Abstract
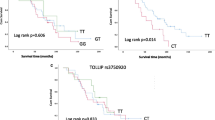
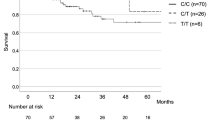
An excess of neutrophils in the alveoli and lung interstitium has been described in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Engagement of neutrophil Fcγ receptors with IgG complexes may contribute to the pathogenesis of IPF. The neutrophil FcγRIIIb receptor occurs in two codominantly expressed allelic variants, NA1 and NA2, which exhibit different binding affinities for IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses. The aim of this study was to investigate whether FcγRIIIb genotype is associated with IPF susceptibility or disease progression. In a case-control study we compared the distribution of FcγRIIIb NA1/2 polymorphisms in 142 patients with IPF and in 218 controls using allele-specific PCR amplification. Significant skewing in the distribution of FcγRIIIb genotypes was observed between patients with IPF and control subjects. In the IPF cohort, there was higher frequency of the NA1/NA1 genotype (0.19 vs. 0.07), and lower NA2/NA2 frequency (0.31 vs. 0.50; χ2 = 17.71, df = 2, P < 0.001). The overall frequency of the NA1 allele was increased in IPF patients compared to controls (0.44 vs. 0.29; P < 0.0001, odds ratio [OR] = 1.93, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.42–2.64). Heterozygotes and homozygotes of the NA1 allele were at higher risk of developing IPF (OR = 2.19, 95% CI = 1.40–3.41, P = 0.0005), whereas the NA2 allele was protective against IPF (OR = 0.34, 95% CI = 0.17–0.65, P = 0.0014). There was no association of FcγRIIIb genotype with disease progression as assessed by serial lung function measurements. FcγRIIIb NA1/2 polymorphisms are associated with IPF disease susceptibility. These results support a role for immunological mechanisms contributing to IPF pathogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flaherty KR, Travis WD, Colby TV, Toews GB, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Jain A, Strawderman RL, Flint A, Lynch JP, Martinez FJ (2001) Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1722–1727
Bellon B, Bernaudin JF, Mandet C, Chamak B, Kuhn J, Druet P (1982) Immune complex-mediated lung injury produced by horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and anti-HRP antibodies in rats. Am J Pathol 107:16–24
Ward PA (1979) Immune complex injury of the lung. Am J Pathol 97:85–92
Wallace WA, Roberts SN, Caldwell H, Thornton E, Greening AP, Lamb D, Howie SE (1994) Circulating antibodies to lung protein(s) in patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Thorax 49:218–224
Dall’Aglio PP, Pesci A, Bertorelli G, Brianti E, Scarpa S (1988) Study of immune complexes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids. Respiration 54(Suppl 1):36–41
Dreisin RB, Schwarz MI, Theofilopoulos AN, Stanford RE (1978) Circulating immune complexes in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. N Engl J Med 298:353–357
Gelb AF, Dreisen RB, Epstein JD, Silverthorne JD, Bickel Y, Fields M, Border WA, Taylor CR (1983) Immune complexes, gallium lung scans, and bronchoalveolar lavage in idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis-fibrosis. Chest 84:148–153
Haslam PL, Thompson B, Mohammed I, Townsend PJ, Hodson ME, Holborow EJ, Turner-Warwick M (1979) Circulating immune complexes in patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Exp Immunol 37:381–390
Martinet Y, Haslam PL, Turner-Warwick M (1984) Clinical significance of circulating immune complexes in ‘lone’ cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and those with associated connective tissue disorders. Clin Allergy 14:491–497
Dobashi N, Fujita J, Murota M, Ohtsuki Y, Yamadori I, Yoshinouchi T, Ueda R, Bandoh S, Kamei T, Nishioka M, Ishida T, Takahara J (2000) Elevation of anti-cytokeratin 18 antibody and circulating cytokeratin 18: anti-cytokeratin 18 antibody immune complexes in sera of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung 178:171–179
Dobashi N, Fujita J, Ohtsuki Y, Yamadori I, Yoshinouchi T, Kamei T, Tokuda M, Hojo S, Bandou S, Ueda Y, Takahara J (2000) Circulating cytokeratin 8:anti-cytokeratin 8 antibody immune complexes in sera of patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Respiration 67:397–401
Takahashi T, Wada I, Ohtsuka Y, Munakata M, Homma Y, Kuroki Y (2007) Autoantibody to alanyl-tRNA synthetase in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 12:642–653
Gadek J, Hunninghake G, Zimmerman R, Kelman J, Fulmer J, Crystal RG (1979) Pathogenetic studies in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Control of neutrophil migration by immune complexes. Chest 75:264–265
Hunninghake GW, Gadek JE, Lawley TJ, Crystal RG (1981) Mechanisms of neutrophil accumulation in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 68:259–269
Bradley B, Branley HM, Egan JJ, Greaves MS, Hansell DM, Harrison NK, Hirani N, Hubbard R, Lake F, Millar AB, Wallace WAH, Wells AU, Whyte MK, Wilsher ML (2008) Interstitial lung disease guideline: the British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Thorax 63(Suppl 5):v1–v58
American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (2002) American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:277–304
Bournazos S, Hart SP, Chamberlain LH, Glennie MJ, Dransfield I (2009) Association of FcγRIIa (CD32a) with lipid rafts regulates ligand binding activity. J Immunol 182:8026–8036
Green JM, Schreiber AD, Brown EJ (1997) Role for a glycan phosphoinositol anchor in Fcγ receptor synergy. J Cell Biol 139:1209–1217
Nathan C (2006) Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol 6:173–182
Bournazos S, Woof JM, Hart SP, Dransfield I (2009) Functional and clinical consequences of Fc receptor polymorphic and copy number variants. Clin Exp Immunol 157:244–254
Salmon JE, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP (1990) Fcγ receptor III on human neutrophils. Allelic variants have functionally distinct capacities. J Clin Invest 85:1287–1295
Ory PA, Clark MR, Kwoh EE, Clarkson SB, Goldstein IM (1989) Sequences of complementary DNAs that encode the NA1 and NA2 forms of Fc receptor III on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest 84:1688–1691
Ory PA, Clark MR, Talhouk AS, Goldstein IM (1991) Transfected NA1 and NA2 forms of human neutrophil Fc receptor III exhibit antigenic and structural heterogeneity. Blood 77:2682–2687
De Haas M, Kleijer M, van Zwieten R, Roos D, von dem Borne AE (1995) Neutrophil FcγRIIIb deficiency, nature, and clinical consequences: a study of 21 individuals from 14 families. Blood 86:2403–2413
Bournazos S, Rennie J, Hart S, Fox KAA, Dransfield I (2008) Monocyte functional responsiveness after PSGL-1-mediated platelet adhesion is dependent on platelet activation status. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:1491–1498
Trounstine ML, Peltz GA, Yssel H, Huizinga TW, Von dem Borne AE, Spits H, Moore KW (1990) Reactivity of cloned, expressed human FcγRIII isoforms with monoclonal antibodies which distinguish cell-type-specific and allelic forms of FcγRIII. Int Immunol 2:303–310
Hanson D, Winterbauer RH, Kirtland SH, Wu R (1995) Changes in pulmonary function test results after 1 year of therapy as predictors of survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 108:305–310
Latsi PI, du Bois RM, Nicholson AG, Colby TV, Bisirtzoglou D, Nikolakopoulou A, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Wells AU (2003) Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: the prognostic value of longitudinal functional trends. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:531–537
Flaherty KR, Mumford JA, Murray S, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Colby TV, Travis WD, Flint A, Toews GB, Lynch JP, Martinez FJ (2003) Prognostic implications of physiologic and radiographic changes in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:543–548
Weiss SJ (1989) Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med 320:365–376
Ravetch JV, Bolland S (2001) IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 19:275–290
Whyte M, Hubbard R, Meliconi R, Whidborne M, Eaton V, Bingle C, Timms J, Duff G, Facchini A, Pacilli A, Fabbri M, Hall I, Britton J, Johnston I, Di Giovine F (2000) Increased risk of fibrosing alveolitis associated with interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor-α gene polymorphisms. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:755–758
Checa M, Ruiz V, Montaño M, Velázquez-Cruz R, Selman M, Pardo A (2008) MMP-1 polymorphisms and the risk of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum Genet 124:465–472
Molina-Molina M, Xaubet A, Li X, Abdul-Hafez A, Friderici K, Jernigan K, Fu W, Ding Q, Pereda J, Serrano-Mollar A, Casanova A, Rodríguez-Becerra E, Morell F, Ancochea J, Picado C, Uhal BD (2008) Angiotensinogen gene G-6A polymorphism influences idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression. Eur Respir J 32:1004–1008
Mushiroda T, Wattanapokayakit S, Takahashi A, Nukiwa T, Kudoh S, Ogura T, Taniguchi H, Kubo M, Kamatani N, Nakamura Y, Group PCS (2008) A genome-wide association study identifies an association of a common variant in TERT with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Med Genet 45:654–656
Pantelidis P, Fanning GC, Wells AU, Welsh KI, Du Bois RM (2001) Analysis of tumor necrosis factor-α, lymphotoxin-α, tumor necrosis factor receptor II, and interleukin-6 polymorphisms in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:1432–1436
Riha RL, Yang IA, Rabnott GC, Tunnicliffe AM, Fong KM, Zimmerman PV (2004) Cytokine gene polymorphisms in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern Med J 34:126–129
Selman M, Lin HM, Montaño M, Jenkins AL, Estrada A, Lin Z, Wang G, DiAngelo SL, Guo X, Umstead TM, Lang CM, Pardo A, Phelps DS, Floros J (2003) Surfactant protein A and B genetic variants predispose to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum Genet 113:542–550
Vasakova M, Striz I, Dutka J, Slavcev A, Jandova S, Kolesar L, Sulc J (2007) Cytokine gene polymorphisms and high-resolution-computed tomography score in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med 101:944–950
Vasakova M, Striz I, Slavcev A, Jandova S, Kolesar L, Sulc J (2006) Th1/Th2 cytokine gene polymorphisms in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Tissue Antigens 67:229–232
Whittington HA, Freeburn RW, Godinho SIH, Egan J, Haider Y, Millar AB (2003) Analysis of an IL-10 polymorphism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Genes Immun 4:258–264
Xaubet A, Marin-Arguedas A, Lario S, Ancochea J, Morell F, Ruiz-Manzano J, Rodriguez-Becerra E, Rodriguez-Arias JM, Inigo P, Sanz S, Campistol JM, Mullol J, Picado C (2003) Transforming growth factor-β1 gene polymorphisms are associated with disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:431–435
Zorzetto M, Ferrarotti I, Trisolini R, Agli LL, Scabini R, Novo M, De Silvestri A, Patelli M, Martinetti M, Cuccia M, Poletti V, Pozzi E, Luisetti M (2003) Complement receptor 1 gene polymorphisms are associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:330–334
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Andrew Robson for his help in obtaining lung function measurements and Dr. Zhe Hui Hoo for his help and comments. We also thank all the past members from our group (Centre for Inflammation Research, UK) and all the subjects who participated in this study. This work was supported by grants from the British Heart Foundation (FS/05/119/19568) and the Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bournazos, S., Bournazou, I., Murchison, J.T. et al. Fcγ Receptor IIIb (CD16b) Polymorphisms are Associated with Susceptibility to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 188, 475–481 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-010-9262-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-010-9262-3