1991) The Libyan Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease focus in Israel: an epidemiologic evaluation. Neurology 41:1385–1389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meiner, Z., Kahana, E., Baitcher, F. et al. Tau and 14-3-3 of genetic and sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease patients in Israel. J Neurol 258, 255–262 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5738-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5738-6