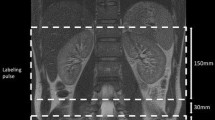
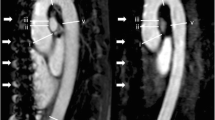
Abstract
Abdominal contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA) is routinely performed in children. CE-MRA is challenging in children because of patient motion, difficulty in obtaining intravenous access, and the inability of young patients to perform a breath-hold during imaging. The combination of pediatric-specific difficulties in imaging and the safety concerns regarding the risk of gadolinium-based contrast agents in patients with impaired renal function has renewed interest in the use of non-contrast (NC) MRA techniques. At our institution, we have optimized 3-D NC-MRA techniques for abdominal imaging. The purpose of this work is to demonstrate the utility of an inflow-enhanced, inversion recovery balanced steady-state free precession-based (b-SSFP) NC-MRA technique.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcos HB, Choyke PL (2000) Magnetic resonance angiography of the kidney. Semin Nephrol 20:450–455
Hollingsworth CL, Yoshizumi TT, Frush DP et al (2007) Pediatric cardiac-gated CT angiography: assessment of radiation dose. AJR 189:12–18
Krishnamurthy R, Muthupillai R, Chung T (2009) Pediatric body MR angiography. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 17:133–144
Thomsen HS (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamide. Eur Radiol 16:2619–2621
Cowper SE, Robin HS, Steinberg SM et al (2000) Scleromyxoedema-like cutaneous disease in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet 356:1000–1001
Silverman JM, Friedman ML, Van Allan RJ (1996) Detection of main renal artery stenosis using phase-contrast cine MR angiography. AJR 166:1131–1137
Maki JH, Wilson GJ, Eubank WB (2007) Steady-state free precession MRA of the renal arteries: breath-hold and navigated techniques vs. CE-MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:966–973
Glockner JF, Takahashi N, Kawashima A et al (2010) Non-contrast renal artery MRA using an inflow inversion recovery steady-state free precession technique (Inhance): comparison with 3-D contrast-enhanced MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:1411–1418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serai, S., Towbin, A.J. & Podberesky, D.J. Non-contrast MRA using an inflow-enhanced, inversion recovery SSFP technique in pediatric abdominal imaging. Pediatr Radiol 42, 364–368 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2275-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2275-0