Abstract
Purpose
The nonthermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE) is a novel nonthermal tissue ablation technique by local application of high-voltage current within microseconds leading to a delayed apoptosis. The purpose of this experimental study was the first angiographic evaluation of the acute damage of renal vascular structure in NTIRE.
Methods
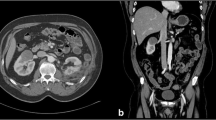
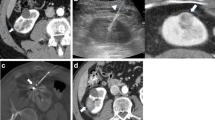
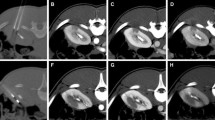
Results of conventional dynamic digital substraction angiography (DSA) and visualization of the terminal vascular bed of renal parenchyma by high-resolution X-ray in mammography technique were evaluated before, during, and after NTIRE of three isolated perfused porcine ex vivo kidneys.
Results
In the dedicated investigation, no acute vascular destruction of the renal parenchyma and no dysfunction of the kidney perfusion model were observed during or after NTIRE. Conspicuous were concentric wave-like fluctuations of the DSA contrast agent simultaneous to the NTIRE pulses resulting from NTIRE pulse shock wave.
Conclusion
The NTIRE offers an ablation method with no acute collateral vascular damage in angiographic evaluation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubinsky B, Onik G, Mikus P (2007) Irreversible electroporation: a new ablation modality—clinical implications. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6(1):37–48
Tracy CR, Kabbani W, Cadeddu JA (2010) Irreversible electroporation (IRE): a novel method for renal tissue ablation. BJU Int. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09797.x
Onik G, Mikus P, Rubinsky B (2007) Irreversible electroporation: implications for prostate ablation. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6(4):295–300
Dupuy DE, Aswad B, Ng T (2011) Irreversible electroporation in a swine lung model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:391–395
Sano MB, Neal RE 2nd, Garcia PA, Gerber D, Robertson J, Davalos RV (2010) Towards the creation of decellularized organ constructs using irreversible electroporation and active mechanical perfusion. Biomed Eng Online 9(1):83
Deodhar A, Monette S, Single GW Jr, Hamilton WC Jr, Thornton R, Maybody M, Coleman JA, Solomon SB (2011) Renal tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation: preliminary results in a porcine model. Urology 77:754–760
Garcia PA, Neal RE, Rossmeisl JH, Davalos RV (2010) Non-thermal irreversible electroporation for deep intracranial disorders. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 1:2743–2746
Charpentier KP, Wolf F, Noble L, Winn B, Resnick M, Dupuy DE (2010) Irreversible electroporation of the pancreas in swine: a pilot study. HPB (Oxford) 12(5):348–351
Maor E, Ivorra A, Mitchell JJ, Rubinsky B (2010) Vascular smooth muscle cells ablation with endovascular nonthermal irreversible electroporation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21(11):1708–1715
Al-Sakere B, André F, Bernat C, Connault E, Opolon P, Davalos RV, Rubinsky B, Mir LM (2007) Tumor ablation with irreversible electroporation. PLoS One 2(11):e1135
Lee EW, Chen C, Prieto VE, Dry SM, Loh CT, Kee ST (2010) Advanced hepatic ablation technique for creating complete cell death: irreversible electroporation. Radiology 255(2):426–433
Hong J, Stewart MT, Cheek DS, Francischelli DE, Kirchhof N (2009) Cardiac ablation via electroporation. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009:3381–3384
Lee EW, Thai S, Kee ST (2010) Irreversible electroporation: a novel image-guided cancer therapy. Gut Liver 4(Suppl 1):S99–S104
Goldberg SN, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, Gervais DA, Gillams AR, Kane RA, Lee FT Jr, Livraghi T, McGahan JP, Rhim H, Silverman SG, Solbiati L, Vogl TJ, Wood BJ, International Working Group on Image-Guided Tumor Ablation (2003) Image-guided tumor ablation: proposal for standardization of terms and reporting criteria. Radiology 228(2):335–345
Granot Y, Ivorra A, Maor E, Rubinsky B (2009) In vivo imaging of irreversible electroporation by means of electrical impedance tomography. Phys Med Biol 54(16):4927–4943
Lee EW, Loh CT, Kee ST (2007) Imaging guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation: ultrasound and immunohistological correlation. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6(4):287–294
Thomson KR, Cheung W, Ellis SJ, Park D, Kavnoudias H, Loader-Oliver D, Roberts S, Evans P, Ball C, Haydon A (2011) Investigation of the safety of irreversible electroporation in humans. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22(5):611–621
Pech M, Janitzky A, Wendler JJ, Strang C, Blaschke S, Dudeck O, Ricke J, Liehr UB (2011) Irreversible electroporation of renal cell carcinoma: a first-in-man phase I clinical study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:132–138
Ball C, Thomson KR, Kavnoudias H (2010) Irreversible electroporation: a new challenge in “out of operating theater” anesthesia. Anesth Analg 110(5):1305–1309
Ljungberg B, Cowan N, Hanbury DC, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Mulders PFA, Patard JJ, Sinescu IC (2010) Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma. European Association of Urology (EAU). http://www.uroweb.org/. Accessed 25 May 2011
Maor E, Ivorra A, Leor J, Rubinsky B (2007) The effect of irreversible electroporation on blood vessels. Technol Cancer Res Treat 6(4):307–312
Häcker A, Chauhan S, Peters K, Hildenbrand R, Marlinghaus E, Alken P, Michel MS (2005) Multiple high-intensity focused ultrasound probes for kidney-tissue ablation. J Endourol 19(8):1036–1040
Köhrmann KU, Back W, Bensemann J, Florian J, Weber A, Kahmann F, Rassweiler J, Alken P (1994) The isolated perfused kidney of the pig: new model to evaluate shock wave-induced lesions. J Endourol 8(2):105–110
Peters K (2007) Experimetelle Untersuchungen zur nichtinvasiven Gewebeablation durch hochenergetischen fokussierten Ultraschall (HIFU). Dissertation, Tierärztliche Fakultät der LMU München. http://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/6643/1/Peters_Kristina.pdf
Duffey BG, Kyle Anderson J (2010) Current and future technology for minimally invasive ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Indian J Urol 26(3):410–417
Sersa G, Jarm T, Kotnik T, Coer A, Podkrajsek M, Sentjurc M, Miklavcic D, Kadivec M, Kranjc S, Secerov A, Cemazar M (2008) Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine sarcoma. Br J Cancer 98(2):388–398
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This study was performed independently of the manufacturer of the devices used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Johann Jakob Wendler and Maciej Pech are contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendler, J.J., Pech, M., Blaschke, S. et al. Angiography in the Isolated Perfused Kidney: Radiological Evaluation of Vascular Protection in Tissue Ablation by Nonthermal Irreversible Electroporation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 383–390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0187-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0187-x