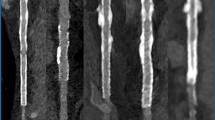
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of sub-milliSievert (mSv) coronary CT angiography (cCTA) using prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral CT acquisition combined with iterative image reconstruction.
Methods
Forty consecutive patients (52.9 ± 8.7 years; 30 men) underwent dual-source cCTA using prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition. The tube current-time product was set to 50 % of standard-of-care CT examinations. Images were reconstructed with sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction. Image quality was scored and diagnostic performance for detection of ≥50 % stenosis was determined with catheter coronary angiography (CCA) as the reference standard.
Results
CT was successfully performed in all 40 patients. Of the 601 assessable coronary segments, 543 (90.3 %) had diagnostic image quality. Per-patient sensitivity for detection of ≥50 % stenosis was 95.7 % [95 % confidence interval (CI), 76.0-99.8 %] and specificity was 94.1 % (95 % CI, 69.2-99.7 %). Per-vessel sensitivity was 89.5 % (95 % CI, 77.8-95.6 %) with 93.2 % specificity (95 % CI, 86.0-97.0 %). The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve on per-patient and per-vessel levels was 0.949 and 0.913. Mean effective dose was 0.58 ± 0.17 mSv. Mean size-specific dose estimate was 3.14 ± 1.15 mGy.
Conclusions
High-pitch prospectively ECG-triggered cCTA combined with iterative image reconstruction provides high diagnostic accuracy with a radiation dose below 1 mSv for detection of coronary artery stenosis.
Key Points
• Cardiac CT with sub-milliSievert radiation dose is feasible in many patients
• High-pitch spiral CT acquisition with iterative reconstruction detects coronary stenosis accurately.
• Iterative reconstruction increases who can benefit from low-radiation cardiac CT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- CCA:
-
Catheter coronary angiography
- cCTA:
-
Coronary computed tomography angiography
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CTDIvol :
-
CT volume dose index
- DLP:
-
Dose-length product
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- ED:
-
Effective dose
- FBP:
-
Filtered back projection
- LAD:
-
Left anterior descending coronary artery
- LCx:
-
Left circumflex coronary artery
- LM:
-
Left main coronary artery
- ROC:
-
Receiver-operating characteristics
- RCA:
-
Right coronary artery
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
References
Taylor AJ, Cerqueira M, Hodgson JM et al (2010) ACCF/SCCT/ACR/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCMR 2010 appropriate use criteria for cardiac computed tomography. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol 56:1864–1894
Alkadhi H, Stolzmann P, Desbiolles L et al (2010) Low-dose, 128-slice, dual source CT coronary angiography: accuracy and radiation dose of the high-pitch and the step-and-shoot mode. Heart 96:933–938
Achenbach S, Goroll T, Seltmann M et al (2011) Detection of coronary artery stenoses by low-dose, prospectively ECG-triggered, high-pitch spiral coronary CT angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 4:328–337
Tricarico F, Hlavacek AM, Schoepf UJ et al (2013) Cardiovascular CT angiography in neonates and children: Image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction with iterative image reconstruction techniques. Eur Radiol 3:1306–1315
Renker M, Nance JW, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography: comparison of iterative and filtered back projection image reconstruction. Radiology 260:390–399
Schuhbaeck A, Achenbach S, Layritz C et al (2013) Image quality of ultra-low radiation exposure coronary CT angiography with an effective dose <0.1 mSv using high-pitch spiral acquisition and raw data-based iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol 23:597–606
Baek J, Pelc NJ (2010) The noise power spectrum in CT with direct fan beam reconstruction. Med Phys 37:2074–2081
Renker M, Ramachandra A, Schoepf UJ et al (2011) Iterative image reconstruction techniques: Applications for cardiac CT. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 5:225–230
Winklehner A, Karlo C, Puippe G et al (2011) Raw data-based iterative reconstruction in body CTA: evaluation of radiation dose saving potential. Eur Radiol 21:2521–2526
Boone J, Strauss K, Cody D et al (2011) Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in pediatric and adult body CT examinations. Report of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) Task Group 204. American Association of Physicists in Medicine, College Park
Raff GL, Abidov A, Achenbach S et al (2009) SCCT guidelines for the interpretation and reporting of coronary computed tomographic angiography. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 3:122–136
Sun ML, Lu B, Wu RZ et al (2011) Diagnostic accuracy of dual-source CT coronary angiography with prospective ECG-triggering on different heart rate patients. Eur Radiol 21:1635–1642
Rixe J, Rolf A, Conradi G et al (2008) Image quality on dual-source computed-tomographic coronary angiography. Eur Radiol 18:1857–1862
Budoff MJ, Dowe D, Jollis JG et al (2008) Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenoses in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1724–1732
Ebersberger U, Tricarico F, Schoepf UJ et al (2013) CT evaluation of coronary artery stents with iterative image reconstruction: improvements in image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction. Eur Radiol 23:125–132
Bastarrika G, Broncano J, Arraiza M et al (2011) Systolic prospectively ECG-triggered dual-source CT angiography for evaluation of the coronary arteries in heart transplant recipients. Eur Radiol 21:1887–94
Gosling O, Loader R, Venables P et al (2010) A comparison of radiation doses between state-of-the-art multislice CT coronary angiography with iterative reconstruction, multislice CT coronary angiography with standard filtered back-projection and invasive diagnostic coronary angiography. Heart 96:922–926
Acknowledgement
This study received a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, grant No. 2007BAI05B02, and was supported in part by a research grant provided by Bayer Healthcare, Berlin, Germany.
UJS is a consultant for and receives research support from Bayer Healthcare, Bracco, GE Healthcare, and Siemens. The other authors have no industry relationships or conflicts of interest relevant to this investigation to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, WH., Lu, B., Hou, ZH. et al. Detection of coronary artery stenosis with sub-milliSievert radiation dose by prospectively ECG-triggered high-pitch spiral CT angiography and iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol 23, 2927–2933 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2920-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2920-0