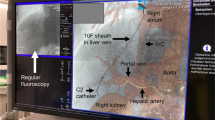
Purpose: We retrospectively evaluated the technical and long-term clinical results of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS) in children with portal hypertension and biliary atresia (BA). Methods: Nine children with BA and recurrent bleeding from esophagogastric and/or intestinal varices were treated by TIPS at the age of 34–156 months and followed-up in two centers. Different types of stents were used. Results: Shunt insertion succeeded in all patients, but in two a second procedure was necessary. Seven procedures lasted more than 3 hr, mainly due to difficult portal vein puncture. Variceal bleeding ceased in all patients; however, 16 reinterventions were performed in eight patients for clinical reasons (n = 11) and sonographically suspected restenosis (n = 5). Four patients underwent successful liver transplantation 4–51 months after TIPS and five are in good clinical conditions 64–75 months after TIPS. Conclusions: TIPS in children with BA is technically difficult, mainly due to periportal fibrosis and small portal veins. Frequency of reinterventions seems to be higher compared with adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huppert, P., Goffette, P., Astfalk, W. et al. Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Children with Biliary Atresia. CVIR 25, 484–493 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-002-1913-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-002-1913-1