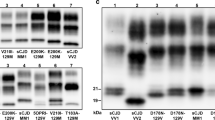
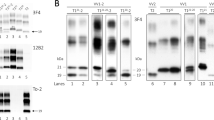
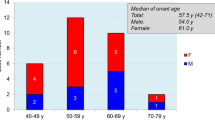
Abstract
Incidences of human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies are monitored by national registries in the majority of countries in Western Europe. During the past 13 years incidences for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in Switzerland fluctuated between 0.4 and 2.63 cases/106 inhabitants. We have compared clinicpathological patient profiles including geographic and gender distribution, age at disease onset, duration of disease, clinical symptoms, and recognized or hypothetical risk factors for CJD, genetic risk factors, biochemical and histopathological data for two cohorts of Swiss sporadic CJD patients from years of regular sporadic CJD incidence (1996–2000, mean incidence 1.3 cases/106 inhabitants, n = 47) to Swiss sporadic CJD patients from years of elevated sporadic CJD incidence (2001–2004, mean incidence 2.3 cases/106 inhabitants, n = 73). Sporadic CJD patients from the cohort with elevated sporadic CJD incidence presented with a higher frequency of rare sporadic CJD subtypes. Patients of these subtypes were significantly older and showed a skewed male/female ratio when compared to published patients of identical sporadic CJD-types or to patients from the 1996–2000 cohort and indicates that improved detection of rare sporadic CJD subtypes may have contributed to increased incidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alperovitch A, Zerr I, Pocchiari M, Mitrova E, de Pedro Cuesta J, Hegyi I, Collins S, Kretzschmar H, van Duijn C, Will RG (1999) Codon 129 prion protein genotype and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 353:1673–1674
Brown P, Preece M, Brandel JP, Sato T, McShane L, Zerr I, Fletcher A, Will RG, Pocchiari M, Cashman NR, d’Aignaux JH, Cervenakova L, Fradkin J, Schonberger LB, Collins SJ (2000) Iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease at the millennium. Neurology 55:1075–1081
Bruce ME, Will RG, Ironside JW, McConnell I, Drummond D, Suttie A, McCardle L, Chree A, Hope J, Birkett C, Cousens S, Fraser H, Bostock CJ (1997) Transmissions to mice indicate that ‘new variant’ CJD is caused by the BSE agent Nature 389:498–501
Budka H, Aguzzi A, Brown P, Brucher JM, Bugiani O, Collinge J, Diringer H, Gullotta F, Haltia M, Hauw JJ, et al. (1995) Tissue handling in suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases). Brain Pathol 5:319–322
Cali I, Castellani R, Yuan J, Al-Shekhlee A, Cohen ML, Xiao X, Moleres FJ, Parchi P, Zou WQ, Gambetti P (2006) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease revisited. Brain 129:2266–2277
Castellani RJ, Colucci M, Xie Z, Zou W, Li C, Parchi P, Capellari S, Pastore M, Rahbar MH, Chen SG, Gambetti P (2004) Sensitivity of 14-3-3 protein test varies in subtypes of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 63:436–442
Collinge J, Sidle KC, Meads J, Ironside J, Hill AF (1996) Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the aetiology of ‘new variant’ CJD. Nature 383:685–690
Collins SJ, Sanchez-Juan P, Masters CL, Klug GM, van Duijn C, Poleggi A, Pocchiari M, Almonti S, Cuadrado-Corrales N, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Budka H, Gelpi E, Glatzel M, Tolnay M, Hewer E, Zerr I, Heinemann U, Kretszschmar HA, Jansen GH, Olsen E, Mitrova E, Alperovitch A, Brandel JP, Mackenzie J, Murray K, Will RG (2006) Determinants of diagnostic investigation sensitivities across the clinical spectrum of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 129:2278–2287
Glatzel M, Ott PM, Lindner T, Gebbers JO, Gmur A, Wuest W, Huber G, Moch H, Podvinec M, Stamm B, Aguzzi A (2003) Human prion diseases: epidemiology and integrated risk assessment. The Lancet Neurology 2:757–763
Glatzel M, Rogivue C, Ghani A, Streffer JR, Amsler L, Aguzzi A (2002) Incidence of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Switzerland. Lancet 360:139–141
Glatzel M, Stoeck K, Seeger H, Luhrs T, Aguzzi A (2005) Human prion diseases: molecular and clinical aspects. Arch Neurol 62:545–552
Head MW, Ritchie D, Smith N, McLoughlin V, Nailon W, Samad S, Masson S, Bishop M, McCardle L, Ironside JW (2004) Peripheral tissue involvement in sporadic, iatrogenic, and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: an immunohistochemical, quantitative, and biochemical study. Am J Pathol 164:143–153
Hill AF, Desbruslais M, Joiner S, Sidle KC, Gowland I, Collinge J, Doey LJ, Lantos P (1997) The same prion strain causes vCJD and BSE (letter). Nature 389:448–450
Hill AF, Joiner S, Wadsworth JD, Sidle KC, Bell JE, Budka H, Ironside JW, Collinge J (2003) Molecular classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 126:1333–1346
Kovacs GG, Puopolo M, Ladogana A, Pocchiari M, Budka H, van Duijn C, Collins SJ, Boyd A, Giulivi A, Coulthart M, Delasnerie-Laupretre N, Brandel JP, Zerr I, Kretzschmar HA, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Calero-Lara M, Glatzel M, Aguzzi A, Bishop M, Knight R, Belay G, Will R, Mitrova E (2005) Genetic prion disease: the EUROCJD experience. Hum Genet 118:166–174
Krasnianski A, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Kallenberg K, Meissner B, Collie DA, Roeber S, Bartl M, Heinemann U, Varges D, Kretzschmar HA, Zerr I (2006) Clinical findings and diagnostic tests in the MV2 subtype of sporadic CJD. Brain 129:2288–2296
Meissner B, Kortner K, Bartl M, Jastrow U, Mollenhauer B, Schroter A, Finkenstaedt M, Windl O, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA, Zerr I (2004) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: magnetic resonance imaging and clinical findings. Neurology 63:450–456
Mollenhauer B, Zerr I, Ruge D, Krause G, Mehnert WH, Kretzschmar HA, Poser S (2002) Epidemiology and clinical symptomatology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 127:312–317
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, Brown P, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Windl O, Zerr I, Budka H, Kopp N, Piccardo P, Poser S, Rojiani A, Streichemberger N, Julien J, Vital C, Ghetti B, Gambetti P, Kretzschmar H (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233
Peden AH, Head MW, Ritchie DL, Bell JE, Ironside JW (2004) Preclinical vCJD after blood transfusion in a PRNP codon 129 heterozygous patient. Lancet 364:527–529
Polymenidou M, Stoeck K, Glatzel M, Vey M, Bellon A, Aguzzi A (2005) Coexistence of multiple PrPSc types in individuals with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet Neurol 4:805–814
Prusiner SB (1982) Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science 216:136–144
Prusiner SB (2001) Shattuck lecture – neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N Engl J Med 344:1516–1526
Saiz A, Nos C, Yague J, Dominguez A, Graus F, Munoz P (2001) The impact of the introduction of the 14-3-3 protein assay in the surveillance of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Catalonia. J Neurol 248:592–594
Schoch G, Seeger H, Bogousslavsky J, Tolnay M, Janzer RC, Aguzzi A, Glatzel M (2005) Analysis of Prion Strains by PrP(Sc) Profiling in Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. PLoS Med 3:e14
Steinhoff BJ, Zerr I, Glatting M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA (2004) Diagnostic value of periodic complexes in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 56:702–708
Ukisu R, Kushihashi T, Kitanosono T, Fujisawa H, Takenaka H, Ohgiya Y, Gokan T, Munechika H (2005) Serial diffusion-weighted MRI of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:560–566
Van Everbroeck B, Michotte A, Sciot R, Godfraind C, Deprez M, Quoilin S, Martin JJ, Cras P (2006) Increased incidence of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the age groups between 70 and 90 years in Belgium. Eur J Epidemiol 21:443–447
Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SN, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, Poser S, Pocchiari M, Hofman A, Smith PG (1996) A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet 347:921–925
Windl O, Giese A, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Zerr I, Skworc K, Arendt S, Oberdieck C, Bodemer M, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA (1999) Molecular genetics of human prion diseases in Germany. Hum Genet 105:244–252
Zerr I, Bodemer M, Gefeller O, Otto M, Poser S, Wiltfang J, Windl O, Kretzschmar HA, Weber T (1998) Detection of 14-3-3 protein in the cerebrospinal fluid supports the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (In Process Citation). Ann Neurol 43:32–40
Zerr I, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Giese A, Bodemer M, Schroter A, Henkel K, Tschampa HJ, Windl O, Pfahlberg A, Steinhoff BJ, Gefeller O, Kretzschmar HA, Poser S (2000) Current clinical diagnosis in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: identification of uncommon variants. Ann Neurol 48:323–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
M. Glatzel and A. Aguzzi coordinated the design and operation of the study. Katharina Stoeck and Klaus Hess were involved in clinical assessment of patients. M. Glatzel and Dieter Zimmermann were involved in assessment of specimen. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the final version. M. Glatzel and A. Aguzzi had full access to all data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
The study was performed according to established ethical guidelines
This study was supported by grants of the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health and the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoeck, K., Hess, K., Amsler, L. et al. Heightened incidence of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is associated with a shift in clinicopathological profiles. J Neurol 255, 1464–1472 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0900-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0900-0