Abstract
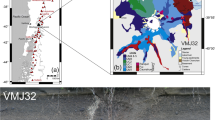
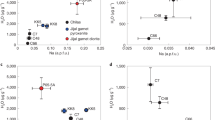
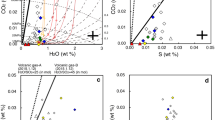
The >60 km3 rhyolitic Kos Plateau Tuff provides an exceptional probe into the behavior of volatile components in highly evolved arc magmas: it is crystal-rich (30–40 vol% crystals), was rapidly quenched by the explosive eruptive process, and contains abundant homogeneous melt inclusions in large quartz crystals. Several methods for measuring major, trace and volatile element concentrations (SIMS, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, electron microprobe, LA–ICPMS) were applied to these melt inclusions. We found a ~2 wt% range of H2O contents (4.5–6.5 wt% H2O, measured independently by SIMS, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy) and relatively low CO2 concentrations (15–140 ppm measured by FTIR, with most analyses <100 ppm). No obvious correlations between H2O, CO2, major and trace elements are observed. These observations require a complex, protracted magma evolution in the upper crust that included: (1) vapor-saturated crystallization in a chamber located between 1.5 and 2.5 kb pressure, (2) closed-system degassing (with up to 10 vol% exsolved gas) as melts percolated upwards through a vertically extensive mush zone (2–4 km thick), and (3) periodic gas fluxing from subjacent, more mafic and more CO2-rich magma, which is preserved as andesite bands in pumices. These processes can account for the range of observed H2O and CO2 values and the lack of correlation between volatiles and trace elements in the melt inclusions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen SR (2001) Reconstruction of a major caldera-forming eruption from pyroclastic deposit characteristics: Kos Plateau Tuff, eastern Aegean Sea. J Volcanol Geoth Res 105:141–162
Allen SR, Cas RAF (1998a) Lateral variations within coarse co-ignimbrite lithic breccias of the Kos Plateau Tuff, Greece. Bull Volcanol 59(5):356–377
Allen SR, Cas RAF (1998b) Rhyolitic fallout and pyroclastic density current deposits from a phreatoplinian eruption in the eastern Aegean Sea, Greece. J Volcanol Geoth Res 86:219–251
Allen SR, McPhie J (2001) Syn-eruptive chaotic breccia on Kos, Greece, associated with an energetic pyroclastic flow. Bull Volcanol 63(6):421–432
Allen SR, Stadlbauer E, Keller J (1999) Stratigraphy of the Kos Plateau Tuff: product of a major Quaternary explosive rhyolitic eruption in the eastern Aegean, Greece. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 88:132–156
Anderson AT, Newman S, Williams SN, Druitt TH, Skirius C, Stolper E (1989) H2O, CO2, Cl, and gas in Plinian and ash-flow Bishop rhyolite. Geology 17:221–225
Anderson AT, Davis AM, Fangqiong L (2000) Evolution of the Bishop Tuff rhyolitic magma based on melt and magnetite inclusions and zoned phenocrysts. J Petrol 41(3):449–473
Angelier J, Lyberis N, Le Pichon X, Barrier E, Huchon P (1982) The tectonic development of the hellenic arc and the sea of crete: a synthesis. Tectonophysics 86(1–3):159–163
Bachmann O, Bergantz GW (2003) Rejuvenation of the Fish Canyon magma body: a window into the evolution of large-volume silicic magma systems. Geology 31(9):789–792
Bachmann O, Bergantz GW (2004) On the origin of crystal-poor rhyolites: extracted from batholithic crystal mushes. J Petrol 45:1565–1582
Bachmann O, Bergantz GW (2006) Gas percolation in upper-crustal silicic crystal mushes as a mechanism for upward heat advection and rejuvenation of near-solidus magma bodies. J Volcanol Geoth Res 149(1–2):85–102
Bachmann O, Charlier BLA, Lowenstern JB (2007a) Zircon crystallization and recycling in the magma chamber of the rhyolitic Kos Plateau Tuff (Aegean Arc). Geology 35(1):73–76
Bachmann O, Miller CF, de Silva S (2007b) The volcanic-plutonic connection as a stage for understanding crustal magmatism. J Volcanol Geoth Res 167:1–23
Blank JG, Stolper EM, Carroll MR (1993) Solubilities of carbon dioxide and water in rhyolitic melt at 850°C and 750 bars. Earth Planet Sci Lett 119:27–36
Bouvet de Maisonneuve C, Bachmann O, Burgisser A (2008) Characterization of juvenile pyroclasts from the Kos Plateau Tuff (Aegean Arc): insights into the eruptive dynamics of a rhyolitic caldera-forming eruption. Bull Volcanol. doi: 10.1007/s00445-008-0250-x
Burgisser A, Scaillet B (2008) Chemical patterns of erupting silicic magmas and their influence on the amount of degassing during ascent. J Geophys Res 113: B07209. doi:10.1029/2007JB005049
Cardoso SSS, Woods AW (1999) On convection in a volatile-saturated magma. Earth Planet Sci Lett 168:301–310
Chaigneau M (1975) Essai sur la composition des gaz magmatiques profonds. Bull Volcanol 39(3):407–419
Dawson PB, Evans JR, Iyer HM (1990) Teleseismic tomography of the compressional wave velocity structure beneath the Long Valley region. J Geophys Res 95(B7):11021–11050
Dufek J, Bergantz GW (2007) Dynamics and deposits generated by the Kos Plateau Tuff Eruption: the controls on basal particle loss on pyroclastic flow transport. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 8:Q12007. doi:10.1029/2007GC001741
Dunbar NW, Hervig RL (1992) Volatile and trace element composition of melt inclusions from the lower Bandelier Tuff: implications for magma chamber processes and eruptive style. J Geophys Res 97(B11):15151–15170
Fytikas M, Giuliani O, Innocenti F, Marinelli G, Mazzuoli R (1976) Geochronological data on recent magmatism of the Aegean Sea. Tectonophysics 31:129–134
Goff F, Janik CJ, Delgado H, Werner C, Counce D, Stimac JA, Siebe C, Love SP, Williams SN, Fisher T, Johnson L (1998) Geochemical surveillance of magmatic volatiles at Popocatepetl volcano, Mexico. Geol Soc Am Bull 110(6):695–710
Hildreth W (1981) Gradients in silicic magma chambers: implications for lithospheric magmatism. J Geophys Res 86(B11):10153–10192
Hildreth W (2004) Volcanological perspectives on Long Valley, Mammoth Mountain, and Mono Craters: several contiguous but discrete systems. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 136(3–4):169–198
Husen S, Smith RB, Waite GP (2004) Evidence for gas and magmatic sources beneath the Yellowstone volcanic field from seismic tomographic imaging. J Volcanol Geoth Res 131(3–4):397–410
Ihinger PD, Hervig RL, McMillan PM (1994) Analytical methods for volatiles in glasses. In: Carroll M, Holloway JR (eds) Volatiles in Magmas, vol 30. Reviews in mineralogy, Mineralogical Society of America, pp 67–121
Jackson J (1993) Rates of active deformation in the Eastern Mediterranean. In: Boschi E et al (eds) Recent evolution and seismicity of the mediterranean region. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 53–64
Jellinek AM, DePaolo DJ (2003) A model for the origin of large silicic magma chambers: precursors of caldera-forming eruptions. Bull Volcanol 65:363–381
Johnson ER, Wallace PJ, Cashman KV, Granados HD, Kent AJR (2008) Magmatic volatile contents and degassing-induced crystallization at Volcan Jorullo, Mexico: implications for melt evolution and the plumbing systems of monogenetic volcanoes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 269(3–4):478–487
Kamiyama H, Nakajima T, Kamioka H (2007) Magmatic Stratigraphy of the Tilted Tottabetsu Plutonic Complex, Hokkaido, North Japan: magma Chamber Dynamics and Pluton Construction. J Geol 115:295–314
Keller J (1969) Origin of rhyolites by anatectic melting of granitic crustal rocks; the example of rhyolitic pumice from the island of Kos (Aegean sea). Bull Volcanol 33(3):942–959
Kent AJR, Blundy J, Cashman KV, Cooper KM, Donnelly C, Pallister JS, Reagan M, Rowe MC, Thornber CR (2007) Vapor transfer prior to the October 2004 eruption of Mount St. Helens, Washington. Geology 35(3):231–234
Lees JM (2007) Seismic studies of magmatic systems. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 167(1–4):37–56
LePichon X, Angelier J (1979) The hellenic arc and trench system: a key to the Neotectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterrenean area. Tectonophysics 60:1–42
Lipman PW (1984) The roots of ash-flow calderas in western North America: windows into the tops of granitic batholiths. J Geophys Res 89(B10):8801–8841
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Behrens H (2005) Solubility of H2O in rhyolitic melts at low pressures and a new empirical model for mixed H2O-CO2 solubility in rhyolitic melts. J Volcanol Geoth Res 143(1–3):219–235
Liu Y, Anderson A, Wilson C, Davis A, Steele I (2006) Mixing and differentiation in the Oruanui rhyolitic magma, Taupo, New Zealand: evidence from volatiles and trace elements in melt inclusions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 151(1):71–87
Lowenstern JB (2003) Melt inclusions come of age: volatiles, volcanoes, and Sorby’s legacy. In: De Vivo B, Bodnar RJ (eds) Melt inclusions in volcanic systems: methods, applications and problems. Developments in volcanology, vol 5. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, pp 1–22
Lowenstern JB, Bacon CR, Calk LC, Hervig RL, Aines RD (1994) Major-element, trace-element, and volatile concentrations in silicate melt inclusions from the tuff of Pine Grove, Wah Wah Mountains, Utah. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 94–242, p 20
Mahood GA, Nibler GE, Halliday AN (1996) Zoning patterns and petrologic processes in peraluminous magma chambers; Hall Canyon Pluton, Panamint Mountains, California. Geol Soc Am Bull 108(4):437–453
Marsh BD (1989) Magma chambers. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 17:439–474
Massare D, Chaineau M, Clocchatti R (1978) Composition chimique (éléments majeurs et volatils) des inclusions vitreuses des phénocristaux contenus dans les ponces rhyolitiques de l’île de Kos (Arc égéen): conséquences pétrogénétiques. C.R. somm. Soc Géol Fr 5:246–249
Mckenzie DP (1970) Plate tectonics of the mediterranean region. Nature 226(5242):239–243
McKenzie D (1972) Active tectonics of the mediterranean region. Geophys J Roy Astron Soc 30(2):109–185
Miller CF, Miller JS (2002) Contrasting stratified plutons exposed in tilt blocks, Eldorado Mountains, Colorado River Rift, NV, USA. Lithos 61:209–224
Mitropolous P, Tarney J, Saunders AD, Marsh NG (1987) Petrogenesis of cenozoic rocks from the aegean island arc. J Volcanol Geoth Res 32:177–193
Morgan GB, London D (1996) Optimizing the electron microprobe analysis of hydrous alkali aluminosilicate glasses. Am Miner 81(9–10):1176–1185
Newman S, Lowenstern JB (2002) VolatileCalc: a silicate melt-H2O-CO2 solution model written in Visual Basic for excel. Comput Geosci 28(5):597–604
Pe-Piper G, Piper DJW, Perissoratis C (2005) Neotectonics and the Kos Plateau Tuff eruption of 161 ka, South Aegean arc. J Volcanol Geoth Res 139(3–4):315–338
Peppard BT, Steele IM, Davis AM, Wallace PJ, Anderson AT (2001) Zoned quartz phenocrysts from the rhyolitic Bishop Tuff. Am Mineral 86:1034–1052
Phillips JC, Woods AW (2002) Suppression of large-scale magma mixing by melt-volatile separation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 204:47–60
Qin L, Fangqiong L, Andersen AT (1992) Diffusive reequilibration of melt and fluid inclusions. Am Miner 77:565–576
Rowe MC, Kent AJR, Thornber CR (2008) Using amphibole phenocrysts to track vapor transfer during magma crystallization and transport: an example from Mount St. Helens, Washington. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 178(4):593–607
Schmitt AK (2001) Gas-saturated crystallization and degassing in large-volume, crystal-rich dacitic magmas from the Altiplano-Puna, northern Chile. J Geophys Res 106(B12):30561–30578
Severs MJ, Azbej T, Thomas JB, Mandeville CW, Bodnar RJ (2007) Experimental determination of H2O loss from melt inclusions during laboratory heating: evidence from Raman spectroscopy. Chem Geol 237(3–4):358–371
Shimizu A, Sumino H, Nagao K, Notsu K, Mitropoulos P (2005) Variation in noble gas isotopic composition of gas samples from the Aegean arc, Greece. J Volcanol Geoth Res 140(4):321–339
Smith PE, York D, Chen Y, Evensen NM (1996) Single crystal 40Ar/39Ar dating of a late Quaternary paroxysm on Kos, Greece; concordance of terrestrial and marine ages. Geophys Res Lett 23(21):3047–3050
Smith PE, Evensen NM, York D (2000) Under the volcano; a new dimension in Ar-Ar dating of volcanic ash. Geophys Res Lett 27(5):585–588
Spilliaert N, Allard P, Métrich N, Sobolev AV (2006) Melt inclusion record of the conditions of ascent, degassing, and extrusion of volatile-rich alkali basalt during the powerful 2002 flank eruption of Mount Etna (Italy). J Geophys Res 111:B04203. doi:10.1029/2005JB003934
Stadlbauer E (1988) Vulkanologishe-geochemische Analyse eines jungen Ignimbrites: Der Kos-Plateau-Tuff (Südost-Ägäïs). Freiburg, p 182
Tait S, Jaupart C (1992) Compositional convection in a reactive crystalline mush and melt differentiation. J Geophys Res 97(B5):6735–6756
Walker BJ, Miller CF, Lowery LE, Wooden JL, Miller JS (2007) Geology and geochronology of the Spirit Mountain batholith, southern Nevada: implications for timescales and physical processes of batholith construction. J Volcanol Geoth Res 167:239–262
Wallace P (2003) From mantle to atmosphere: magma degassing, explosive eruptions, and volcanic volatile budgets. In: De Vivo B, Bodnar RJ (eds) Melt inclusions in volcanic systems: methods, applications and problems, vol 5. Developments in volcanology, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 105–127
Wallace PJ, Gerlach TM (1994) Magmatic vapor source for sulfur dioxide released during volcanic eruptions: evidence from Mount Pinatubo. Science 265:497–499
Wallace PJ, Anderson AT, Davis AM (1995) Quantification of pre-eruptive exsolved gas contents in silicic magmas. Nature 377:612–615
Wallace PJ, Anderson AT, Davis AM (1999) Gradients in H2O, CO2, and exsolved gas in a large-volume silicic magma chamber: interpreting the record preserved in the melt inclusions from the Bishop Tuff. J Geophys Res 104(B9):20097–20122
Wark D, Watson E (2006) TitaniQ: a titanium-in-quartz geothermometer. Contrib Miner Petrol 152(6):743–754
Wark DA, Hildreth W, Spear FS, Cherniak DJ, Watson EB (2007) Pre-eruption recharge of the Bishop magma system. Geology 35(3):235–238
Westrich HR (1987) Determination of water in volcanic glasses by Karl Fischer titration. Chem Geol 63:335–340
Wilson L, Sparks RSJ, Walker GPL (1980) Explosive volcanic eruptions-IV. The control of magma properties and conduit geometry on eruption column behavior. Geophys J Res Astron Soc 63:117–148
Witter JB, Kress VC, Delmelle P, Stix J (2004) Volatile degassing, petrology, and magma dynamics of the Villarrica Lava Lake, Southern Chile. J Volcanol Geoth Res 134(4):303–337
Witter JB, Kress VC, Newhall CG (2005) Volcan popocatepetl, mexico petrology, magma. mixing, and immediate sources of volatiles for the 1994-present eruption. J Petrol 46(11):2337–2366
Wortel MJR, Spakman W (2000) Subduction and slab detachment in the Mediterranean-Carpathian Region. Science 290:1910–1917
Wysoczanski R, Tani K (2006) Spectroscopic FTIR imaging of water species in silicic volcanic glasses and melt inclusions: an example from the Izu-Bonin arc. J Volcanol Geoth Res 156(3–4):302–314
Zajacz Z, Halter W, Malfait WJ, Bachmann O, Bodnar RJ, Hirschmann MM, Mandeville CW, Morizet Y, Müntener O, Ulmer P, Webster JD (2005) A composition-independent quantitative determination of the water content in silicate glasses and silicate melt inclusions by confocal Raman spectroscopy. Contrib Mineral Petrol 150(6):631–642
Zhang Y, Belcher R, Ihinger PD, Wang L, Xu Z, Newman S (1997) New calibration of infrared measurement of dissolved water in rhyolitic glasses. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(15):3089–3100
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Swiss NSF grants # 200021-103441 and 200021-111709/1 to Bachmann. We thank Robert Moritz for his help on the Raman instrument at the University of Geneva and Colleen Donegan for assistance with the FTIR analyses. Georgia Pe-Piper and an anonymous reviewer are thanked for providing constructive comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T.L. Grove.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachmann, O., Wallace, P.J. & Bourquin, J. The melt inclusion record from the rhyolitic Kos Plateau Tuff (Aegean Arc). Contrib Mineral Petrol 159, 187–202 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0423-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0423-4