Abstract
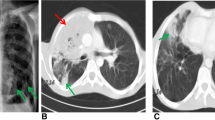
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is an inherited disorder characterized by the inability of phagocytes to generate normal amounts of superoxide (O2 –), leaving patients susceptible to life-threatening infections. It was previously assumed that once carriers of the X-linked form of CGD were found to have 30% or more of functionally normal neutrophils, they would be free of risk for infection because the lyonization ratio was believed to be constant. Our report strongly contradicts this assumption. A 45-year-old X-CGD carrier had approximately 40% of normal neutrophils in her peripheral blood at age 21 years. Recently, she contracted a life-threatening pulmonary infection with Aspergillus fumigatus. After recovery, the ratio of normal-to-nonfunctional neutrophils was re-evaluated. She was found to have only 6–8% of normal neutrophils, suggesting that a striking decrease in the number of normal cells over the past 25 years was the reason for an increased susceptibility to Aspergillus infection. We conclude that age-related acquired skewing of the lyonization ratio can result in an increased susceptibility to life-threatening infections in X-CGD carriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 April 2000 / Accepted: 4 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rösen-Wolff, A., Soldan, W., Heyne, K. et al. Increased susceptibility of a carrier of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) to Aspergillus fumigatus infection associated with age-related skewing of lyonization. Ann Hematol 80, 113–115 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770000230
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770000230