Abstract
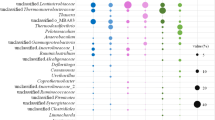
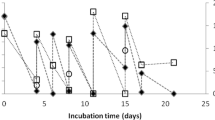
Stable-isotope probing (SIP) was used to identify acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria under nitrate-reducing conditions in activated sludge. A sludge sample obtained from wastewater treatment systems was incubated in a denitrifying batch reactor fed with synthetic wastewater containing [13C]acetate or [13C]methanol as the main carbon source and nitrate as the electron acceptor. We analyzed how growth of bacterial populations was stimulated by acetate or methanol as the external carbon source in nitrogen-removal systems. Most of the acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria identified by SIP have been known as denitrifiers in wastewater treatment systems. When acetate was used as the carbon source, 16S rRNA gene sequences retrieved from 13C-labeled DNA were closely related to the 16S rRNA genes of Comamonadaceae (e.g., Comamonas and Acidovorax) and Rhodocyclaceae (e.g., Thauera and Dechloromonas) of the Betaproteobacteria, and Rhodobacteraceae (e.g., Paracoccus and Rhodobacter) of the Alphaproteobacteria. When methanol was used as the carbon source, 16S rRNA gene sequences retrieved from 13C-DNA were affiliated with Methylophilaceae (e.g., Methylophilus, Methylobacillus, and Aminomonas) and Hyphomicrobiaceae. Rarefaction curves for clones retrieved from 13C-DNA showed that the diversity levels for methanol-assimilating bacteria were considerably lower than those for acetate-assimilating bacteria. Furthermore, we characterized nitrite reductase genes (nirS and nirK) as functional marker genes for denitrifier communities in acetate- or methanol-assimilating populations and detected the nirS or nirK sequence related to that of some known pure cultures, such as Alcaligenes, Hyphomicrobium, and Thauera. However, most of the nirS or nirK sequences retrieved from 13C-DNA were clustered in some unidentified groups. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene clone libraries retrieved from 13C-DNA, these unidentified nir sequences might be identified by examining the nir gene in candidates for true denitrifiers (e.g., the families Comamonadaceae, Hyphomicrobiaceae, Methylophilaceae, and Rhodobacteraceae).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasen, K, Nielsen, PH (1997) Application of microautoradiography to the study of substrate uptake by filamentous microorganisms in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 3662–3668
Braker, G, Ayala-del Rio, HL, Devol, AH, Fesefeldt, A, Tiedje, JM (2001) Community structure of denitrifiers, bacteria, and archaea along redox gradients in Pacific Northwest marine sediments by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of amplified nitrite reductase (nirS) and 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 1893–1901
Braker, G, Fesefeldt, A, Witzel, KP (1998) Development of PCR primer systems for amplification of nitrite reductase genes (nirK and nirS) to detect denitrifying bacteria in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 3769–3775
Braker, G, Tiedje, JM (2003) Nitric oxide reductase (norB) genes from pure cultures and environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 3476–3483
Cheneby, D, Hallet, S, Mondon, M, Martin-Laurent, F, Germon, JC, Philippot, L (2003) Genetic characterization of the nitrate reducing community based on narG nucleotide sequence analysis. Microb Ecol 46: 113–121
Claus, G, Kutzner, HJ (1985) Denitrification of nitrate and nitric acid with methanol as carbon source. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22: 378–381
Coates, JD, Chakraborty, R, Lack, JG, O'Connor, SM, Cole, KA, Bender, KS, Achenbach, LA (2001) Anaerobic benzene oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in pure culture by two strains of Dechloromonas. Nature 411: 1039–1043
Flanagan, DA, Gregory, LG, Carter, JP, Karakas-Sen, A, Richardson, DJ, Spiro, S (1999) Detection of genes for periplasmic nitrate reductase in nitrate respiring bacteria and in community DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177: 263–270
Gregory, LG, Karakas-Sen, A, Richardson, DJ, Spiro, S (2000) Detection of genes for membrane-bound nitrate reductase in nitrate respiring bacteria and in community DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 183: 275–279
Hallin, S, Lindgren, PE (1999) PCR detection of genes encoding nitrite reductase in denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65: 1652–1657
Holm, NC, Gliesche, CG, Hirasch, P (1996) Diversity and structure of Hyphomicrobium populations in a sewage treatment plant and its adjacent receiving lake. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 522–528
Ito, T, Nielsen, JL, Okabe, S, Watanabe, Y, Nielsen, PH (2002) Phylogenetic identification and substrate uptake patterns of sulfate reducing bacteria inhabiting an oxic–anoxic sewer biofilm determined by combining microautoradiography and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 356–364
Kelly, DP, Rainey, FA, Wood, AP (2001) The genus Paracoccus. In: Prokaryotes, An Evolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community, Release 3.7, 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York. http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/books/10125/. 2 Nov.
Labbe, N, Juteau, P, Parent, S, Villemur, R (2003) Bacterial diversity in a marine methanol-fed denitrification reactor at the Montreal biodome, Canada. Microb Ecol 46: 12–21
Lee, N, Nielsen, PH, Andreasen, KH, Juretschko, S, Nielsen, JL, Schleifer, KH, Wagner, M (1999) Combination of fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography—a new tool for structure–function analyses in microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 65: 1289–1297
Lemmer, H, Zaglaure, A, Metzner, G (1997) Denitrification in a methanol-fed fixed-bed reactor. Part 1: Physico-chemical and biological characterization. Water Res 31: 1897–1902
Lemmer, H, Zaglaure, A, Neef, A, Meier, H, Amann, R (1997) Denitrification in a methanol-fed fixed-bed reactor. Part 2: Composition and ecology of the bacterial community in the biofilm. Water Res 31: 1903–1908
Liu, X, Tiquia, SM, Holguin, G, Wu, L, Nold, SC, Devol, AH, Luo, K, Palumbo, AV, Tiedje, JM, Zhou, J (2003) Molecular diversity of denitrifying genes in continental margin sediments within the oxygen-deficient zone off the Pacific coast of Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 3549–3560
Lueders, T, Friedrich, M (2003) Evaluation of PCR amplification bias by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of small-subunit rRNA and mcrA genes by using defined template mixtures of methanogenic pure cultures and soil DNA extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 320–326
Maneesha, PG, Hugenholtz, P, Daimes, H, Wagner, M, Keller, J, Blackall, LL (2004) Use of stable-isotope probing, full-cycle rRNA analysis, and fluorescence in situ hybridization–microautoradiography to study a methanol-fed denitrifying microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 588–596
Manefield, M, Whiteley, AS, Griffiths, RI, Bailey, MJ (2002) RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community function to phylogeny. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 5367–5373
Nielsen, JP, Nielsen, PH (2002) Quantification of functional groups in activated sludge by microautoradiography. Water Sci Technol 46: 389–395
Morris, SA, Radajewski, S, Willison, TW, Murrel, JC (2002) Identification of the functionally active methanotroph population in a peat soil microcosm by stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 1446–1453
Muyzer, G, Brinkhoff, T, Nubel, U, Santegoeds, C, Schafer, H, Wawer, C. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) in microbial ecology. In: Akkermans, ADL, v. Elsas, JD, de Bruijin, FJ (Eds.) Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 3.4.4., pp 1–27
Neef, A, Zaglaure, A, Meier, H, Amann, R, Lemmer, H, Schleifer, KH (1996) Population analysis in a denitrifying sand filter: conventional and in situ identification of Paracoccus spp. in methanol-fed biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 4329–4339
Nogales, B, Timmis, KN, Nedwell, DB, Osborn, AM (2002) Detection and diversity of expressed denitrification genes in estuarine sediments after reverse transcription–PCR amplification from mRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 5017–5025
Nyberg, U, Aspegren, H, Andersson, B, Jansen, J, Cour, L, Villadsen, IS (1992) Full-scale application of nitrogen removal with methanol as carbon source. Water Sci Technol 26(5–6): 1077
Padmanabhan, P, Padmanabhan, S, Derito, C, Gray, A, Gannon, D, Snape, JR, Tsai, CS, Park, W, Jeon, C, Madsen, EL (2003) Respiration of 13C-labeled substrates added to soil in the field and subsequent 16S rRNA gene analysis of 13C-labeled soil DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 1614–1622
Page, RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12: 357–358
Poindexter, JS (1992) Dimorphic prosthecate bacteria: the genera Caulobacter, Asticcacaulis, Hyphomicrobium, Pedomicrobium, Hyphomonas, and Thiodendron. In: Balows, A, Truper, HG, Dworkin, M, Harder, W, Schleifer, K-H (Eds.) The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Ecophysiology, Isolation, Identification, Application, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 2176–2196
Prieme, A, Braker, G, Tiedje, JM (2002) Diversity of nitrite reductase (nirK and nirS) gene fragments in forested upland and wetland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 1893–1900
Radajewski, S, Ienson, P, Parekh, NR, Murrell, JC (2000) Stable-isotope probing as a tool in microbial ecology. Nature 403: 646–649
Radajewski, S, Webster, G, Reay, DS, Morris, SA, Ineson, P, Nedwell, DB, Prosser, JI, Murrel, JC (2002) Identification of active methylotroph populations in an acidic forest soil by stable isotope probing. Microbiology 148: 2331–2342
Saitou, N, Nei, M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4: 406–425
Scala, D, Kerkhof, LJ (1998) Nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) gene-specific PCR primers for detection of denitrifiers and three nosZ genes from marine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 162: 61–68
Scala D, Kerkhof, LJ (1999) Diversity of nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) genes in continental shelf sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1681–1687
Snaidr, J, Amann, R, Huber, I, Ludwig, W, Schleifer, KH (1997) Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 2884–2896
Song, B, Ward, BB (2003) Nitrite reductase genes in halobenzoate degradation denitrifier. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43: 349–357
Teske, A, Sigalevich, P, Cohen, Y, Muyzer, G (1996) Molecular identification of bacteria from a coculture by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S ribosomal DNA fragments as a tool for isolation in pure cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 4210–4215
Thompson, JD, Higgins, DG, Gibson, TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequencing weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22: 4673–4680
Trotsenko, YA, Doronina, NV, Hirsch, P (1989) Genus Blastobacter Zavarzin 1961, 962AL. In: Staley, JT, Bryant, MP, Pfennig, N, Holt, JG (Eds.) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol 3. Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, pp 1963–1968
Voordouw, G, Armstrong, SM, Reimer, MF, Fouts, B, Telang, AJ, Shen, Y, Gevertz, D (1996) Characterization of 16S rRNA genes from oil field microbial communities indicates the presence of a variety of sulfate-reducing, fermentative, and sulfide-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 1623–1629
Wagner, M, Loy, A (2002) Bacterial community composition and function in sewage treatment systems. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13: 218–227
Whitby, CB, Hall, G, Pickup, R, Saunders, JR, Ineson, P, Parekh, NR, McCarthy, A (2001) 13C incorporation into DNA as a means of identifying the active components of ammonia-oxidizer populations. Lett Appl Microbiol 32: 398–401
Willems, A, Vos, P (2001) The genus Comamonas. In: Prokaryotes, An Evolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community, 3rd edn., release 3.7, Springer-Verlag, New York. http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/books/10125/. Cited 2 Nov 2001
Wirsen, CO, Sievert, SM, Cavanaugh, CM, Molyneaux, SJ, Ahmad, A, Taylor, LT, DeLong, EF, Taylor, CD (2002) Characterization of an autotrophic sulfide-oxidizing marine Arcobacter sp. that produces filamentous sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 316–325
Yoshie, S, Noda, N, Tsuneda, S, Hirata, A, Inamori, Y (2004) Salinity decreases nitrite reductase gene diversity in denitrifying bacteria of wastewater treatment systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 3152–3157
Zhao JS, Ward, OP (1999) Microbial degradation of nitrobenzene and mono-nitrophenol by bacteria enriched from municipal activated sludge. Can J Microbiol 45: 427–432
Zumft, WG (1997) Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61: 533–616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osaka, T., Yoshie, S., Tsuneda, S. et al. Identification of Acetate- or Methanol-Assimilating Bacteria under Nitrate-Reducing Conditions by Stable-Isotope Probing. Microb Ecol 52, 253–266 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-006-9071-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-006-9071-7