Abstract
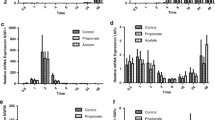
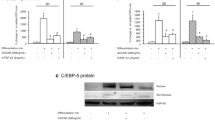
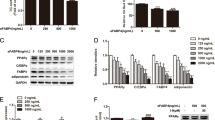
Defects in fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36) have been identified as a major factor in insulin resistance and defective fatty acid and glucose metabolism. Therefore, understanding of the regulation of FAT/CD36 expression and function is important for a potential therapeutic target for type II diabetes. We differentiated 3T3-L1 preadipocytes into matured adipocytes and examined the roles of insulin and long chain fatty acids on FAT/CD36 expression and function. Our results indicate that FAT/CD36 mRNA expression was not detected at preadipocyte but was significantly increased at matured adipocyte. In fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes, insulin significantly increased FAT/CD36 mRNA and protein expression in a dose dependent manner. The free fatty acid stearic acid reduced FAT/CD36 mRNA expression while the non-metabolizable free fatty acid alpha-bromopalmitate (2-BP) significantly increased FAT/CD36 mRNA and protein expression. Isoproterenol, in contrast, dose-dependently reduced FAT/CD36 mRNA expression and increased free fatty acid release. Mechanism analysis indicated that the effect of insulin and 2-BP on the FAT/CD36 mRNA gene expression may be mediated through activation of PPAR-γ, suggesting that FAT/CD36 may have important implications in the pathophysiology of defective fatty acid metabolism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopelman PG (2000) Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404:635–643
Hotu S, Carter B, Watson P, Cutfield W, Cundy T (2004) Increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adolescents. J Paediatr Child Health 40:201–204
Bhargava SK, Sachdev HS, Fall CH et al (2004) Relation of serial changes in childhood body-mass index to impaired glucose tolerance in young adulthood. N Engl J Med 350:865–875
Nammi S, Koka S, Chinnala KM, Boini KM (2004) Obesity: an overview on its current perspectives and treatment options. Nutr J 3:3
Kissebah AH, Krakower GR (1994) Regional adiposity and morbidity. Physiol Rev 74:761–811
Reaven GM (1993) Role of insulin resistance in human disease (syndrome X): an expanded definition. Annu Rev Med 44:121–131
Lean ME, Han TS, Seidell JC (1998) Impairment of health and quality of life in people with large waist circumference. Lancet 351:853–856
Han TS, van Leer EM, Seidell JC, Lean ME (1995) Waist circumference action levels in the identification of cardiovascular risk factors: prevalence study in a random sample. Bmj 311:1401–1405
Lapidus L, Bengtsson C, Larsson B, Pennert K, Rybo E, Sjostrom L (1984) Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: a 12 year follow up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289:1257–1261
Felber JP, Ferrannini E, Golay A et al (1987) Role of lipid oxidation in pathogenesis of insulin resistance of obesity and type II diabetes. Diabetes 36:1341–1350
Fujioka S, Matsuzawa Y, Tokunaga K et al (1991) Improvement of glucose and lipid metabolism associated with selective reduction of intra-abdominal visceral fat in premenopausal women with visceral fat obesity. Int J Obes 15:853–859
Dennis KE, Goldberg AP (1993) Differential effects of body fatness and body fat distribution on risk factor for cardiovascular disease in women. Impact of weight loss. Arterioscler Thromb 13:1487–1494
Okamoto F, Tanaka T, Sohmiya K, Kawamura K (1998) CD36 abnormality and impaired myocardial long-chain fatty acid uptake in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Jpn Circ J 62:499–504
Lefebvre M, Paulweber B, Fajas L et al (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is induced during differentiation of colon epithelium cells. J Endocrinol 162:331–340
Lowell BB (1999) PPARgamma: an essential regulator of adipogenesis and modulator of fat cell function. Cell 99:239–242
Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T et al (2001) PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 50:2094–2099
Tanaka T, Sohmiya K, Kawamura K (1997) Is CD36 deficiency an etiology of hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:121–127
Sfeir Z, Ibrahimi A, Amri E, Grimaldi P, Abumrad N (1997) Regulation of FAT/CD36 gene expression: further evidence in support of a role of the protein in fatty acid binding/transport. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 57:17–21
Sfeir Z, Ibrahimi A, Amri E, Grimaldi P, Abumrad N (1999) CD36 antisense expression in 3T3-F442A preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 192:3–8
Van Nieuwenhoven FA, Luiken JJ, De Jong YF, Grimaldi PA, van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF (1998) Stable transfection of fatty acid translocase (CD36) in a rat heart muscle cell line (H9c2). J Lipid Res 39:2039–2047
Abumrad NA, el-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, Grimaldi PA (1993) Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. J Biol Chem 268:17665–17668
Abumrad NA, Sfeir Z, Connelly MA, Coburn C (2000) Lipid transporters: membrane transport systems for cholesterol and fatty acids. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 3:255–262
Abumrad N, Coburn C, Ibrahimi A (1999) Membrane proteins implicated in long-chain fatty acid uptake by mammalian cells: CD36, FATP and FABPm. Biochim Biophys Acta 1441:4–13
Coburn CT, Hajri T, Ibrahimi A, Abumrad NA (2001) Role of CD36 in membrane transport and utilization of long-chain fatty acids by different tissues. J Mol Neurosci 16:117–21
Moore KJ, Rosen ED, Fitzgerald ML et al (2001) The role of PPAR-gamma in macrophage differentiation and cholesterol uptake. Nat Med 7:41–47
Koonen DP, Glatz JF, Bonen A, Luiken JJ (2005) Long-chain fatty acid uptake and FAT/CD36 translocation in heart and skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1736:163–180
Mackall JC, Student AK, Polakis SE, Lane MD (1976) Induction of lipogenesis during differentiation in a “preadipocyte” cell line. J Biol Chem 251:6462–6464
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Courtneidge SA, Smith AE (1983) Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature 303:435–439
Schaffer JE, Lodish HF (1994) Expression cloning and characterization of a novel adipocyte long chain fatty acid transport protein. Cell 79:427–436
Chen M, Yang Y, Braunstein E, Georgeson KE, Harmon CM (2001) Gut expression and regulation of FAT/CD36: possible role in fatty acid transport in rat enterocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281:E916–E923
Langin D (2006) Adipose tissue lipolysis as a metabolic pathway to define pharmacological strategies against obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol Res 53:482–491
Akahoshi T, Namai R, Murakami Y et al (2003) Rapid induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression in human monocytes by monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Arthritis Rheum 48:231–239
Yu S, Matsusue K, Kashireddy P et al (2003) Adipocyte-specific gene expression and adipogenic steatosis in the mouse liver due to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 (PPARgamma1) overexpression. J Biol Chem 278:498–505
Vosper H, Patel L, Graham TL et al (2001) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta promotes lipid accumulation in human macrophages. J Biol Chem 276:44258–44265
Singh Ahuja H, Liu S, Crombie DL et al (2001) Differential effects of rexinoids and thiazolidinediones on metabolic gene expression in diabetic rodents. Mol Pharmacol 59:765–773
Wu Q, Ortegon AM, Tsang B, Doege H, Feingold KR, Stahl A (2006) FATP1 is an insulin-sensitive fatty acid transporter involved in diet-induced obesity. Mol Cell Biol 26:3455–3467
Man MZ, Hui TY, Schaffer JE, Lodish HF, Bernlohr DA (1996) Regulation of the murine adipocyte fatty acid transporter gene by insulin. Mol Endocrinol 10:1021–1028
Unterman TG, Fareeduddin A, Harris MA et al (1994) Hepatocyte nuclear factor-3 (HNF-3) binds to the insulin response sequence in the IGF binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) promoter and enhances promoter function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 203:1835–1841
Tebbey PW, McGowan KM, Stephens JM, Buttke TM, Pekala PH (1994) Arachidonic acid down-regulates the insulin-dependent glucose transporter gene (GLUT4) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by inhibiting transcription and enhancing mRNA turnover. J Biol Chem 269:639–644
O’Brien RM, Noisin EL, Suwanichkul A et al (1995) Hepatic nuclear factor 3-and hormone-regulated expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 genes. Mol Cell Biol 15:1747–1758
Spiegelman BM, Choy L, Hotamisligil GS, Graves RA, Tontonoz P (1993) Regulation of adipocyte gene expression in differentiation and syndromes of obesity/diabetes. J Biol Chem 268:6823–6826
Facchini FS, Stoohs RA, Reaven GM (1996) Enhanced sympathetic nervous system activity. The linchpin between insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and heart rate. Am J Hypertens 9:1013–1017
Gerich JE (1998) The genetic basis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: impaired insulin secretion versus impaired insulin sensitivity. Endocr Rev 19:491–503
Boden G (2003) Effects of free fatty acids (FFA) on glucose metabolism: significance for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 111:121–124
Fasshauer M, Klein J, Ueki K et al (2000) Essential role of insulin receptor substrate-2 in insulin stimulation of Glut4 translocation and glucose uptake in brown adipocytes. J Biol Chem 275:25494–25501
Fasshauer M, Klein J, Kriauciunas KM, Ueki K, Benito M, Kahn CR (2001) Essential role of insulin receptor substrate 1 in differentiation of brown adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 21:319–329
Teboul L, Febbraio M, Gaillard D, Amri EZ, Silverstein R, Grimaldi PA (2001) Structural and functional characterization of the mouse fatty acid translocase promoter: activation during adipose differentiation. Biochem J 360:305–312
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Chen, M., Loux, T.J. et al. Regulation of FAT/CD36 mRNA gene expression by long chain fatty acids in the differentiated 3T3-L1 cells. Pediatr Surg Int 23, 675–683 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-007-1942-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-007-1942-6