Abstract
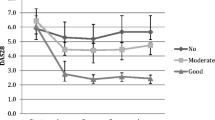
To examine whether -174G/C interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene polymorphism, previously reported to correlate with IL-6 level, influences response to etanercept therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Seventy-seven patients with active RA were studied, at baseline and 6- and 12-month follow-up after etanercept therapy. Treatment response was estimated according to the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria. RA patients were genotyped for -174G/C IL-6 gene polymorphism by the PCR–RFLP method, and influence of genotype at this polymorphism to clinical response to etanercept was assessed. After 12 months of treatment, the percentage of responders (patients who had DAS28 improvement >1.2) was significantly increased in patients carrying the IL-6 -174G/G genotype (95.7 %) compared with those with the G/C (75.6 %) or CC (44.4 %) genotype (p = 0.006 by Chi-square test). No significant difference in the mean values of DAS28 improvement was observed between groups with different genotype. RA patients with an IL-6 -174GG genotype respond to etanercept better than patients with GC or CC genotype. This finding, if confirmed in future studies, suggests that the -174G/C IL-6 polymorphism may be a genetic marker of responsiveness to tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) blockers in RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM et al (2000) A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1586–1593
Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F et al (1999) Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 354:1932–1939
Weyand CM, Klimiuk PA, Goronzy JJ (1998) Heterogeneity of rheumatoid arthritis: from phenotypes to genotypes. Springer Semin Immunopathol 20:5–22
Miterski B, Drynda S, Böschow G et al (2004) Complex genetic predisposition in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Genet 5:2
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN (1996) Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol 14:397–440
Dasgupta B, Corkill M, Kirkham B, Gibson T, Panayi G (1992) Serial estimation of interleukin-6 as a measure of systemic disease in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 19:22–25
Kotake S, Sato K, Kim KJ et al (1996) Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res 11:88–95
Ishibashi T, Kimura H, Shikama Y et al (1989) Interleukin-6 is a potent thrombopoietic factor in vivo in mice. Blood 74:1241–1244
Choy EH, Isenberg DA, Garrood T et al (2002) Therapeutic benefit of blocking interleukin-6 activity with an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Arthritis Rheum 46:3143–3150
Wilson AG, Symons JA, McDowell TL, McDevitt HO, Duff GW (1997) Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor α promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3195–3199
Eskdale J, Gallagher G, Verweij CL, Keijsers V, Westerndrop RGJ, Huizinga TWJ (1998) IL-10 secretions in relation to the haplotypic structure of the human IL-10 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9465–9470
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R et al (1998) The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest 102:1369–1376
Jones KG, Brull DJ, Brown LC et al (2001) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and the prognosis of abdominal aortica neurysms. Circulation 103:2260–2265
Jerrard-Dunne P, Sitzer M, Risley P et al (2003) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism modulates the effects of heavy alcohol consumption on early carotid artery atherosclerosis: the Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study (CAPS). Stroke 34:402–407
Panoulas VF, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Metsios GS et al (2009) Association of interleukin-6 (IL-6)-174G/C gene polymorphism with cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the role of obesity and smoking. Atherosclerosis 204:178–183
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR et al (2000) Consensus statement on the initiation and continuation of tumour necrosis factor blocking therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 59:504–505
Danila MI, Hughes LB, Bridges SL (2008) Pharmacogenetics of etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 9:1011–1015
Ohshima S, Saeki Y, Mima T et al (1998) Interleukin 6 plays a key role in the development of antigen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8222–8226
Madhok R, Crilly A, Watson J, Capell HA (1993) Serum interleukin 6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis: correlations with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis 52:232–234
Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Miyasaka N et al (2004) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 50:1761–1769
Barrera P, Boerbooms AMT, Janssen EM et al (1993) Circulating soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors, interleukin-2 receptors, tumor necrosis factor α, and interleukin-6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis: longitudinal evaluation during methotrexate and azathioprine therapy. Arthritis Rheum 36:1070–1079
Crily A, McInness IB, McDonald AG, Watson J, Capell HA, Madhok R (1995) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-2 receptor levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with low dose oral methotrexate. J Rheumatol 22:224–226
Pascual M, Nieto A, Matarán L, Balsa A, Pascual-Salcedo D, Martín J (2000) IL-6 promoter polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun 1:338–340
Ceccarelli F, Perricone C, Fabris M et al (2011) Transforming growth factor β 869C/T and interleukin 6–174G/C polymorphisms relate to the severity and progression of bone-erosive damage detected by ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R111
Pawlik A, Wrzesniewska J, Florczak M, Gawronska-Szklarz B, Herczynska M (2005) IL-6 promoter polymorphism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 34:109–113
Drynda S, Kühne C, Kekow J (2002) Soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor treatment does not affect raised transforming growth factor beta levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 61:254–256
Zivojinovic SM, Pejnovic NN, Sefik-Bukilica MN, Kovacevic LV, Soldatovic II, Damjanov NS (2012) Tumor necrosis factor blockade differentially affects innate inflammatory and Th17 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 39:18–21
Cuchacovich M, Soto L, Edwardes M et al (2006) Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) alpha -308 G/G promoter polymorphism and TNF alpha levels correlate with a better response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 35:435–440
Guis S, Balandraud N, Bouvenot J et al (2007) Influence of -308 A/G polymorphism in the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene on etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 57:1426–1430
Seitz M, Wirthmüller U, Möller B, Villiger PM (2007) The -308 tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism predicts therapeutic response to TNF alpha-blockers in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis patients. Rheumatology 46:93–96
Di Renzo L, Bertoli A, Bigioni M et al (2008) Body composition and -174G/C interleukin-6 promoter gene polymorphism: association with progression of insulin resistance in normal weight obese syndrome. Curr Pharm Des 14:2699–2706
Moreland LW, Cohen SB, Baumgartner SW et al (2001) Long-term safety and efficacy of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:1238–1244
Fife MS, Ogilvie EM, Kelberman D et al (2005) Novel IL-6 haplotypes and disease association. Genes Immun 6:367–370
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Education and Science of Republic of Serbia (grant numbers, 175050, 175065, III41004).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jančić, I., Arsenović-Ranin, N., Šefik-Bukilica, M. et al. -174G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism predicts therapeutic response to etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 33, 1481–1486 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2586-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2586-y