Abstract
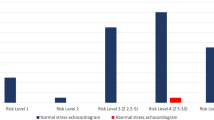
There has been no consistent approach to the follow-up of Kawasaki disease patients for remote coronary perfusion abnormalities. Dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE) has become a standard method for evaluation of perfusion abnormalities in adults with coronary artery disease. In addition, DSE has been used with success in some pediatric patients. The purposes of this study were to evaluate safety and accuracy of DSE in the follow-up of patients with Kawasaki disease, to evaluate whether DSE adds any additional value to the resting echocardiogram, and to determine the association of DSE results with American Heart Association (AHA) risk level categories. DSE was performed 1 month to 13 years after acute Kawasaki disease in 47 patients (range, 3.8–22.6 years; 33 males and 16 females). Patients were stratified according to AHA risk level categories (I–V). Ischemia was defined as a new or worsening regional wall motion abnormality or >1 mm ST segment depression on the electrocardiogram during DSE. In 45/47 patients, DSE was completed successfully (i.e., achievement of target heart rate or development of ischemia). No patients in risk levels lower than V (i.e., patients without coronary artery stenoses) had positive DSE, whereas 2/4 (50%) in the risk level V category had positive DSE, both of whom had coronary occlusion >50% confirmed by angiography. Of the 2 AHA risk level V patients with negative DSE, 1 had extensive collateralization and the other had coronary obstruction <50%. DSE is a safe and feasible method for the evaluation of children with Kawasaki disease. DSE provides a confirmatory benefit and may be a useful screening alternative to cardiac catheterization during follow-up. Patients in AHA risk levels I–IV are unlikely to have dobutamine-induced coronary perfusion abnormalities. Patients in the risk level V category may or may not have positive DSE depending on the degree of both coronary obstruction and collateralization.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
T Akagi V Rose LN Benson A Newman RM Freeman (1992) ArticleTitleOutcome of coronary artery aneurysms after Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 121 689–694 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD2MfhsFw%3D Occurrence Handle1432415
SW Allen EM Shaffer LA Harrigan et al. (1992) ArticleTitleMaximal voluntary work and cardiorespiratory fitness in patients who have had Kawasaki syndrome. J Pediatr 121 221–225 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A2cbhsVQ%3D Occurrence Handle1640287
InstitutionalAuthorNameAmerican Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Sub-Committee on Quantification of 2-Dimensional Echocardiograms (1989) ArticleTitleRecommendations for quantification of the left ventricle by 2-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2 358–367 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC1Mfjs1U%3D Occurrence Handle2698218
AS Dadiani KA Taubert M Takahashi et al. (1994) ArticleTitleGuidelines for long-term management of patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 89 916–922 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC2cjmtlA%3D Occurrence Handle8313588
Y Genma S Ogawa J Zhang Y Yamamoto (1997) ArticleTitleEvaluation of myocardial ischemia in Kawasaki disease by dobutamine stress signal-average ventricular late potentials. Cardiovasc Res 36 323–329 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0008-6363(97)00196-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmvFCgug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9534852
K Hamaoka Z Onouchi Y Kamiya K Sakata (1998) ArticleTitleEvaluation of coronary flow velocity dynamics and flow reserve in patients with Kawasaki disease by means of Doppler guide wire. J Am Coll Cardiol 31 833–840 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00019-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7osVClug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9525556
Y Hino T Ohkubo Y Katsube S Ogawa (1999) ArticleTitleChanges in endothelium-derived vascular regulatory factors during dobutamine stress-induced silent ischemia in patients with Kawasaki disease. Jpn Circ J 63 503–508 Occurrence Handle10.1253/jcj.63.503 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzovFWisg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10462014
H Kato T Sugamura T Akagi et al. (1994) ArticleTitleLong-term consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10 to 21 year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation 94 1379–1385
TR Kimball SA Witt SR Daniels (1997) ArticleTitleDobutamine stress echocardiography in the assessment of suspected myocardial ischemia in children and young adults. Am J Cardiol 95 1837–1843
RL Larsen PM Applegate DA Dyar et al. (1998) ArticleTitleDobutamine stress echocardiography for assessing coronary artery disease after transplantation in children. J Am Coll Cardiol 30 512–515
H Mertes SG Sawada T Ryan et al. (1993) ArticleTitleSymptoms, adverse effects, and complications associated with dobutamine stress echocardiography: experience in 1118 patients. Circulation 88 15–19 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA3cnnvFM%3D Occurrence Handle8319327
O Muzik SM Paridon TP Singh et al. (1996) ArticleTitleQuantification of myocardial blood flow and flow reserve in children with history of Kawasaki disease and normal coronary arteries using positron emission tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 28 757–762 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0735-1097(96)00199-4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA28fns1Q%3D Occurrence Handle8772768
JW Newburger M Takahashi JC Burns et al. (1986) ArticleTitleThe treatment of Kawasaki syndrome with intravenous gammaglobulin. N Engl J Med 315 341–347 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimB1cvosVM%3D Occurrence Handle2426590
N Noto M Ayusawa K Karasawa et al. (1996) ArticleTitleDobutamine stress echocardiography for detection of coronary artery stenosis in children with Kawasaki disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 27 1251–1256 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0735-1097(95)00570-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XivVegurc%3D Occurrence Handle8609352
E Pahl R Segal D Chrystof et al. (1995) ArticleTitleFeasibility of exercise stress echocardiography for the follow up of children with coronary involvement secondary to Kawasaki disease. Circulation 91 122–128 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC3czntVA%3D Occurrence Handle7805193
SM Paridon RD Ross LR Kuhns WW Pinsky (1990) ArticleTitleMyocardial performance and perfusion during exercise in patients with coronary artery disease caused by Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 116 52–56 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC3M7pt1E%3D Occurrence Handle2295963
SG Sawada DS Segar T Ryan et al. (1991) ArticleTitleEchocardiographic detection of coronary artery disease during dobutamine infusion. Circulation 83 1605–1614 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B3MrnsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle1673646
DS Segar SE Brown SG Sawada T Ryan H Feigenbaum (1992) ArticleTitleDobutamine stress echocardiography: correlation with coronary lesion severity as determined by quantitative angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 19 1197–1202 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B38njslc%3D Occurrence Handle1564220
A Suzuki M Yamagishi K Kimura et al. (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional behavior and morphology of the coronary artery wall in patients with Kawasaki disease assessed by intravascular ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol 27 291–296 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0735-1097(95)00447-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2M3ivFU%3D Occurrence Handle8557896
R Yamakawa M Ishii T Sugimura et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCoronary endothelial dysfunction after Kawasaki disease evaluation by intracoronary injection of acetylcholine. J Am Coll Cardiol 31 1074–1080 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00033-3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3itVCktA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9562009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zilberman, M., Goya, G., Witt, S. et al. Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Young Patients with Kawasaki Disease . Pediatr Cardiol 24, 338–343 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-002-0327-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-002-0327-9