Abstract
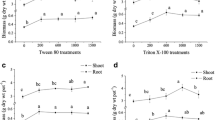
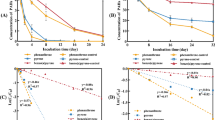
Two surfactants, Tween 80 and JBR, were investigated for their effect on fluoranthene degradation by a Pseudomonad. Both surfactants enhanced fluoranthene degradation by Pseudomonas alcaligenes PA-10 in shake flask culture. This bacterium was capable of utilising the synthetic surfactant and the biosurfactant as growth substrates and the critical micelle concentration of neither compound inhibited bacterial growth. The biosurfactant JBR significantly increased polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) desorption from soil. Inoculation of fluoranthene-contaminated soil microcosms with P. alcaligenes PA-10 resulted in the removal of significant amounts (45 ± 5%) of the PAH after 28 days compared to an uninoculated control. Addition of the biosurfactant increased the initial rate of fluoranthene degradation in the inoculated microcosm. The presence of a lower molecular weight PAH, phenanthrene, had a similar effect on the rate of fluoranthene removal.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronstein BN, Calvillo YM, Alexander M (1991) Effect of surfactants at low concentrations on the desorption and biodegradation of sorbed aromatic compounds in soil. Environ Sci Technol 25:1728–1731
Banat IM, Makkar RS, Cameotra SS (2000) Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:495–508
Bramwell DA, Laha S (2000) Effects of surfactant addition on the biomineralization and microbial toxicity of phenanthrene. Biodegradation 11:263–277
Briglia M, Nurmiaho-Lassila E-L, Vallini G, Salkinoja-Salonen M (1990) The survival of the pentachlorophenol-degrading Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus PCP-1 and Flavobacterium sp. in natural soil. Biodegradation 1:273–281
Cerniglia CE (1997) Fungal metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: past, present and future applications in bioremediation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19:324–333
Chen SH, Aitken MD (2001) Salicylate stimulates the degradation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas saccharophila P15. Environ Sci Technol 33:435–439
Deschênes L, Lafrance P, Villeneuve JP, Samson R (1996) Adding sodium dodecyl sulfate and Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 biosurfactants inhibits polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation in a weathered creosote-contaminated soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:638–646
Doong RA, Lei WG (2003) Solubilization and mineralization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas putida in the presence of surfactant. J Hazard Mater B96:15–27
Gordon L, Dobson ADW (2001) Fluoranthene degradation in Pseudomonas alcaligenes PA-10. Biodegradation 12:393–400
Grant RJ (2001) A bioassay for the measurement of insecticide concentration. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41:319–324
Herman DC, Zhang Y, Miller RM (1997) Rhamnolipid (biosurfactant) effects on cell aggregation and biodegradation of residual hexadecane under saturated flow conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3622–3627
Juhasz AL, Naidu R (2000) Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45:57–88
Kanaly RA, Harayama S (2000) Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. J Bacteriol 182:2059–2067
Keith LH, Telliard WA (1979) Priority pollutants. I—A perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13:416–423
Lageveen RG, Huisman HP, Ketelaar P, Eggink G, Witholt B (1988) Formation of polyesters by Pseudomonas oleovorans: effect of substrates on formation and composition of poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkenoates. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2924–2932
Laha S, Luthy RG (1991) Inhibition of phenanthrene mineralization by non-ionic surfactants in soil–water systems. Environ Sci Technol 25:1920–1930
Laha S, Luthy RG (1992) Effects of non-ionic surfactants on the solubilization and mineralization of phenanthrene in soil–water systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:1367–1380
McGrath R, Singleton I (2000) Pentachlorophenol transformation in soil: a toxicological assessment. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1311–1314
Meador JP, Stein JE, Reichert WL, Aranasi U (1995) Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by marine organisms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 143:79–165
Mueller JG, Cerniglia CE, Pritchard PH (1996) Bioremediation of environments contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In: Crawford RL, Crawford DL (eds) Bioremediation: principles and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 125–194
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Smith MR (1990) The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation 1:191–206
Smith MJ, Lethbridge G, Burns RG (1997) Bioavailability and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils. FEMS Microbiol Lett 152:141–147
Sobisch T, Heá H, Niebelschutz H, Schmidt U (2000) Effect of additives on biodegradation of PAH in soils. Colloid Surf A 162:1–14
Stelmack PL, Gray MR, Pickard MA (1999) Bacterial adhesion to soil contaminants in the presence of surfactants. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:163–168
Tiehm A (1994) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of synthetic surfactants. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:258–263
Tiehm A, Stieber M, Werner P, Frimmel FH (1997) Surfactant-enhanced mobilization and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in manufactured gas plant soil. Environ Sci Technol 31:2570–2576
US EPA (1994) Method 3541. Automated Soxhlet extraction. Revision 0
Van Dyke MI, Couture P, Brauer M, Lee H, Trevors JT (1993) Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 rhamnolipid biosurfactants: structural characterization and their use in removing hydrophobic compounds from soil. Can J Microbiol 39:1071–1078
Willumsen PA, Karlson U, Pritchard PH (1998) Response of fluoranthene-degrading bacteria to surfactants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:475–483
Wilson SC, Jones KC (1993) Bioremediation of soil contaminated with polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. Environ Pollut 81:229–249
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by contributory scholarships from Enterprise Ireland and the Environmental Protection Agency under the Environmental Research Technological Development and Innovation (ERTDI) programme 2000–2006. We wish to thank Jeneil Biosurfactant Company for supplying JBR, the biosurfactant used in these analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickey, A.M., Gordon, L., Dobson, A.D.W. et al. Effect of surfactants on fluoranthene degradation by Pseudomonas alcaligenes PA-10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 851–856 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0719-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0719-5