Abstract
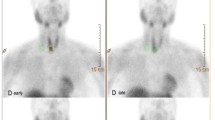
We prospectively studied 43 patients with solitary cold thyroid nodules greater than 1.5 cm in diameter to determine the comparative diagnostic value of radionuclide thyroid angiography (RTA), technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (99mTc-MIBI) scintigraphy and power Doppler ultrasonography (PDUS) in the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Perfusion of the nodules in RTA was compared with the perfusion in the surrounding normal thyroid tissue and classified as follows: 0, avascular; 1, hypovascular; 2, isovascular; 3, hypervascular. 99mTc-MIBI uptake in the nodules compared with that in surrounding thyroid tissue was scored for both early and delayed images as follows: 0, cold; 1, decreased; 2, equal; 3, increased. PDUS patterns were classified as nodule vascularisation patterns. The malignancy criteria were set as follows: hypervascular nodule with rapid washout in RTA; complex ring sign with anarchic structure or delta sign in PDUS, and positive retention and increased uptake in the nodule in the early and delayed 99mTc-MIBI images. These data were compared with the histopathological results. Histology revealed thyroid carcinoma in nine patients (five cases of papillary carcinoma, three of follicular carcinoma and one of medullary carcinoma) and benign conditions in 34 patients (30 cases of nodular goitre, three of lymphocytic thyroiditis and one of follicular adenoma). Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were, respectively, 0.89, 1.00 and 0.97 for RTA, 1.00, 0.76 and 0.81 for PDUS, and 0.67, 0.91 and 0.86 for 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy (when nodules with increased uptake in both the early and the delayed images and a positive retention index were considered as malignant). RTA, 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy and PDUS could be helpful in the preoperative assessment of solitary cold thyroid nodules. In this study, RTA was found to be the most accurate and specific method for differentiation of malignant from benign thyroid nodules.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burguera B, Gharib H. Thyroid incidentalomas. Prevalence, diagnosis, significance, and management. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2000; 29:187–203.
Mazzaferri EL. Thyroid carcinoma in a thyroid nodule. Finding a needle in the haystack. Am J Med 1992; 93:359–362.
Belfiore A, Rosa GL. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2001; 30:361–398.
Gharib H. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules: advantages, limitations, and effect. Mayo Clin Proc 1994; 69:44–49.
Mazzaferri EL. Current concepts: management of the solitary thyroid nodule. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:553–559.
Gharib H, Goellner JR. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid: an appraisal. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118:283–289.
Belfiore A, Rosa GL. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2001; 30:361–398.
Meier CA. Thyroid nodules: pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Bailiere's Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 14:559–575.
Gharib H, Goellner JR, Zinsmeister AR, Grant CS, Van Heerden JA. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid. The problem of suspicious cytologic findings. Ann Intern Med 1984; 101:25–28.
Block MA, Dalley GE, Robb JA. Thyroid nodules indeterminate by needle biopsy. Am J Surg 1983; 146:72–78.
Robbins SL. Pathological basis of diseases. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1974:1336–1395.
Ramsden JD. Angiogenesis in the thyroid gland. J Endocrinol 2000; 166:475–480.
Taylor JW, Ramos I, Carter D, Morse SS. Correlation of Doppler US tumor signals with neovascular morphologic features. Radiology 1988; 166:57–62.
Aggarwal SK, Jayaram G, Kakar A, Goel GD, Prakash R, Pant CS. Fine needle aspiration cytologic diagnosis of the solitary cold tyroid nodule: comparison with ultrasonography, radionuclide perfusion study and xeroradiography. Acta Cytol 1989; 33:41–47.
Natarajan V, Jayaram G, Kakar A, Prakash R. Solitary cold thyroid nodules: a correlation of fine needle aspiration cytology with pentavalent technetium DMSA scanning and radionuclide perfusion scanning. Malays J Pathol 1994; 16:127–135.
Prakash R, Lakshmipathi N, Jena A, Narayanan RV, Behari V. Computer-assisted radionuclide perfusion study in solitary cold thyroid nodules for diagnosis of malignancy. Eur J Nucl Med 1985; 11:143–146.
Prakash R, Narayanan RV, Shankar LR, Kakar A. Radionuclide angiography in evaluation of cold solitary thyroid nodules. Improved diagnostic accuracy using flow and washout analysis. Clin Nucl Med 1995; 20:878–883.
Hegedüs L. Thyroid ultrasound. Endocrinol Metabol Clin North Am 2001; 30:339–360.
Murphy KJ, Rubin JM. Power Doppler: it's a good thing. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 1997; 18:13–21.
Derchi LE, Martinoli C, Solbiati L, Rizzatto G. Power Doppler: physical and constructive principles and comparison with Doppler color. Radiol Med 1997; 93:329–335.
Martinoli C, Pretolesi F, Crespi G, Bianchi S, Gandolfo N, Valle M, Derchi LE. Power Doppler sonography: clinical applications. Power Doppler sonography: clinical applications. Eur J Radiol 27 Suppl 2:133–140.
Casara D, Rubello D, Saladini G. Role of scintigraphy with tumor-seeking agent in the diagnosis and preoperative staging of malignant thyroid nodules. Biomed Pharmacother 2000; 54:334–336.
Erdil TY, Ozker K, Kabasakal L, Kanmaz B, Sonmezoglu K, Atasoy KC, Turoglu HT, Uslu I, Isitman AT, Onsel C. Correlation of technetium-99m MIBI and thallium-201 retention in solitary cold thyroid nodules with postoperative histopathology. Eur J Nucl Med 2000; 27:713–720.
Sharma R, Mondal A, Sahoo M, Kakar A, Shankar LR, Khanna CM, Chopra MK, Soni NL. Role of radionuclide perfusion study in cold solitary thyroid nodule for diagnosis of malignancy: a complementary diagnostic modality to fine needle aspiration cytology. J Assoc Physicians India 1999; 47:488–491.
Moe RD, Frankel SF, Chacko AK, Yim DW, Clark MW 3rd. Radionuclide thyroid angiography and surgical correlation. A five-year study. Arch Otolaryngol 1984; 110:717–720.
Sathekge MM, Mageza RB, Muthuphei MN, Modiba MCM, Clauss RC. Evaluation of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m MIBI and technetium-99m pertechnetate. Head Neck 2001; 23:305–310.
Nathan AR, Raines KB. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of cold thyroid nodules. Cancer 1988; 62:1337–1342.
Rausch P, Nowels K, Jeffrey B. Ultrasonographically guided thyroid biopsy. J Ultrasound Med 2001; 20:79–85.
Kresnik E, Gallowitsch HJ, Mikosch P, Gomez I, Lind P. Technetium-99m-MIBI scintigraphy of thyroid nodules in an endemic goiter area. J Nucl Med 1997; 38:62–65.
Foldes I, Levay A, Stotz G. Comparative scanning of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m pertechnetate and technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile. Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20:330–333.
Mezosi E, Bajnok L, Gyory F, Varga J, Sztojka I, Szabo J, Galuska L, Leovey A, Kakuk G, Nagy E. The role of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of cold thyroid nodules. Eur J Nucl Med 1999; 26:798–803.
Wei JP, Burke GJ. Characterization of the neoplastic potential of solitary solid thyroid lesions with Tc-99m-pertechnetate and Tc-99m-sestamibi scanning. Ann Surg Oncol 1995; 2:233–237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirel, K., Kapucu, Ö., Yücel, C. et al. A comparison of radionuclide thyroid angiography, 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy and power Doppler ultrasonography in the differential diagnosis of solitary cold thyroid nodules. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30, 642–650 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1124-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1124-2