Abstract
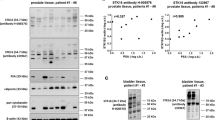
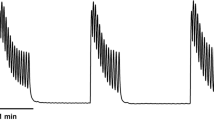
Anticholinergic drugs are currently the therapy of choice to treat urgency and urge incontinence. However, muscarinergic receptor blockers with adequate selectivity for detrusor smooth muscle are not available. Also, in contrast to the normal detrusor, the unstable detrusor neurotransmission seems to be at least partially regulated by non-cholinergic (NANC) pathways. These factors may explain the common side effects and the limited clinical efficacy of these compounds. Specific modulation of intracellular second messenger pathways offers the possibility of organ selective manipulation of tissue function, specifically contraction and relaxation of smooth musculature. Because of their central role in the intracellular regulation of smooth muscle tone phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are an attractive pharmacological targets. The PDE 5 specific inhibitor sildenafil (Viagra) has revolutionized the treatment of patients with erectile dysfunction. Numerous other PDE inhibitors are currently under investigation for the treatment of various disorders. We investigated the role of PDEs in human detrusor smooth muscle. Our data demonstrate the presence of five PDE isoenzymes in human detrusor and suggest, for the first time, that the cAMP pathway and the calcium/calmodulin-stimulated PDE (PDE 1) are of functional importance in the intracellular regulation in this tissue in vitro. In addition, initial clinical data with the PDE 1 inhibitor vinpocetine in patients not responding to standard anticholinergic therapy indicate a possible role for vinpocetine in the treatment of urgency, urge incontinence and, possibly, low compliance bladder and interstitial cystitis. The results of a larger randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial with vinpocetine show a tendency in favor of vinpocetine over placebo; however, statistically significant results were documented for one parameter only. This might be due to the rather low dosage chosen and the small sample size. Further studies are necessary and currently underway to delineate the optimal dosage, indications and patient population. Modulation of intracellular key enzymes effecting second messenger metabolism, i.e. isoenzyme-selective PDE inhibition is a novel approach which possibly avoids the limitations of anticholinergic therapy in patients with lower urinary tract dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truss, M., Stief, C., Ückert, S. et al. Phosphodiesterase 1 inhibition in the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction: From bench to bedside. World J Urol 19, 344–350 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450100221
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003450100221